Fenpropathrin
Fenpropathrin (brand names Danitol, Meothrin), or fenopropathrin, is a widely used pyrethroid insecticide in agriculture and household.[1][2][3][4]
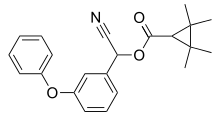 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.049.514 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C22H23NO3 |
| Molar mass | 349.430 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
A person developed Parkinson's disease after six months of daily exposure to fenpropathrin, and animal tests subsequently revealed that the compound is a dopaminergic neurotoxin.[4] It has thus been implicated as an environmental risk factor for Parkinson's disease.[4]
See also
References
- Aizawa H (2 December 2012). Metabolic Maps of Pesticides. Elsevier Science. pp. 185–. ISBN 978-0-323-15753-7.
- Abou-Donia MB (15 July 1992). Neurotoxicology. CRC Press. pp. 462–. ISBN 978-1-4398-0542-8.
- Johansen CA, Mayer DF (1990). Pollinator Protection: A Bee & Pesticide Handbook. Wicwas Press. ISBN 978-1-878075-00-0.
- Xiong J, Zhang X, Huang J, Chen C, Chen Z, Liu L, et al. (March 2016). "Fenpropathrin, a Widely Used Pesticide, Causes Dopaminergic Degeneration". Molecular Neurobiology. 53 (2): 995–1008. doi:10.1007/s12035-014-9057-2. PMC 5333774. PMID 25575680.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.
