Cystic duct
The cystic duct is the short duct that joins the gallbladder to the common hepatic duct. It usually lies next to the cystic artery. It is of variable length. It contains 'spiral valves of Heister', which do not provide much resistance to the flow of bile.
| Cystic duct | |
|---|---|
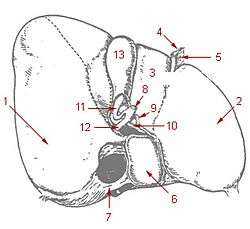 1: Right lobe of liver 2: Left lobe of liver 3: Quadrate lobe of liver 4: Round ligament of liver 5: Falciform ligament 6: Caudate lobe of liver 7: Inferior vena cava 8: Common bile duct 9: Hepatic artery 10: Portal vein 11: Cystic duct 12: Hepatic duct 13: Gallbladder | |
| Details | |
| Artery | cystic artery |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | ductus cysticus |
| MeSH | D003549 |
| TA | A05.8.02.011 |
| FMA | 14539 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
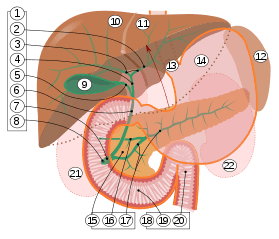
9. Gallbladder, 10–11. Right and left lobes of liver. 12. Spleen.
13. Esophagus. 14. Stomach. 15. Pancreas: 16. Accessory pancreatic duct, 17. Pancreatic duct.
18. Small intestine: 19. Duodenum, 20. Jejunum
21–22. Right and left kidneys.
The front border of the liver has been lifted up (brown arrow).[1]
Function
Bile can flow in both directions between the gallbladder and the common bile duct and the hepatic duct.
In this way, bile is stored in the gallbladder in between meal times. The hormone cholecystokinin, when stimulated by a fatty meal, promotes bile secretion by increased production of hepatic bile, contraction of the gall bladder, and relaxation of the Sphincter of Oddi.
Clinical significance
Gallstones can enter and obstruct the cystic duct, preventing the flow of bile. The increased pressure in the gallbladder leads to swelling and pain. This pain, known as biliary colic, is sometimes referred to as a gallbladder "attack" because of its sudden onset.
During a cholecystectomy, the cystic duct is clipped two or three times and a cut is made between the clips, freeing the gallbladder to be taken out.
See also
Additional images
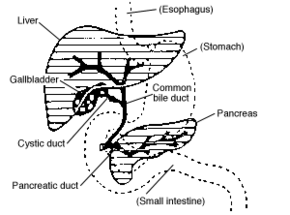 Digestive system diagram showing the cystic duct
Digestive system diagram showing the cystic duct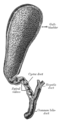 The gall-bladder and bile ducts laid open.
The gall-bladder and bile ducts laid open.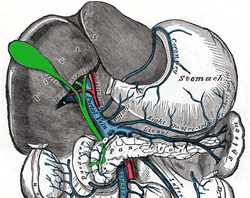 The portal vein and its tributaries.
The portal vein and its tributaries.- Cystic duct.Visceral surface of liver.
References
- Standring S, Borley NR, eds. (2008). Gray's anatomy : the anatomical basis of clinical practice. Brown JL, Moore LA (40th ed.). London: Churchill Livingstone. pp. 1163, 1177, 1185–6. ISBN 978-0-8089-2371-8.
External links
- Anatomy figure: 38:06-03 at Human Anatomy Online, SUNY Downstate Medical Center - "The gallbladder and extrahepatic bile ducts."
- Anatomy photo:38:14-0106 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center - "Stomach, Spleen and Liver: The Gallbladder and the Bile System"
- liver at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University) (liverinferior, biliarysystem)