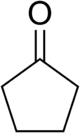
Cyclopentanone
Cyclopentanone is the organic compound with the formula (CH2)4CO. This cyclic ketone is a colorless volatile liquid.
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Cyclopentanone | |
| Other names
Ketocyclopentane Adipic ketone | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.004.033 |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID |
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C5H8O | |
| Molar mass | 84.12 g/mol |
| Appearance | clear, colorless liquid |
| Odor | peppermint-like |
| Density | 0.95 g/cm3, liquid |
| Melting point | −58.2 °C (−72.8 °F; 215.0 K) |
| Boiling point | 130.6 °C (267.1 °F; 403.8 K) |
| Slightly soluble | |
| -51.63·10−6 cm3/mol | |
| Hazards | |
| Safety data sheet | Cyclopentanone |
| Flash point | 26 °C (79 °F; 299 K) |
| Related compounds | |
Related ketones |
cyclohexanone 2-pentanone 3-pentanone cyclopentenone |
Related compounds |
cyclopropane |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Preparation
Upon treatment with barium hydroxide at elevated temperatures, adipic acid undergoes ketonization to give cyclopentanone:[2]
- (CH2)4(CO2H)2 → (CH2)4CO + H2O + CO2
Uses
Cyclopentanone is common precursor to fragrances, especially those related to jasmine and jasmone. Examples include 2-pentyl- and 2-heptylcyclopentanone.[3] It is a versatile synthetic intermediate, being a precursor to cyclopentobarbital.[4]
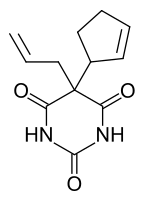
Cyclopentobarbital is a drug made from cyclopentanone.
Cyclopentanone is also used to make cyclopentamine, the pesticide pencycuron, and pentethylcyclanone.[4]
gollark: If the gnomes are invisible how are they considered infected?
gollark: Plotting out your entire study of things years in advance is probably not useful.
gollark: Sign errors really are highly.
gollark: Something something semipermeable membrane something something concentration gradient.
gollark: Fascinating.
References
- Merck Index, 11th Edition, 2748.
- J. F. Thorpe and G. A. R. Kon (1925). "Cyclopentanone". Organic Syntheses. 5: 37.; Collective Volume, 1, p. 192.
- Johannes Panten and Horst Surburg "Flavors and Fragrances, 2. Aliphatic Compounds" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, 2015, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim.doi:10.1002/14356007.t11_t01
- Hardo Siegel, Manfred Eggersdorfer (2005). "Ketones". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a15_077.CS1 maint: uses authors parameter (link)
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.