Cousin marriage in the Middle East
Cousin marriage is allowed and often encouraged throughout the Middle East.[1] The bint 'amm marriage, or marriage with one's father's brother's daughter (bint al-'amm) is especially common, especially in tribal and traditional communities.[2] Anthropologists have debated the significance of the practice; some view it as the defining feature of the Middle Eastern kinship system while others note that overall rates of cousin marriage have varied sharply between different Middle Eastern communities. There is very little numerical evidence of rates of cousin marriage in the past.[3]
Relationships (Outline) |
|---|
|
Endings |
History
Ancient Persia
The Persian king Ardashir I of the Sasanian Empire advised his lawyers, secretaries, officers, and husbandmen to "marry near relatives for the sympathy of kinship is kept alive thereby." The same motivation is given in ancient Arabic sources referring to the practice of marriage between paternal cousins prevalent in pre-Islamic Arabia. The Kitab al-Aghani similarly features the story of Qays ibn Dharih, who was not allowed by his father to marry a beautiful maiden from another tribe because, in the words of the father felt that as rich and wealthy man he did not want his son to take the side of a stranger. There is the related consideration that a man who grows up with a cousin in the intimate setting of one extended family knows her and so may develop his own liking or love for her. There is also the benefit of knowing the qualities of the spouse: a Syrian proverb reads, "Ill luck which you know is better than good luck with which you get acquainted." Keeping property in the family is a final reason for cousin marriage. One of the earliest examples of this is the five daughters of Zelophehad from ancient Israel (Numbers 36:10-13) who upon inheriting from their father all married their father's brother's sons. The Quranic law dictating that daughters receive a portion of the inheritance appears to have had the effect of increasing cousin marriage rate.[4]
Relation with spread of Islam
An area's inclusion in the eighth-century Omayyid Khalifate (and its persistence within the Islamic world afterwards) has been demonstrated by Andrey Korotayev to be a strong and significant predictor of parallel-cousin (Father's Brother's Daughter - FBD) marriage. He has shown that while there is some functional connection between Islam and FBD marriage, the permission to marry a FBD does not appear to be sufficient to persuade people to actually marry thus, even if the marriage brings with it economic advantages. According to Korotayev, a systematic acceptance and practice of parallel-cousin marriage took place when Islamized non-Arab groups adopted Arab norms and practices even if they had no direct connection with Islam to raise their social standing.[5]
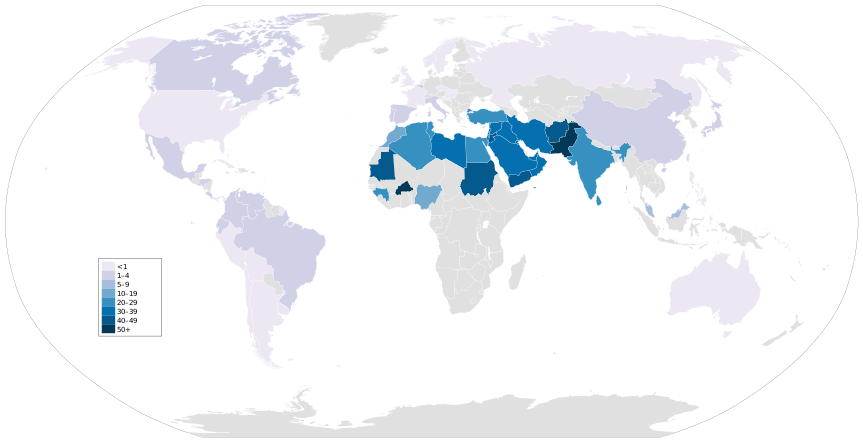
Prevalence
Prevalence of marriages up to and including distance of second-degree cousin in the world according to The National Center for Biotechnology Information in 2012.[6]
Regions and ethnic groups
Arabian Peninsula
Raphael Patai reports that in central Arabia no relaxation of a man's right to the father's brother's daughter (FBD, or paternal female cousin) seems to have taken place in the past hundred years before his 1962 work. Here the girl is not forced to marry her paternal male cousin but she cannot marry another unless he gives consent. Among the Jews of Yemen this rule is also followed albeit not as rigidly. In northern Arabia the custom is very strong and any outsider wishing to marry a woman must first come to the paternal male cousin, ask his permission, and pay him what he wants, and a man who marries off his daughter without the consent of the paternal male cousin may be killed by family members. The right of the paternal male cousin is such that a shaykh may not be able to prevail against it. Among the Bedouin it can happen that a paternal male cousin can lodge a complaint after the marriage has taken place, compelling the father to reimburse the bride price or have the marriage annulled. If the paternal male cousin cannot marry his paternal female cousin immediately due to financial or other considerations, the paternal male cousin can also "reserve" her by making a public and formal statement of his intentions to marry her at a future date. A more distant relative acquires priority to marry a girl over her paternal male cousin by reserving her soon after her birth...[7]
Egypt
In Egypt cousin marriage may have been even more prevalent than in Arabia in past periods, with one source from the 1830s observing that it was common among Egyptian Arabs and native Egyptian Muslims in villages within Egypt but less so in Cairo where first cousin marriage accounts 35 percent of marriages in Cairo than in other parts of Egypt. Reportedly the husband and wife would continue to call each other "cousin" because the tie of blood was seen as indissoluble while the marriage was not. In the upper and middle classes the young man was seldom allowed to see the face of his female cousin after she reached puberty. Cousin marriage was not only among Muslims but also among Egyptian Copts in the past century although to lesser extent amounting 7% of all Coptic marriages.[8] Estimates from the late 19th and early 20th century state variously that either 80 percent of the Egyptian fellahin marry first cousins or two-thirds marry them if they exist. Cousin marriage was also practiced in the Sinai Peninsula, where a girl is sometimes reserved by her cousin with money long before puberty, and among Bedouins in the desert between the Nile and the Red Sea. Cousin marriage was practiced in Medina during Muhammad's time, but out of 113 recorded marriages in one sample only 15 were between abnaa 'amm or paternal cousins of any degree.[9]
Iran
Cousin marriages are decreasing among Iranians. Since the Pahlavi era less Iranians has practised cousin marriages.[10][11][12] There is a strong preference for marrying a first cousin, but no specific preference for the father's brother's daughter. For the quarter of women married after age 21 it was found that the incidence of consanguinity declined to 28%. Additionally, the proportion of cousin marriage among urban families stayed constant: it was only rural families that drove the increase. For all periods the proportion of cousin marriage among highly educated women was somewhat lower than among uneducated women. It is hypothesized that decreases in infant mortality during the period may have created a larger pool of eligible cousins to marry.[13]
Iraq
In Iraq the right of the cousin has also traditionally been followed as cousin marriage accounts 50%.[14] The Uncle of the girl -or father of the boy- assigns or reserves his niece to his son at an early age, the parents from both families arrange for the marriage usually early. This is usually done to preserve wealth in the family and is more common in rural areas. Among the Jews of Iraq, if the cousin cannot be persuaded to forgo his rights, then he is paid a sum of money by the girl's father. Among the Kurdish Hamawand tribe the paternal male cousin must give his consent for the marriage to take place, though in the southern Kurdish regions the cousin right is not as strongly emphasized. Among Arabs and Berbers in Morocco[15] the cousin right has also traditionally prevailed.
Israel
Patai states in his other book The Myth of the Jewish Race that percentage of cousin marriage among Jews varies extensively with geographic location. Among Israeli Ashkenazi Jews, who originate mainly from Europe, the first-cousin marriage rate was measured in a 1955-7 study at 1.4% and other cousin marriages at 1.06% of all marriages. But among non-Ashkenazim the first-cousin marriage rate was 8.8% and an additional 6.0% of marriages were between more distant cousins. Thus a total 14.6% of marriages between non-Askenazim were consanguineous compared with only 2.5% for Ashkenazim. The highest frequencies of cousin marriages were found among Jews from Iraq (28.7%) and Iran (26.3%). High rates were also found among couples from Yemen (18.3%), Aden (17.8%), Tunisia (13.4%), and among Oriental Jews from the USSR (6.9%). Jews from Egypt, Syria, Lebanon, and Turkey saw rates of 7–10.7%. A later 1969–70 study rated the first-cousin marriage rate among Ashkenazim at 0.3% and other cousin marriages at 1.0%, while for non-Askenazim the respective figures were 6.2% and 8.1%. Among the Habbani Jews in Israel, 56% of marriages are between first cousins. The Samaritans also had very high rates of inbreeding, with 43% of marriages between first cousins and 33.3% between other cousins.
Syria
In Syria the right belongs to the paternal male cousin alone and the maternal male cousin has no special rights. The custom is however less frequent in big cities such as Damascus and Aleppo. Patai reports that in the decades preceding 1962 the right was often ignored among the Syrian urban middle class. Among the upper classes it appeared to be again more common, as certain leading families protected their wealth and status by reserving daughters for their cousins, though sons had more freedom of choice. This situation was also loosening at the time of Patai's work. This holds also among the Syrian Turks and Kurds. But the Syrian Circassians hold cousin marriage absolutely forbidden, similar to the Circassians of the Caucasus.[16]
In her discussion of the city of Aleppo during the Ottoman Empire, Meriwether finds a rate of cousin marriage among the elite of 24%. Father's brother's daughter was most common but still only represented 38% of all cousin marriages, while 62% were with first or second cousins. But most families had either no cousin marriages or only one, while for a few the rate was as high as 70%. Cousin marriage rates were higher among women, merchant families, and older well-established families.[17] Meriwether cites one case of cousin marriage increasing in a prominent family as it consolidated its position and forging new alliances became less critical. Marriage patterns among the elite were, however, always diverse and cousin marriage was only one option of many. Rates were probably lower among the general population.
Turkey
In Turkey the rate of consanguineous marriage is 8.5%, indicating a preference for this traditional form of marital union. Social and cultural factors are especially important in marriages between first and second cousins. The highest rate of consanguineous marriage can be found in South Eastern and Eastern Anatolia regions of Turkey due to a significant Kurdish population.[18]
Other areas
Barth finds in his study of southern Kurdistan that in tribal villages 57% of all marriages were cousin marriages (48% bint 'amm marriages) while in a nontribal village made up of recent immigrant families only 17% were cousin marriages (13% bint 'amm). In the South Palestinian village of Artas in the 1920s, of 264 marriages 35, or 13.3%, were paternal male cousin marriages; 69, or 26.1%, were cousin marriages. In the oasis-village of Sidi Khaled, some 170 miles south of Algiers, among the Mzabites further south, among the Chaamba, and among the Moors of the extreme western Sahara, cousin marriage is preferred. In the town of Timbuctoo, a field investigator found that among the Arabs one third of marriages are with first cousins. Half of these are with the father's brother's daughter and slightly fewer with the mother's brother's daughter. It is possible that the high MBD marriage rate is the result of Songhoi influence, one group of which prefers the MBD type and shuns the FBD type, and another group of which have a preference for both. The third ethnic group of Timbuctoo are the Bela, who are Tuareg slaves, and among whom marriage between cross cousins is preferred in principle, though in practice FBD marriage also occurs.[19] In Lebanon first-cousin marriage rates differs among religious affiliation as it is found to be 17% for Christians and 30% for Muslims throughout the past century, however first-cousin marriage is declining among all marriages in Lebanon.[20]
Social aspects
Familial responsibility and honor
Of particular significance in the Middle East is marriage to a father's brother's daughter. Many Middle Eastern peoples express a preference for this form of marriage. Ladislav Holý explains that it is not an independent phenomenon but merely one expression of a wider preference for agnatic solidarity, or solidarity with one's father's lineage. Due to placing emphasis on the male line, the daughter of the father's brother is seen as the closest marriageable relation. According to Holý the oft-quoted reason for cousin marriage of keeping property in the family is, in the Middle Eastern case, just one specific manifestation of keeping intact a family's whole "symbolic capital." Along with an aversion to hypogamy that prevents the loss of a man's loyalties to the higher ranking relatives of his wife, FBD marriage more closely binds the agnatic group by ensuring that wives are agnatic as well as affinal relatives. In fact cousin marriage in general can be seen as trading off one socially valuable outcome, namely marital alliances with outsiders and the resulting integration of society, with the alternative outcome of greater group solidarity. But for demographic reasons the ideal of in-marriage can never be fully realized and hence societies allowing it can always draw on the advantageous aspects of both in- and out-marriage.[21]
The notion of honor is another social characteristic Holý identifies as being related to Middle Eastern cousin marriage. The honor of the males surrounding a woman is sullied in many societies when she misbehaves or when she is attacked. In societies like Europe that place greater value on affinal relations, responsibility for a married woman rests with both her husband's family and her own. In the Middle East the situation is different in that primary responsibility continues to rest with the woman's own family even after she is married. Her agnates therefore cannot release her from control upon marriage due to the risk to their honor. They and not the husband may be responsible for killing her, or sometimes her lover, if she commits adultery. Similar rules may apply in case of the payment if she is killed and for the inheritance of her property if she has no male heirs. Her natal family may continue supporting her even against her husband. This is an idealized system: some Middle Eastern societies do mix it with other systems that assign more responsibility to the husband's family.[22]
Berti people in Pakistan
Holý's field experience among the Berti people of Pakistan allowed him to undertake an extensive study of cousin marriage in their culture. Holý believed that many of his findings from field experience among the Berti people of Pakistan could generalize to other Middle Eastern groups. He noted that stated reasons for cousin marriage could be both pragmatic and symbolic. Stated pragmatic reasons for cousin marriage might be stated in terms of advantages for the husband such as warmer relations with his father-in-law, quicker entertainment of the husband's family by the wife in the case of a visit due to them being her relations, greater loyalty and devotion of the wife, and the ease of regaining a wife after a serious quarrel where she has withdrawn to the house of her own family. Stated pragmatic reasons for the parents included gaining access to the labor of a daughter's children by marrying her to a kinsman and thereby keeping her family close by, increased attentiveness on the part of a wife to her aging in-laws if she is related to them, and the ease of marital negotiations if the parents are brothers, or in the next best case, if the mother of one child is the sister of the father of the other child.[23]
Holý states that despite all this, creating a general theory of the existence of a preference for FBD marriage in terms of pragmatic reasons is not possible. Instead any realistic theory must take into account the symbolic reasons that both are created by and help to create Berti culture. Frequently such reasons protected the symbolic but vitally important honor of the stakeholders involved. One reason was that in Berti (and Middle Eastern) culture one's honor is affected if a cousin becomes pregnant out of wedlock. The responsibility to see her married is directly proportional to the responsibility for her chastity and one's genealogical distance from her. One can eliminate this directly by becoming her husband. Another reason is the relationship between cousin marriage and agnatic solidarity. Holý argues from the case of the Palestinians that FBD marriage should not be viewed as simply "adding" affinal ties to previous agnatic ones. Instead they recognize the strength of the existing ties. Distant agnates can increase their bond and become close agnates via intermarriage.[24]
Discouragement
Advice on cousin marriage in the Middle East has not always been positive, however. Al-Maydani makes the following exhortation: "Marry the distant, but not the near." The reason given for the inadvisability of cousin marriages is most frequently the belief that the offspring of such marriages will be feeble.[25] An early Arab author, Ibn 'Abd Rabbihi, states in his work Kitab al-'iqd al-farid of a hero that "He is a hero not borne by the cousin (of his father), he is not weakly; for the seed of relations brings forth feeble fruit." Abu Hamid al-Ghazali (1059–1111) in his principal ethical work, the Ihya 'ulum al-din, gives the different reason that "the woman should not be a near relative of the husband, because near relationship diminishes the sensuous desire." Finally the ancient Arabic poet 'Amr b. Kulthum states, "Do not marry in your own family, for domestic enmity arises therefrom." Similar sentiments are expressed by certain Moroccan and Syrian proverbs.[26]
Patai summarizes the Middle Eastern situation by saying that a preference for paternal male cousin marriage exists in many Middle Eastern ethnic groups but that right to the bint 'amm exists in only some of these. The cousin right is the "complete" form of the institution of the cousin marriage and preference without right the "incomplete" form. Patai explains the differences between cultures exhibiting these two forms in terms of the geographic centrality to Middle Eastern culture, with groups on the outskirts of the Middle East likely to fall into the "incomplete" category, in terms of the cultural marginality of the group, with groups adhering tightly to older traditions better able to resist the "complete" form, in terms of modernization and Westernization, with this tending to discourage cousin marriage. The Copts of Egypt who chose to marry a cousin is considered unideal among Copts due to cultural traditions although not common among Copts in comparison to other ethnic groups and those of different beliefs.[27]
Bride prices
Cousin marriage normally results in a reduced bride price. Patai states that bride price to a cousin is usually about half as high as to a nonrelative. Due to the poverty of many families this outlay often requires exceptional effort, and especially because the decision traditionally is in the hands of the groom's father, these considerations may weigh heavily on the outcome. The bride's family moreover is expected to spend much of the bride price on the bride herself, so there is a reduced incentive to gain a higher price by avoiding cousin marriage.[28]
Biological aspects
Marriage between first cousins doubles the risk of children being born with birth defects, according to a study noting higher than expected rates of deaths and congenital abnormalities in babies born from such marriages.[29]
See also
- Coefficient of relationship
- Consanguinity
- Cousin marriage
- Endogamy
- Exogamy
- Genetic distance
- Genetic diversity
- Inbreeding
- Inbreeding avoidance
- Inbreeding depression
- Incest
- Incest taboo
- Legality of incest
- Mahram
- Polygyny in Islam
- Prohibited degree of kinship
- Proximity of blood
- Sexual taboo in the Middle East
- Watta satta
References
- Holy
- Halim Barakat (14 October 1993). The Arab World: Society, Culture, and State. University of California Press. pp. 109–. ISBN 978-0-520-91442-1.
- Holy, also Patai, p. 140
- Patai 169-72
- Korotayev, A.V. "Parallel Cousin (FBD) Marriage, Islamization, and Arabization" // Ethnology 39/4 (2000): 395–407.
- Hamamy, H. (2011). "Consanguineous marriages Preconception consultation in primary health care settings". Journal of Community Genetics. US National Library of Medicine National Institutes of Health. 3 (3): 185–192. doi:10.1007/s12687-011-0072-y. PMC 3419292. PMID 22109912.
- Patai 145-153
- Patai, p. 139-40
- Patai 141
- Golden River to Golden Road, R. Patai, 136
- Women in Ancient Persia, 559-331 BC By Maria Brosius, p. 68
- Patai, p. 139
- Givens 1994
- Times, John Tierney The New York. "MARRYING A COUSIN IS WAY OF LIFE FOR MANY IRAQIS". Sun-Sentinel.com. Retrieved 2019-05-28.
- Patai 168
- Patai 153-161
- Meriwether, p. 135
- "İstatistiklerle Aile, 2019". Turkish Statistical Institute.
- Patai 141-3
- Marcia C.Inhorn 141-142
- Holý, 110-17
- Holý, 120-7
- Holý, Chapter 2
- Holy, Chapter 3
- Safdar, Anealla. "Marriage between close relations debated in Doha". The National.
- Patai 173-75
- Patai 175-6
- Patai 144-145
- Boseley, Sarah; editor, health (3 July 2013). "Marriage between first cousins doubles risk of birth defects, say researchers" – via The Guardian.CS1 maint: extra text: authors list (link)