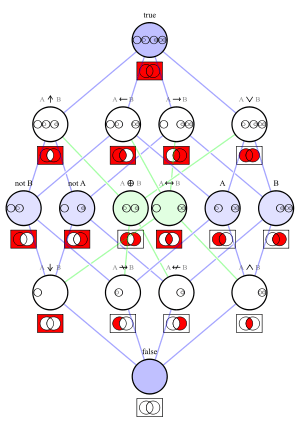
Converse nonimplication
In logic, converse nonimplication[1] is a logical connective which is the negation of converse implication (equivalently, the negation of the converse of implication).
Definition
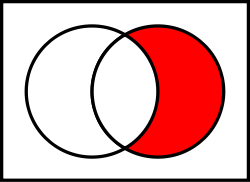
Converse nonimplication is notated , or , and is logically equivalent to
Notation
Converse nonimplication is notated , which is the left arrow from converse implication (), negated with a stroke (/).
Alternatives include
- , which combines converse implication's , negated with a stroke (/).
- , which combines converse implication's left arrow() with negation's tilde().
- Mpq, in Bocheński notation
Properties
falsehood-preserving: The interpretation under which all variables are assigned a truth value of 'false' produces a truth value of 'false' as a result of converse nonimplication
Natural language
Grammatical
"p from q."
Classic passive aggressive: "yeah, no"
Rhetorical
"not A but B"
Colloquial
Boolean algebra
Converse Nonimplication in a general Boolean algebra is defined as .
Example of a 2-element Boolean algebra: the 2 elements {0,1} with 0 as zero and 1 as unity element, operators as complement operator, as join operator and as meet operator, build the Boolean algebra of propositional logic.
|
and |
|
and |
|
then means |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| (Negation) | (Inclusive or) | (And) | (Converse nonimplication) |
Example of a 4-element Boolean algebra: the 4 divisors {1,2,3,6} of 6 with 1 as zero and 6 as unity element, operators (codivisor of 6) as complement operator, (least common multiple) as join operator and (greatest common divisor) as meet operator, build a Boolean algebra.
|
and |
|
and |
|
then means |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| (Codivisor 6) | (Least common multiple) | (Greatest common divisor) | (x's greatest divisor coprime with y) |
Properties
Non-associative
iff #s5 (In a two-element Boolean algebra the latter condition is reduced to or ). Hence in a nontrivial Boolean algebra Converse Nonimplication is nonassociative.
Clearly, it is associative iff .
Non-commutative
- iff #s6. Hence Converse Nonimplication is noncommutative.
Neutral and absorbing elements
- 0 is a left neutral element () and a right absorbing element ().
- , , and .
- Implication is the dual of converse nonimplication #s7.
| Converse Nonimplication is noncommutative | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Step | Make use of | Resulting in | ||
| Definition | ||||
| Definition | ||||
| - expand Unit element | ||||
| - evaluate expression | ||||
| - regroup common factors | ||||
| - join of complements equals unity | ||||
| - evaluate expression | ||||
| Implication is the dual of Converse Nonimplication | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Step | Make use of | Resulting in | ||
| Definition | ||||
| - .'s dual is + | ||||
| - Involution complement | ||||
| - De Morgan's laws applied once | ||||
| - Commutative law | ||||
Computer science
An example for converse nonimplication in computer science can be found when performing a right outer join on a set of tables from a database, if records not matching the join-condition from the "left" table are being excluded.[3]
References
- Lehtonen, Eero, and Poikonen, J.H.
- Knuth 2011, p. 49
- http://www.codinghorror.com/blog/2007/10/a-visual-explanation-of-sql-joins.html
- Knuth, Donald E. (2011). The Art of Computer Programming, Volume 4A: Combinatorial Algorithms, Part 1 (1st ed.). Addison-Wesley Professional. ISBN 0-201-03804-8.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
External links