Combat Aviation Brigade
A Combat aviation brigade (CAB) is a multi-functional brigade-sized unit in the United States Army that fields military helicopters, offering a combination of attack/reconnaissance helicopters (Boeing AH-64 Apache), medium-lift helicopters (Sikorsky UH-60 Black Hawk), heavy-lift helicopters (Boeing CH-47 Chinook), and MEDEVAC capability.
History
Combat aviation brigades (CABs) were introduced during the transformation of the United States Army to a modular force. There were three types of combat aviation brigades.
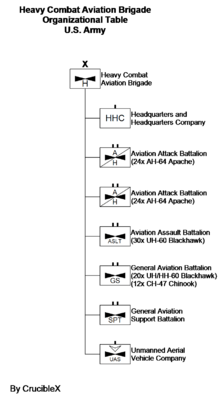
Heavy combat aviation brigades
- Two attack reconnaissance battalions (ARB) (each with 24 Boeing AH-64 Apache)
- Assault helicopter battalion (AHB) (30 Sikorsky UH-60 Black Hawk)
- General support aviation battalion or GSAB (8 UH-60 Command Aviation, 12 Boeing CH-47 Chinook and 15 Sikorsky HH-60M Black Hawk)
- UAV company[1]
- Aviation support battalion (ASB)
Medium combat aviation brigades
- Attack reconnaissance battalion (ARB) (24 AH-64 Apache)
- Reconnaissance squadrons (ARS) (30 OH-58)
- Assault helicopter battalion (AHB) (30 UH-60 Black Hawk)
- General support aviation battalion (GSAB) (8 UH-60 Command Aviation, 12 CH-47 Chinook and 15 HH-60M)
- UAV company[1]
- Aviation support battalion (ASB)
Light combat aviation brigades
- Two Reconnaissance squadrons (ARS) (each with 30 OH-58)
- Assault helicopter battalion (AHB) (30 UH-60 Black Hawk)
- General support aviation battalion (GSAB) (8 UH-60 Command Aviation, 12 CH-47 Chinook and 15 HH-60M)
- UAV company[1]
- Aviation support battalion (ASB)
Full spectrum capability
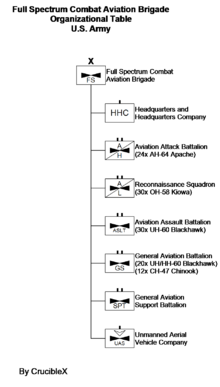
Starting in 2010, the Army began to replace the medium and light CABs with multipurpose brigades, called "full spectrum CABs". The ultimate goal is eight full spectrum CABs and four heavy CABs in active service, and respectively six and two CABs in the Army National Guard. Four brigades must be deployment-ready on a permanent basis.
The Army stated that they need the CAB to be modular designed to enable task organization and optimize aviation capability for specific mission of specified duration. Full spectrum CAB will standardize the CAB design across the branch to deliver maximum aviation capability in the most timely and flexible manner. The Army also said that the new CAB design is doctrinally sound which delivers the combat, combat support, and combat service support to "enable steady state" operations required in an era of persistent conflict, and this new CAB will be constructed to deliver combat power while maximizing efficiencies in training, maintenance and support across the Army.[2][3]
Full spectrum combat aviation brigades design includes:
- Headquarters and headquarters company (HHC)
- Attack reconnaissance squadron (ARS) (three troops with 7 OH-58D Kiowa Warrior each, and a UAS company with two platoons with 4 AAI RQ-7B Shadow UAV each)
- Attack reconnaissance battalion (ARB) (three companies with 8 AH-64 Apache each)
- Assault helicopter battalion (AHB) (three companies with 10 UH-60 Black Hawk each, and a pathfinder company)
- General support aviation battalion (GSAB) (a command aviation company or CAC with 4 UH-60 Black Hawk and 4 EH-60 equipped with AN/ASC-38 Army Airborne Command and Control System [A2C2S], a heavy helicopter company (HvyHC) with three platoons with 4 CH-47 Chinook each, an air ambulance medical company (AAMC) with five forward support MEDEVAC platoons (FSMP) with 3 HH-60M each equipped with MEDEVAC mission equipment, and an air traffic services (ATS) company consisting of a two tactical tower control teams, a mobile tower team, an airspace control flight following team and a local surveillance and ground controlled approach (GCA) radar team)
- UAS company (three platoons with 4 General Atomics MQ-1C Gray Eagle UAV each)
- Aviation support battalion (ASB)
Active component
With the retirement of the OH-58D Kiowa Warrior helicopters in 2017 the army concentrated all AH-64E Apache attack helicopters in the active CABs, which now are all Heavy. As of 2018 each CAB fields:
- 1x Headquarters and Headquarters Company (HHC)
- 1x Air Cavalry Reconnaissance Squadron (ACRS) (24 × AH-64E Apache and 12 × RQ-7 Shadow)
- 1x Attack Reconnaissance Battalion (ARB) (24 × AH-64E Apache)
- 1x Assault Helicopter Battalion (AHB) (30 × UH-60 Black Hawk)
- 1x General Support Aviation Battalion (GSAB) (8 × UH-60 Command Aviation, 12 × CH-47F Chinook, 12 × HH-60M and ATS)
- 1x UAS Company (12 x MQ-1C)
- 1x Aviation Support Battalion (ASB)
Divisional CABs
- Combat Aviation Brigade, 1st Cavalry Division
- Combat Aviation Brigade, 1st Armored Division
- Combat Aviation Brigade, 1st Infantry Division
- 2nd Combat Aviation Brigade, 2nd Infantry Division – based in South Korea – brigade's Air Cavalry Reconnaissance Squadron rotates from CONUS's based CABs
- 3rd Combat Aviation Brigade, 3rd Infantry Division
- 4th Combat Aviation Brigade, 4th Infantry Division
- Combat Aviation Brigade, 10th Mountain Division
- 25th Combat Aviation Brigade, 25th Infantry Division
- 82nd Combat Aviation Brigade, 82nd Airborne Division
- Combat Aviation Brigade, 101st Airborne Division
Separate CABs
- 12th Combat Aviation Brigade – based in Germany – reduced strength: 1x Attack Reconnaissance Battalion and 1x General Support Aviation Battalion + 1x rotational Assault Helicopter Battalion from CONUS
- 16th Combat Aviation Brigade
Former CABs
Reserve component
The Army National Guard (ARNG) fields eight combat aviation brigades within its eight divisions as well as one theater aviation command which oversees two additional aviation brigades. The Army Reserve fields one theater aviation command which oversees two brigades (one USAR and one ARNG). The Army National Guard brigade is different from the Army's full spectrum combat aviation brigade as it replaces the OH-58D Kiowa Warrior of attack reconnaissance squadron with the Eurocopter UH-72 Lakota and organized into support and security battalion (S&S BN). Thus all ARNG aviation brigades consist of attack reconnaissance battalion (24 AH-64 Apache), security and support battalion (24 UH-72 Lakota), assault helicopter battalion (30 UH-60 Black Hawk), general support aviation battalion (8 UH-60, 12 CH-47 Chinook and 15 HH-60M), UAV company (12 MQ-1C Gray Eagle), and aviation support battalion.
Divisional CABs
- 28th Expeditionary Combat Aviation Brigade (PA ARNG and NJ ARNG) (Heavy CAB)
- Combat Aviation Brigade, 29th Infantry Division (MD ARNG) (Heavy CAB)
- 34th Combat Aviation Brigade (MN ARNG, ND ARNG and ID ARNG)
- Combat Aviation Brigade, 35th Infantry Division, (MO ARNG, NE ARNG and UT ARNG)
- Combat Aviation Brigade, 36th Infantry Division (TX ARNG, CO ARNG, AL ARNG and KS ARNG)
- Combat Aviation Brigade, 38th Infantry Division (IN ARNG)
- Combat Aviation Brigade, 40th Infantry Division (CA ARNG)
- Combat Aviation Brigade, 42nd Infantry Division (NY NG)
Separate CABs
- 11th Expeditionary Combat Aviation Brigade (Army Reserve)
- 63rd Aviation Brigade (KY ARNG) (one GSAB, one theater aviation battalion)
- 77th Combat Aviation Brigade (AR ARNG) (three AHBs, one GSAB)
- 185th Aviation Brigade (MS ARNG) (two GSABs)
- 244th Expeditionary Combat Aviation Brigade (Army Reserve)
- 449th Aviation Brigade (NC ARNG) (Light CAB)
See also
References
- John Lheureux (May 16, 2019) Accomplishing the UAS mission safely
- "Army Aviation: Full Spectrum Capability" (PDF). Army Aviation Association of America. 10 February 2010. Archived from the original (PDF) on 17 March 2012. Retrieved 12 April 2013.
- "Role played by US army aviation in the US tactical maneuver" (PDF). Doctrine Tactique. March 2012. Retrieved 12 April 2013.