Columbia and Port Deposit Railroad
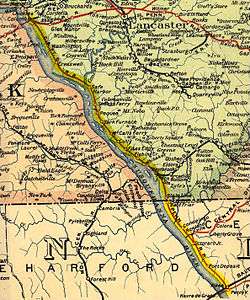
The Columbia and Port Deposit Railroad (C&PD) was a railroad that operated in Pennsylvania and Maryland in the 19th and early 20th centuries. It operated a 34-mile long (55 km) main line between Columbia, Pennsylvania, and Port Deposit, Maryland, generally along the eastern shore of the Susquehanna River. It later acquired a branch line to Perryville, Maryland. The C&PD was subsequently purchased by the Pennsylvania Railroad (PRR) and, since the 1996 breakup of Conrail, is owned by Norfolk Southern Railway.
 | |
| Overview | |
|---|---|
| Headquarters | Philadelphia |
| Locale | Pennsylvania and Maryland |
| Dates of operation | 1868–1916 |
| Successor | Philadelphia, Wilmington and Baltimore Railroad |
| Technical | |
| Track gauge | 4 ft 8 1⁄2 in (1,435 mm) standard gauge |
| Electrification | 11 kV AC, 25 Hz, operational 1938-1981 |
| Length | 44 miles (71 km) |
History
The C&PD, originally called the Washington and Maryland Line Railroad and then the Columbia and Maryland Line Railroad, was chartered in 1858.[1][2] The C&PD began construction in 1866, as another rail line, a branch built by the Philadelphia, Wilmington and Baltimore Railroad (PW&B), approached Port Deposit from the southeast. The PRR, which controlled the PW&B, also purchased a controlling interest in the C&PD in 1866. The first completed section of the C&PD opened in 1868 and connected the newly built Philadelphia and Baltimore Central Railroad at Rowlandsville (4 mi (6.4 km) north of Port Deposit) to the PW&B branch line. The remainder of the line to Columbia was completed in 1877, and all facilities were leased by the PW&B.
The company was reorganized as the Columbia and Port Deposit Railway in 1890.[2] In 1893 the C&PD purchased the Perryville branch line from PW&B,[2] and then PW&B purchased the C&PD.
Successor lines: Late 20th century to present
.jpg)
The PW&B was merged into the Philadelphia, Baltimore and Washington Railroad (PB&W) in 1902, and the C&PD was merged into the PB&W in 1916.[3] The PRR, which controlled all of these companies, labeled the line as the Port Road Branch and electrified the branch in 1938.[4] (The Port Road branch designation continues on the line north of Columbia, to Marysville, along the Enola Branch.)
The PRR merged into Penn Central in 1968, and after the Penn Central bankruptcy in 1970, ownership of the line went to Conrail. Conrail removed electrification equipment on the branch in 1981.[5] There are many remnants of the electrification along much of the line. As part of the Conrail break-up in 1999, the Port Road Branch was sold to Norfolk Southern.[6]
Scheduled passenger service over the Port Road ended on October 29, 1978, when Amtrak re-routed the National Limited's Washington section via Philadelphia.[7]:62
See also
- Atglen and Susquehanna Branch
- Enola Branch
- List of crossings of the Conestoga River
- List of defunct Maryland railroads
- List of defunct Pennsylvania railroads
- List of Pennsylvania Railroad predecessor railroads
References
- Trower, Josh (1999)."History of the Columbia & Port Deposit Railroad." Pennsy Under the Wires. 1999-08-12.
- Wilson, William B. (1895). History of the Pennsylvania Railroad Company. Philadelphia: Henry T. Coates & Co. p. 193.
wilson history pennsylvania railroad.
- Poor's Intermediate Manual of Railroads. New York: Poor's Manual Co. 1917. p. 226.
- Smith, Bruce. "Guide: Columbia and Port Deposit Branch". Keystone Crossings. Jerry Britton. Retrieved 2016-11-28.
- "Electrics". Conrail Historical Society. Marysville, PA. Retrieved 2016-11-28.
- "Brief History of Consolidated Rail Corporation". Conrail. Philadelphia, PA: Consolidated Rail Corporation. Retrieved 2016-11-28.
- Sanders, Craig (2006). Amtrak in the Heartland. Bloomington, Indiana: Indiana University Press. ISBN 978-0-253-34705-3.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Port Road Branch. |
- C & PD Today - Photos and info on Port Road Branch operations
- Conrail's Port Road - Photos from the Conrail era
- Port Road photos (2008)