Colombo Light Rail
The Colombo Light Rail Transit System (Sinhala: කොළඹ සැහැල්ලු දුම්රිය සංක්රමණ පද්ධතිය. Tamil: கொழும்பு இலகு ரக ரயில் கட்டமைப்பு) (also referred to as the Western Region Megapolis Light Rail Transit System) is a metropolitan light rail system under construction serving the designated Western Region Megapolis area within the Colombo District, Sri Lanka.[1] The system is planned to be operated as a public-private partnership between the Government of Sri Lanka and selected private entities.[3]
 | |
| Overview | |
|---|---|
| Area served | Western Region Megapolis |
| Locale | Colombo District/Western Region Megapolis |
| Transit type | Light Rail/Light Metro/Light Rapid Transit |
| Number of lines | 7 (proposed)[1] |
| Operation | |
| Operation will start | 2025[2] |
| Character | Elevated or at grade |
| Train length | 4 compartments (2020s-2035) 6 compartments (2035 and beyond) |
| Technical | |
| System length | 75 km (47 mi) |
Infrastructure
The system is expected to consist of 7 lines (with a mix of both elevated and at grade) and cover a total distance of 75 km.[3] The project's construction is divided into 7 phases, with phase 1 encompassing the construction of part of RTS 1 (Fort to Union Place) and RTS 5 (Battaramulla to Malabe), along with the entirety of RTS 4 (scheduled to begin in late 2018/early 2019), and phases 2 through 7 expanding the network throughout the planned Western Region Megapolis.[3]
Tenders for phases 2 through 6 are scheduled to be called in mid-2018, with construction of the lines taking place simultaneously.[3] All seven phases are expected to be operational by 2023, and cost a total of $6 billion.[3] An extension into the Colombo International Financial City is planned; further expansions beyond 2023 are also planned, with possible extensions of the network to cover Homagama, Horana and Mirigama.[3][4]
Phase 1
Construction/engineering feasibility studies, an environmental impact assessment and a social impact assessment for phase 1 (carried out by Seoyoung Engineering) began in late November 2017, and are slated for completion by June 2018.[3][5] Tenders are also due to be called for the selection of investors for a central maintenance depot.[3] Phase 1 covers 15.8 km with 17 planned stations on two lines, and a planned travel time of 27 minutes.[3][6]
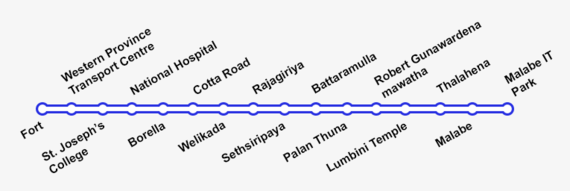
Phase 1, costing $1.25 billion, is funded by a concessionary loan from Japan.[3][7][8] Construction began on 3 July 2019.[9]
Lines[1]
| Name (temporary) | Map colour | Status | Type | Length | Termini | No. Stations | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RTS 1 | Green | Under construction | Elevated | 15.8 kilometres (9.8 mi) | Fort | Malabe IT park | 16 |
| RTS 2 | Orange | Feasibility study pending | Elevated | 11.5 kilometres (7.1 mi) | Fort | Mattakuliya (Western branch) Peliyagoda (Eastern branch) |
TBD |
| RTS 3 | Red | Feasibility study pending | Elevated | 10 kilometres (6.2 mi) | Dematagoda | Bambalapitiya | TBD |
| RTS 4 | Purple | Feasibility study ongoing | Elevated/at grade | 10 kilometres (6.2 mi) | Borella | Battaramulla | TBD |
| RTS 5 | Pink | Feasibility study ongoing (Battaramulla to Malabe) | Elevated/at grade | 9.6 kilometres (6.0 mi) | Battaramulla | Kottawa | TBD |
| RTS 6 | Olive | Feasibility study pending | Elevated/at grade | 6 kilometres (3.7 mi) | Malabe | Kaduwela | TBD |
| RTS 7 | Grey | Feasibility study pending | Elevated/at grade | 10 kilometres (6.2 mi) | Peliyagoda | Kadawatha | TBD |
See also
- Rail transport in Sri Lanka
- Transport in Sri Lanka
- Ministry of Megapolis and Western Development
References
- Western Region Megapolis Transport Master Plan: Final Report, November 2016. Ministry of Megapolis & Western Development. November 2016. Retrieved 6 February 2018.
- "Light Rail Transit operations to commence in 2025". www.dailynews.lk. 11 October 2019. Retrieved 12 October 2019.
- Gunasekara, Skandha (23 November 2017). "Light Rail project to kick off in December 2018". ft.lk. Daily Financial Times. Retrieved 6 February 2018.
- "Expressway, tunnels, LRT to connect reclaimed China Port City in Sri Lanka". economynext.com. EconomyNext. 2 July 2017. Archived from the original on 7 February 2018. Retrieved 6 February 2018.
- "Sri Lanka to conduct feasibility studies for Light Rail Transit systems in Colombo, suburbs". colombopage.com. Colombopage. 3 November 2017. Retrieved 6 February 2018.
- "JICA kicks off study for Colombo-Malabe elevated LRT". lankabusinessonline.com. Lanka Business Online. 3 March 2017. Retrieved 6 February 2018.
- "Sri Lanka Megapolis light rail feasiblity starts, EOIs by year-end". economynext.com. EconomyNext. 28 February 2017. Archived from the original on 7 February 2018. Retrieved 6 February 2018.
- "Japanese loan to fund Colombo light rail project". railwaygazette.com. Railway Gazette. 1 August 2016. Retrieved 6 February 2018.
- "LRT project to be inaugurated today". dailynews.lk. 3 July 2019.