Bivalvulida
Bivalvulida is an order of myxosporean parasites which contains a number of species which cause economically significant losses to aquaculture and fisheries, such as Myxobolus cerebralis and Ceratomyxa shasta. The Myxosporean stages of members of the bivalvulida are characterised by their two spore valves (hence the name), which meet in a "suture line" which encircles the spore. They usually contain two polar capsules, but species have been reported which contain either one or four.
| Bivalvulida | |
|---|---|
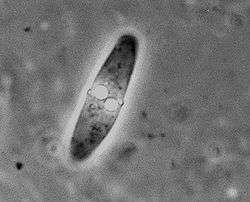 | |
| Alataspora solomoni, a member of the order Bivalvulida | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Cnidaria |
| Class: | Myxosporea |
| Order: | Bivalvulida Shulman, 1959 |
| Suborders | |
| |
Taxonomy and systematics
The order Bivalvulida is composed of three suborders and thirteen families.[1]
- Suborder Platysporina Kudo, 1919[2]
- Myxobolidae Thélohan, 1892[3]
- Suborder Sphaeromyxina Lom & Noble, 1984[4]
- Sphaeromyxidae Lom & Noble, 1984[4]
- Suborder Variisporina Lom & Noble, 1984[4]
- Alatasporidae Shulman, Kovaleva & Dubina, 1979[5]
- Ceratomyxidae Doflein, 1899[6]
- Chloromyxidae Thélohan, 1892[3]
- Coccomyxidae Léger & Hesse, 1907[7]
- Fabesporidae Naidenova & Zaika, 1969[8]
- Myxidiidae Thélohan, 1892[3]
- Myxobilatidae Shulman, 1953[9]
- Ortholineidae Lom & Noble, 1984[4]
- Parvicapsulidae Shulman, 1953[9]
- Sinuolineidae Shulman, 1959[10]
- Sphaerosporidae Davis, 1917[11]
Gallery
Drawings and scanning electron microscopy of species of Chloromyxum
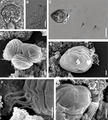 Chloromyxum atlantoraji
Chloromyxum atlantoraji Chloromyxum atlantoraji
Chloromyxum atlantoraji Chloromyxum zearaji
Chloromyxum zearaji
gollark: That's nice. Does it contain Macron?
gollark: Esobot is *so* optimal.
gollark: The PIERB are fine with it. I don't know *what* your "board"'s problem is.
gollark: I'd just have to add you to the list of acceptable IRC bridge targets, reload the IRC link, and manually link the link.
gollark: By implode, I mean discard it.
References
- "WoRMS - World Register of Marine Species - Bivalvulida". marinespecies.org. Retrieved 2018-05-09.
- Kudo, R. (1919). Studies on Myxosporidia. A synopsis of genera and species of Myxosporidia. Illinois Biological Monographs, 5.
- Thélohan, P. (1892). Observation sur les myxosporidies et essai de classification de ces organismes. Bulletin de la Société Philomatique de Paris, 4, 165–178.
- Lom, J. & Noble, E. R. (1984). Revised classification of the class Myxosporea Bütschli, 1881. Folia Parasitologica, 31, 193–205.
- Shulman, S. S., Kovaleva, A. A. & Dubina, V. R. (1979). New myxosporidians from fishes of the Atlantic coast of Africa. Parazitologiya, 13, 71–79.
- Doflein, F. (1899). Amerikanische Dekapoden der k. bayerischen Staatssammlungen. Sitzungberichte der mathematisch-physische Klasse der bayerischen Akademie der Wissenschaften, 29, 177–195.
- Léger, L. & Hesse, E. (1907). Sur une nouvelle Myxosporidie parasite de la sardine. Compte Rendus de l'Académie des Sciences, Paris, 145, 85–87.
- Naidenova, N. N. & Zaika, W. E. (1969). Two new species of Protozoa from the fishes of the Black Sea. Parazitologiya, 3, 97–101.
- Shulman, S. S. (1953). New and little-studied myxosporids. Zoologicheskii Zhurnal, 32(3), 384–393.
- Shulman, S. S. (1959). New classification of Myxosporidia. Trudy Karel'skogo Filiala Akademii Nauk SSSR, Parazitologiya, 33–47.
- Davis, H. S. (1917). The Myxosporidia of the Beaufort Region. A systematic and biologic study. Bulletin of the United States Bureau of Fisheries, 35, 201–243.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.