Chloroalanine
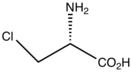
Chloroalanine is an unnatural amino acid with the formula ClCH2CH(NH2)CO2H. It is a white, water-soluble solid. The compound is usually derived from chlorination of serine. The compound is used in the synthesis of other amino acids by replacement of the chloride.[1] Protected forms of the related iodoalanine are also known.[2][3] It is a substrate for 3-chloro-D-alanine dehydrochlorinase.
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
3-chloroalanine, 2-amino-3-chloropropanoic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C3H6ClNO2 | |
| Molar mass | 123.54 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | white solid |
| Melting point | 166–167 °C (331–333 °F; 439–440 K) |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms |  |
| GHS Signal word | Warning |
GHS hazard statements |
H315, H319, H335 |
| P261, P264, P271, P280, P302+352, P304+340, P305+351+338, P312, P321, P332+313, P337+313, P362, P403+233, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
References
- By Hondal, Robert J.; Nilsson, Bradley L.; Raines, Ronald T. (2001). "Selenocysteine in Native Chemical Ligation and Expressed Protein Ligation". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 123: 5140–5141. doi:10.1021/ja005885t.CS1 maint: uses authors parameter (link)
- Richard F. W. Jackson, Manuel Perez-Gonzalez (2005). "Synthesis of N-(Tert-butoxycarbonyl)-β-iodoalanine Methyl Ester: A Useful Building Block in the Synthesis of Nonnatural α-amino Acids via Palladium Catalyzed Cross Coupling Reactions". Org. Synth. 81: 77. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.081.0077.CS1 maint: uses authors parameter (link)
- Atmuri, N. D. P.; Lubell, W. D. (2015). "Preparation of N-(Boc)-Allylglycine Methyl Ester Using a Zinc-mediated, Palladium-catalyzed Cross-coupling Reaction". Org. Synth. 92: 103. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.092.0103.CS1 maint: uses authors parameter (link)
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.