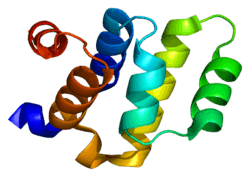
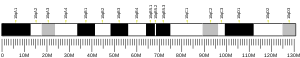
CRADD
Death domain-containing protein CRADD is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CRADD gene.[5][6][7]
Function
The protein encoded by this gene is a death domain (CARD/DD)-containing protein and has been shown to induce cell apoptosis. Through its CARD domain, this protein interacts with, and thus recruits, caspase 2/ICH1 to the cell death signal transduction complex that includes tumor necrosis factor receptor 1 (TNFR1A), RIPK1/RIP kinase, and numbers of other CARD domain-containing proteins.[7]
Interactions
CRADD has been shown to interact with RIPK1[5][6] and Caspase 2.[5][8][9]
gollark: Um.
gollark: ... no.
gollark: I guess we need backpressure.
gollark: Oh. Right. Bridging.
gollark: It's not even running, what.
References
- GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000169372 - Ensembl, May 2017
- GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000045867 - Ensembl, May 2017
- "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- Duan H, Dixit VM (January 1997). "RAIDD is a new 'death' adaptor molecule" (PDF). Nature. 385 (6611): 86–9. doi:10.1038/385086a0. PMID 8985253.
- Ahmad M, Srinivasula SM, Wang L, Talanian RV, Litwack G, Fernandes-Alnemri T, Alnemri ES (March 1997). "CRADD, a novel human apoptotic adaptor molecule for caspase-2, and FasL/tumor necrosis factor receptor-interacting protein RIP". Cancer Res. 57 (4): 615–9. PMID 9044836.
- "Entrez Gene: CRADD CASP2 and RIPK1 domain containing adaptor with death domain".
- Tinel A, Tschopp J (May 2004). "The PIDDosome, a protein complex implicated in activation of caspase-2 in response to genotoxic stress". Science. 304 (5672): 843–6. doi:10.1126/science.1095432. PMID 15073321.
- Droin N, Beauchemin M, Solary E, Bertrand R (December 2000). "Identification of a caspase-2 isoform that behaves as an endogenous inhibitor of the caspase cascade". Cancer Res. 60 (24): 7039–47. PMID 11156409.
External links
- Human CRADD genome location and CRADD gene details page in the UCSC Genome Browser.
Further reading
- Lennon G, Auffray C, Polymeropoulos M, Soares MB (1996). "The I.M.A.G.E. Consortium: an integrated molecular analysis of genomes and their expression". Genomics. 33 (1): 151–2. doi:10.1006/geno.1996.0177. PMID 8617505.
- Hillier LD, Lennon G, Becker M, Bonaldo MF, Chiapelli B, Chissoe S, Dietrich N, DuBuque T, Favello A, Gish W, Hawkins M, Hultman M, Kucaba T, Lacy M, Le M, Le N, Mardis E, Moore B, Morris M, Parsons J, Prange C, Rifkin L, Rohlfing T, Schellenberg K, Bento Soares M, Tan F, Thierry-Meg J, Trevaskis E, Underwood K, Wohldman P, Waterston R, Wilson R, Marra M (1996). "Generation and analysis of 280,000 human expressed sequence tags". Genome Res. 6 (9): 807–28. doi:10.1101/gr.6.9.807. PMID 8889549.
- Chou JJ, Matsuo H, Duan H, Wagner G (1998). "Solution structure of the RAIDD CARD and model for CARD/CARD interaction in caspase-2 and caspase-9 recruitment". Cell. 94 (2): 171–80. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(00)81417-8. PMID 9695946.
- Horvat S, Medrano JF (1998). "A 500-kb YAC and BAC contig encompassing the high-growth deletion in mouse chromosome 10 and identification of the murine Raidd/Cradd gene in the candidate region". Genomics. 54 (1): 159–64. doi:10.1006/geno.1998.5540. PMID 9806843.
- Shearwin-Whyatt LM, Harvey NL, Kumar S (2000). "Subcellular localization and CARD-dependent oligomerization of the death adaptor RAIDD". Cell Death Differ. 7 (2): 155–65. doi:10.1038/sj.cdd.4400632. PMID 10713730.
- Chaudhary PM, Eby MT, Jasmin A, Kumar A, Liu L, Hood L (2000). "Activation of the NF-kappaB pathway by caspase 8 and its homologs". Oncogene. 19 (39): 4451–60. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1203812. PMID 11002417.
- Droin N, Beauchemin M, Solary E, Bertrand R (2000). "Identification of a caspase-2 isoform that behaves as an endogenous inhibitor of the caspase cascade". Cancer Res. 60 (24): 7039–47. PMID 11156409.
- Guo Y, Srinivasula SM, Druilhe A, Fernandes-Alnemri T, Alnemri ES (2002). "Caspase-2 induces apoptosis by releasing proapoptotic proteins from mitochondria". J. Biol. Chem. 277 (16): 13430–7. doi:10.1074/jbc.M108029200. PMID 11832478.
- Tinel A, Tschopp J (2004). "The PIDDosome, a protein complex implicated in activation of caspase-2 in response to genotoxic stress". Science. 304 (5672): 843–6. doi:10.1126/science.1095432. PMID 15073321.
- Rual JF, Venkatesan K, Hao T, Hirozane-Kishikawa T, Dricot A, Li N, Berriz GF, Gibbons FD, Dreze M, Ayivi-Guedehoussou N, Klitgord N, Simon C, Boxem M, Milstein S, Rosenberg J, Goldberg DS, Zhang LV, Wong SL, Franklin G, Li S, Albala JS, Lim J, Fraughton C, Llamosas E, Cevik S, Bex C, Lamesch P, Sikorski RS, Vandenhaute J, Zoghbi HY, Smolyar A, Bosak S, Sequerra R, Doucette-Stamm L, Cusick ME, Hill DE, Roth FP, Vidal M (2005). "Towards a proteome-scale map of the human protein-protein interaction network". Nature. 437 (7062): 1173–8. doi:10.1038/nature04209. PMID 16189514.
- Park HH, Wu H (2006). "Crystal structure of RAIDD death domain implicates potential mechanism of PIDDosome assembly". J. Mol. Biol. 357 (2): 358–64. doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2005.12.082. PMC 2902980. PMID 16434054.
- Vakifahmetoglu H, Olsson M, Orrenius S, Zhivotovsky B (2006). "Functional connection between p53 and caspase-2 is essential for apoptosis induced by DNA damage". Oncogene. 25 (41): 5683–92. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1209569. PMID 16652156.
- Park HH, Wu H (2007). "Crystallization and preliminary X-ray crystallographic studies of the oligomeric death-domain complex between PIDD and RAIDD". Acta Crystallographica Section F. 63 (Pt 3): 229–32. doi:10.1107/S1744309107007889. PMC 2330181. PMID 17329820.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.