Collagen, type IV, alpha 1
Collagen alpha-1(IV) chain (COL4A1) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the COL4A1 gene on chromosome 13.[5][6] It is ubiquitously expressed in many tissues and cell types.[7] COL4A1 is a subunit of the type IV collagen and plays a role in angiogenesis.[8] Mutations in the gene have been linked to diseases of the brain, muscle, kidney, eye, and cardiovascular system.[9][10][11][12] The COL4A1 gene also contains one of 27 SNPs associated with increased risk of coronary artery disease.[13]
Structure
Gene
The COL4A1 gene resides on chromosome 13 at the band 13q34 and contains 54 exons.[5] This gene produces 2 isoforms through alternative splicing.[14]
Protein
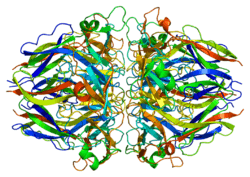
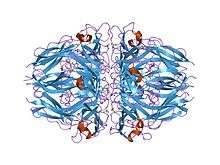
COL4A1 belongs to the type IV collagen family and contains three domains: a short N-terminal domain, a long triple-helical 7S domain at its center, and a non-collagenous 1 (NC1) domain at its C-terminal.[14][15] The triple-helical domain contains interrupted G-X-Y repeats, which is suspected to allow flexibility of the domain.[14] The NC1 domain is composed of two trimeric caps, each containing two alpha 1 fragments and one alpha 2 fragment, that form a sixfold propeller arranged around an axial tunnel. The interaction between these two caps occurs along a large planar interface and is stabilized by a covalent cross-link between the alpha 1 and alpha 2 chains across the two caps.[15]
Function
Type IV collagen is the major structural component of basement membranes, which contains two or three COL4A1 proteins.[9] Thus, COL4A1 is abundant and found in all types of basement membranes.[10] The NC1 domain of COL4A1 is an important antiangiogenic molecule to control the formation of new capillaries.[16] NC1 binds to the α1β1 integrin and inhibits specific integrin signaling pathways in vascular epithelial cells. It also regulates HIF-1α and VEGF expression, presumably by inhibiting the MAPK signaling cascade. These findings may explain the antitumorigenic function of NC1.[17]
Clinical significance
Mutations in COL4A1 exons 24 and 25 are associated with HANAC (autosomal dominant hereditary angiopathy with nephropathy, aneurysms, and muscle cramps).[18] It has also been confirmed that mutations in the COL4A1 gene occur in some patients with porencephaly and schizencephaly.[19][20]
In humans, a novel mutation of the COL4A1 gene coding for collagen type IV was found to be associated with autosomal dominant congenital cataract in a Chinese family. This mutation was not found in unaffected family members or in 200 unrelated controls. In this study, sequence analysis confirmed that the Gly782 amino acid residue was highly conserved.[11] This report of a new mutation in the COL4A1 gene is the first report of a non-syndromic autosomal dominant congenital cataract that highlights an important role for collagen type IV in the physiological and optical properties of the lens.[11]
Additionally, in the cardiovascular field, the COL4A1 and COL4A2 regions on chromosome 13q34 are a highly replicated locus for coronary artery disease. In a normal wall of arteries, collagen type IV acts to inhibit smooth muscle cell proliferation. Accordingly, it was demonstrated that protein expression of collagen type IV in human vascular smooth muscle cells is regulated by both SMAD3 protein and TGFβ mediated stimulation of mRNA.[12] Altogether, it was concluded that the pathogenesis of coronary artery disease may be regulated by COL4A1 and COL4A2 genes.[12]
An autosomal recessive encephalopathy associated with mutations in this gene has also been reported.[21]
Clinical Marker
A multi-locus genetic risk score study based on a combination of 27 loci, including the COL4A1 gene, identified individuals at increased risk for both incident and recurrent coronary artery disease events, as well as an enhanced clinical benefit from statin therapy. The study was based on a community cohort study (the Malmo Diet and Cancer study) and four additional randomized controlled trials of primary prevention cohorts (JUPITER and ASCOT) and secondary prevention cohorts (CARE and PROVE IT-TIMI 22).[13]
References
- GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000187498 - Ensembl, May 2017
- GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000031502 - Ensembl, May 2017
- "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- Soininen R, Haka-Risku T, Prockop DJ, Tryggvason K (December 1987). "Complete primary structure of the alpha 1-chain of human basement membrane (type IV) collagen". FEBS Letters. 225 (1–2): 188–94. doi:10.1016/0014-5793(87)81155-9. PMID 3691802.
- "Entrez Gene: COL4A1 collagen, type IV, alpha 1".
- "BioGPS - your Gene Portal System". biogps.org. Retrieved 2016-10-11.
- Peng, Guicheng; Lin, Maohuan; Zhang, Kun; Chen, Jie; Wang, Yifang; Yang, Yu; Wang, Jingfeng; Huang, Hui (2013-06-19). "Hemoglobin A1c Can Identify More Cardiovascular and Metabolic Risk Profile in OGTT-Negative Chinese Population". International Journal of Medical Sciences. 10 (8): 1028–1034. doi:10.7150/ijms.5905. ISSN 1449-1907. PMC 3691802. PMID 23801890.
- Peng G, Lin M, Zhang K, Chen J, Wang Y, Yang Y, Wang J, Huang H (2013-06-19). "Hemoglobin A1c can identify more cardiovascular and metabolic risk profile in OGTT-negative Chinese population". International Journal of Medical Sciences. 10 (8): 1028–34. doi:10.7150/ijms.5905. PMC 3691802. PMID 23801890.
- Peissel B, Geng L, Kalluri R, Kashtan C, Rennke HG, Gallo GR, Yoshioka K, Sun MJ, Hudson BG, Neilson EG (October 1995). "Comparative distribution of the alpha 1(IV), alpha 5(IV), and alpha 6(IV) collagen chains in normal human adult and fetal tissues and in kidneys from X-linked Alport syndrome patients". The Journal of Clinical Investigation. 96 (4): 1948–57. doi:10.1172/JCI118241. PMC 185832. PMID 7560087.
- Xia XY, Li N, Cao X, Wu QY, Li TF, Zhang C, Li WW, Cui YX, Li XJ, Xue CY (2014-01-01). "A novel COL4A1 gene mutation results in autosomal dominant non-syndromic congenital cataract in a Chinese family". BMC Medical Genetics. 15: 97. doi:10.1186/s12881-014-0097-2. PMC 4236509. PMID 25124159.
- Turner AW, Nikpay M, Silva A, Lau P, Martinuk A, Linseman TA, Soubeyrand S, McPherson R (October 2015). "Functional interaction between COL4A1/COL4A2 and SMAD3 risk loci for coronary artery disease". Atherosclerosis. 242 (2): 543–52. doi:10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2015.08.008. PMID 26310581.
- Mega JL, Stitziel NO, Smith JG, Chasman DI, Caulfield MJ, Devlin JJ, Nordio F, Hyde CL, Cannon CP, Sacks FM, Poulter NR, Sever PS, Ridker PM, Braunwald E, Melander O, Kathiresan S, Sabatine MS (June 2015). "Genetic risk, coronary heart disease events, and the clinical benefit of statin therapy: an analysis of primary and secondary prevention trials". Lancet. 385 (9984): 2264–71. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(14)61730-X. PMC 4608367. PMID 25748612.
- "COL4A1 - Collagen alpha-1(IV) chain precursor - Homo sapiens (Human) - COL4A1 gene & protein". www.uniprot.org. Retrieved 2016-10-11.
- Than, Manuel E.; Henrich, Stefan; Huber, Robert; Ries, Albert; Mann, Karlheinz; Kühn, Klaus; Timpl, Rupert; Bourenkov, Gleb P.; Bartunik, Hans D. (2002-05-14). "The 1.9-A crystal structure of the noncollagenous (NC1) domain of human placenta collagen IV shows stabilization via a novel type of covalent Met-Lys cross-link". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 99 (10): 6607–6612. doi:10.1073/pnas.062183499. ISSN 0027-8424. PMC 124450. PMID 12011424.
- Maragoudakis ME, Missirlis E, Karakiulakis GD, Sarmonica M, Bastakis M, Tsopanoglou N (January 1993). "Basement membrane biosynthesis as a target for developing inhibitors of angiogenesis with anti-tumor properties". Kidney International. 43 (1): 147–50. doi:10.1038/ki.1993.24. PMID 7679456.
- Sudhakar A, Nyberg P, Keshamouni VG, Mannam AP, Li J, Sugimoto H, Cosgrove D, Kalluri R (October 2005). "Human alpha1 type IV collagen NC1 domain exhibits distinct antiangiogenic activity mediated by alpha1beta1 integrin". The Journal of Clinical Investigation. 115 (10): 2801–10. doi:10.1172/JCI24813. PMC 1199529. PMID 16151532.
- Plaisier E, Gribouval O, Alamowitch S, Mougenot B, Prost C, Verpont MC, Marro B, Desmettre T, Cohen SY, Roullet E, Dracon M, Fardeau M, Van Agtmael T, Kerjaschki D, Antignac C, Ronco P (December 2007). "COL4A1 mutations and hereditary angiopathy, nephropathy, aneurysms, and muscle cramps". The New England Journal of Medicine. 357 (26): 2687–95. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa071906. PMID 18160688.
- Yoneda Y, Haginoya K, Kato M, Osaka H, Yokochi K, Arai H, Kakita A, Yamamoto T, Otsuki Y, Shimizu S, Wada T, Koyama N, Mino Y, Kondo N, Takahashi S, Hirabayashi S, Takanashi J, Okumura A, Kumagai T, Hirai S, Nabetani M, Saitoh S, Hattori A, Yamasaki M, Kumakura A, Sugo Y, Nishiyama K, Miyatake S, Tsurusaki Y, Doi H, Miyake N, Matsumoto N, Saitsu H (January 2013). "Phenotypic spectrum of COL4A1 mutations: porencephaly to schizencephaly". Annals of Neurology. 73 (1): 48–57. doi:10.1002/ana.23736. PMID 23225343.
- Smigiel R, Cabala M, Jakubiak A, Kodera H, Sasiadek MJ, Matsumoto N, Sasiadek MM, Saitsu H (April 2016). "Novel COL4A1 mutation in an infant with severe dysmorphic syndrome with schizencephaly, periventricular calcifications, and cataract resembling congenital infection". Birth Defects Research. Part A, Clinical and Molecular Teratology. 106 (4): 304–7. doi:10.1002/bdra.23488. PMID 26879631.
- Yaramis A, Lochmüller H, Töpf A, Sonmezler E, Yilmaz E, Hiz S, Yis U, Gungor S, Ipek Polat A, Edem P, Beltran S, Laurie S, Yaramis A, Horvath R, Oktay Y (2020) COL4A1-related autosomal recessive encephalopathy in 2 Turkish children. Neurol Genet 6(1):e392
Further reading
- Tryggvason K, Soininen R, Hostikka SL, Ganguly A, Huotari M, Prockop DJ (1990). "Structure of the human type IV collagen genes". Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences. 580: 97–111. doi:10.1111/j.1749-6632.1990.tb17922.x. PMID 2186699.
- Hinek A (July 1994). "Nature and the multiple functions of the 67-kD elastin-/laminin binding protein". Cell Adhesion and Communication. 2 (3): 185–93. doi:10.3109/15419069409004436. PMID 7827955.
- Ständer M, Naumann U, Wick W, Weller M (May 1999). "Transforming growth factor-beta and p-21: multiple molecular targets of decorin-mediated suppression of neoplastic growth". Cell and Tissue Research. 296 (2): 221–7. doi:10.1007/s004410051283. PMID 10382266.
- Kurpakus Wheater M, Kernacki KA, Hazlett LD (May 1999). "Corneal cell proteins and ocular surface pathology". Biotechnic & Histochemistry. 74 (3): 146–59. doi:10.3109/10520299909047967. PMID 10416788.
- Ghebrehiwet B, Peerschke EI, Hong Y, Munoz P, Gorevic PD (June 1992). "Short amino acid sequences derived from C1q receptor (C1q-R) show homology with the alpha chains of fibronectin and vitronectin receptors and collagen type IV". Journal of Leukocyte Biology. 51 (6): 546–56. doi:10.1002/jlb.51.6.546. PMID 1377218.
- Gupta S, Batchu RB, Datta K (October 1991). "Purification, partial characterization of rat kidney hyaluronic acid binding protein and its localization on the cell surface". European Journal of Cell Biology. 56 (1): 58–67. PMID 1724753.
- Paralkar VM, Nandedkar AK, Pointer RH, Kleinman HK, Reddi AH (October 1990). "Interaction of osteogenin, a heparin binding bone morphogenetic protein, with type IV collagen". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 265 (28): 17281–4. PMID 2211625.
- Hernandez MR, Igoe F, Neufeld AH (August 1986). "Extracellular matrix of the human optic nerve head". American Journal of Ophthalmology. 102 (2): 139–48. doi:10.1016/0002-9394(86)90134-0. PMID 2426947.
- Aumailley M, Wiedemann H, Mann K, Timpl R (September 1989). "Binding of nidogen and the laminin-nidogen complex to basement membrane collagen type IV". European Journal of Biochemistry / FEBS. 184 (1): 241–8. doi:10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb15013.x. PMID 2506015.
- Pihlajaniemi T, Tryggvason K, Myers JC, Kurkinen M, Lebo R, Cheung MC, Prockop DJ, Boyd CD (June 1985). "cDNA clones coding for the pro-alpha1(IV) chain of human type IV procollagen reveal an unusual homology of amino acid sequences in two halves of the carboxyl-terminal domain". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 260 (12): 7681–7. PMID 2581969.
- Brinker JM, Gudas LJ, Loidl HR, Wang SY, Rosenbloom J, Kefalides NA, Myers JC (June 1985). "Restricted homology between human alpha 1 type IV and other procollagen chains". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 82 (11): 3649–53. doi:10.1073/pnas.82.11.3649. PMC 397843. PMID 2582422.
- Soininen R, Huotari M, Ganguly A, Prockop DJ, Tryggvason K (August 1989). "Structural organization of the gene for the alpha 1 chain of human type IV collagen". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 264 (23): 13565–71. PMID 2701944.
- Siebold B, Deutzmann R, Kühn K (October 1988). "The arrangement of intra- and intermolecular disulfide bonds in the carboxyterminal, non-collagenous aggregation and cross-linking domain of basement-membrane type IV collagen". European Journal of Biochemistry / FEBS. 176 (3): 617–24. doi:10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14321.x. PMID 2844531.
- Pöschl E, Pollner R, Kühn K (September 1988). "The genes for the alpha 1(IV) and alpha 2(IV) chains of human basement membrane collagen type IV are arranged head-to-head and separated by a bidirectional promoter of unique structure". The EMBO Journal. 7 (9): 2687–95. PMC 457057. PMID 2846280.
- Bowcock AM, Hebert JM, Christiano AM, Wijsman E, Cavalli-Sforza LL, Boyd CD (1988). "The pro alpha 1 (IV) collagen gene is linked to the D13S3 locus at the distal end of human chromosome 13q". Cytogenetics and Cell Genetics. 45 (3–4): 234–6. doi:10.1159/000132460. PMID 2891465.
- Solomon E, Hiorns LR, Spurr N, Kurkinen M, Barlow D, Hogan BL, Dalgleish R (May 1985). "Chromosomal assignments of the genes coding for human types II, III, and IV collagen: a dispersed gene family". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 82 (10): 3330–4. doi:10.1073/pnas.82.10.3330. PMC 397769. PMID 2987919.
- Soininen R, Huotari M, Hostikka SL, Prockop DJ, Tryggvason K (November 1988). "The structural genes for alpha 1 and alpha 2 chains of human type IV collagen are divergently encoded on opposite DNA strands and have an overlapping promoter region". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 263 (33): 17217–20. PMID 3182844.
- Brazel D, Oberbäumer I, Dieringer H, Babel W, Glanville RW, Deutzmann R, Kühn K (November 1987). "Completion of the amino acid sequence of the alpha 1 chain of human basement membrane collagen (type IV) reveals 21 non-triplet interruptions located within the collagenous domain". European Journal of Biochemistry / FEBS. 168 (3): 529–36. doi:10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb13450.x. PMID 3311751.