Lymphoblast
A lymphoblast is a modified naive lymphocyte with altered cell morphology. It occurs when the lymphocyte is activated by an antigen (from antigen-presenting cells) and increased in volume by nucleus and cytoplasm growth as well as new mRNA and protein synthesis. The lymphoblast then starts dividing two to four times every 24-hours for 3-5 days, with a single lymphoblast making approximately 1000 clones of its original naive lymphocyte, with each sharing the originally unique antigen specificity. Finally the dividing cells differentiate into effector cells, known as Plasma Cells (for B cells), Cytotoxic T cells, and Helper T cells.[1]
Lymphoblasts can also refer to immature cells which typically differentiate to form mature lymphocytes.[2] Normally lymphoblasts are found in the bone marrow, but in acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL), lymphoblasts proliferate uncontrollably and are found in large numbers in the peripheral blood.
The size is between 10 and 20 μm.[3]
Although commonly lymphoblast refers to a precursor cell in the maturation of leukocytes, the usage of this term is sometimes inconsistent. The Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia Research Consortium defines a lymphoblast as "A lymphocyte that has become larger after being stimulated by an antigen. Lymphoblasts look like immature lymphocytes, and were once thought to be precursor cells."[4] Commonly, when speaking about leukemia, "blast" is used as an abbreviation for lymphoblasts.
Lymphoblasts can be distinguished microscopically from myeloblasts by having less distinct nucleoli, more condensed chromatin, and an absence of cytoplasmic granules. However these morphologic distinctions are not absolute and a definitive diagnosis relies on antibody immunostaining for the presence of unique cluster of differentiation receptors.[5]
Additional images
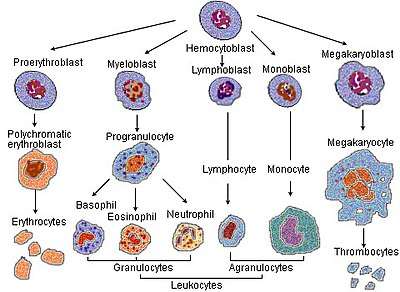 Blood cell lineage
Blood cell lineage
References
- Janeway's Immunobiology, 9th edition, Chapter 1, page 23
- Information, National Center for Biotechnology; Pike, U. S. National Library of Medicine 8600 Rockville; MD, Bethesda; Usa, 20894. "Lymphoblasts - National Library of Medicine". PubMed Health. Retrieved 2015-11-17.CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link)
- Gillian Rozenberg (23 March 2011). Microscopic Haematology: A Practical Guide for the Laboratory. Elsevier Australia. pp. 106–. ISBN 978-0-7295-4072-8. Retrieved 29 May 2011.
- CRC - Glossary L Archived 2006-02-11 at the Wayback Machine
- Kumar, Vinay; Abbas, Abul K.; Fausto, Nelson; Aster, Jon C. (2010). Robbins and Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease. Philadelphia: Saunders. p. 602. ISBN 978-1-4160-3121-5. 8th edition.