Chromatin assembly factor 1
Chromatin assembly factor-1 (CAF-1) is a protein complex — including Chaf1a (p150), Chaf1b (p60), and p50 subunits — that assembles histone tetramers onto replicating DNA.[1][2][3] CAF-1 functions as a histone chaperone that mediates the first step in nucleosome formation by tetramerizing and depositing newly synthesized histone H3/H4 onto DNA rapidly behind replication forks.[4][5] Several studies have shown that the interaction between CAF-1 and PCNA, which stabilizes CAF-1 at replication forks, is important for CAF-1's role in nucleosome assembly[6]
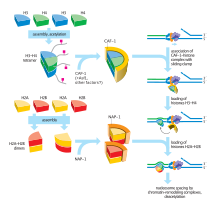
CAF-1 is required for the spatial organization and epigenetic marking of heterochromatin domains in pluripotent embryonic cells, creating a cellular memory of somatic cell identity during cellular differentiation.[7]
Cells resembling 2-cell-stage mouse embryos (totipotent cells) can be induced in vitro through downregulation of the chromatin-assembly activity of CAF-1 in embryonic stem cells.[8]
References
- Kaufman PD, Kobayashi R, Kessler N, Stillman B (1995). "The p150 and p60 subunits of chromatin assembly factor I: a molecular link between newly synthesized histones and DNA replication". Cell. 81 (7): 1105–14. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(05)80015-7. PMID 7600578.
- Smith S, Stillman B (1989). "Purification and characterization of CAF-I, a human cell factor required for chromatin assembly during DNA replication in vitro". Cell. 58 (1): 15–25. doi:10.1016/0092-8674(89)90398-X. PMID 2546672.
- Hoek, M.; Stillman, B. (2003). "Chromatin assembly factor 1 is essential and couples chromatin assembly to DNA replication in vivo". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 100 (21): 12183–12188. Bibcode:2003PNAS..10012183H. doi:10.1073/pnas.1635158100. PMC 218733. PMID 14519857.
- Liu, W. H.; Roemer, S. C.; Zhou, Y; Shen, Z. J.; Dennehey, B. K.; Balsbaugh, J. L.; Liddle, J. C.; Nemkov, T; Ahn, N. G.; Hansen, K. C.; Tyler, J. K.; Churchill, M. E. (2016). "The Cac1 subunit of histone chaperone CAF-1 organizes CAF-1-H3/H4 architecture and tetramerizes histones". eLife. 5: e18023. doi:10.7554/eLife.18023. PMC 5045291. PMID 27690308.
- Sauer, Paul Victor; Timm, Jennifer; Liu, Danni; Sitbon, David; Boeri-Erba, Elisabetta; Velours, Christophe; Mücke, Norbert; Langowski, Jörg; Ochsenbein, Françoise (2017-03-18). "Insights into the molecular architecture and histone H3-H4 deposition mechanism of yeast Chromatin assembly factor 1". eLife. 6: e23474. doi:10.7554/elife.23474. ISSN 2050-084X. PMC 5404918. PMID 28315525.
- Zhang, K; Gao, Y; Li, J; Burgess, R; Han, J; Liang, H; Zhang, Z; Liu, Y (2016). "A DNA binding winged helix domain in CAF-1 functions with PCNA to stabilize CAF-1 at replication forks". Nucleic Acids Research. 44 (11): 5083–5094. doi:10.1093/nar/gkw106. PMC 4914081. PMID 26908650.
- Houlard, Martin; Berlivet, Soizik; Probst, Aline V.; Quivy, Jean-Pierre; Héry, Patrick; Almouzni, Geneviève; Gérard, Matthieu (2006). "CAF-1 Is Essential for Heterochromatin Organization in Pluripotent Embryonic Cells". PLOS Genet. 2 (11): e181. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.0020181. PMC 1630711. PMID 17083276.
- Ishiuchi, T.; Enriquez-Gasca, R.; Mizutani, E.; Bošković, A.; Ziegler-Birling, C.; Rodriguez-Terrones, D.; Torres-Padilla, M. E. (2015). "Early embryonic-like cells are induced by downregulating replication-dependent chromatin assembly". Nature Structural & Molecular Biology. 22 (9): 662–671. doi:10.1038/nsmb.3066. PMID 26237512.
Further reading
- Memory loss enables the production of stem cells. ScienceDaily
- Yu Z, Liu J, Deng WM, Jiao R (2015). "Histone chaperone CAF-1: essential roles in multi-cellular organism development". Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences. 72 (2): 327–337. doi:10.1007/s00018-014-1748-3. PMID 25292338.
- Kaufman, Paul D (2015). "Want reprogramming? Cut back on the chromatin assembly!". Nature Structural & Molecular Biology. 22 (9): 648–650. doi:10.1038/nsmb.3081. PMID 26333710.
- Polo, Sophie E.; Almouzni, Geneviève (2015). "Chromatin dynamics after DNA damage: The legacy of the access–repair–restore model". DNA Repair. 36: 114–21. doi:10.1016/j.dnarep.2015.09.014. PMC 5113751. PMID 26429064.