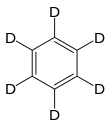
Deuterated benzene
Deuterated benzene (C6D6) is an isotopologue of benzene (C6H6) in which the hydrogen atom ("H") is replaced with deuterium (heavy hydrogen) isotope ("D"). Deuterated benzene is a common solvent used in NMR spectroscopy.[1]
| |||
 | |||
| Identifiers | |||
|---|---|---|---|
3D model (JSmol) |
|||
| 1905426 | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.012.784 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
PubChem CID |
|||
| UN number | 1114 | ||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C62H6 | |||
| Molar mass | 84.1488 g mol−1 | ||
| Density | 0.950 g cm−3 | ||
| Melting point | 7 °C; 44 °F; 280 K | ||
| Boiling point | 79 °C; 174 °F; 352 K | ||
| Thermochemistry | |||
Heat capacity (C) |
152.46 J K−1 mol−1 | ||
| Hazards | |||
| GHS pictograms | 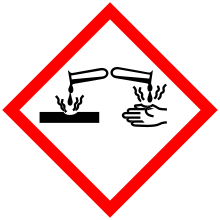   | ||
| GHS Signal word | Danger | ||
GHS hazard statements |
H225, H304, H315, H319, H340, H350, H372 | ||
| P201, P202, P210, P233, P240, P241, P242, P243, P260, P264, P270, P280, P281, P301+310, P302+352, P303+361+353, P305+351+338, P308+313, P314, P321, P331, P332+313, P337+313, P362, P370+378 | |||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |||
| Flash point | −11 °C (12 °F; 262 K) | ||
| Related compounds | |||
Related compounds |
Benzene | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| Infobox references | |||
References
- Fulmer, Gregory R.; Miller, Alexander J. M.; Sherden, Nathaniel H.; Gottlieb, Hugo E.; Nudelman, Abraham; Stoltz, Brian M.; Bercaw, John E.; Goldberg, Karen I. (2010). "NMR Chemical Shifts of Trace Impurities: Common Laboratory Solvents, Organics, and Gases in Deuterated Solvents Relevant to the Organometallic Chemist" (PDF). Organometallics. 29 (9): 2176–2179. doi:10.1021/om100106e.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.