Butyl methacrylate
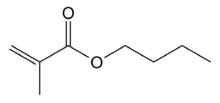
Butyl methacrylate is the organic compound with the formula C4H9O2CC(CH3)=CH2. A colorless liquid, it is a common monomer for the preparation of acrylate polymers.[1] It is typically polymerized under free-radical conditions.[2]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
Butyl 2-methylpropenoate, Acryester B, Acryester BMA, n-butyl methacrylate | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.002.378 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 2227 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C8H14O2 | |
| Molar mass | 142.198 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | colorless liquid |
| Density | 0.8936 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | −25 °C (−13 °F; 248 K) |
| Boiling point | 160 °C (320 °F; 433 K) |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms |   |
| GHS Signal word | Danger |
GHS hazard statements |
H226, H315, H317, H319, H335 |
| P210, P233, P240, P241, P242, P243, P261, P264, P271, P272, P280, P302+352, P303+361+353, P304+340, P305+351+338, P312, P321, P332+313, P333+313, P337+313, P362, P363, P370+378, P403+233, P403+235 | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Flash point | 50 °C (122 °F; 323 K) |
| 290 °C (554 °F; 563 K) | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Health hazards
In terms of the acute toxicity of butyl methacrylate, the LD50 is 20 g/kg (oral, rat). It is an irritant to the eyes and can cause blindness.[1]
gollark: Well, yes, much of the UK's governance is fairly bees?
gollark: Yes, this is quite uncool.
gollark: What if we make it so that you can appoint lords much more easily, but they can only vote on one thing before they have to resign?
gollark: Fascinating.
gollark: I thought they stopped hereditary peerages from hereditating.
See also
References
- Bauer, Jr., William (2002). "Methacrylic Acid and Derivatives". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a16_441..
- Granel, C.; Dubois, Ph.; Jérôme, R.; Teyssié, Ph. (1996). "Controlled Radical Polymerization of Methacrylic Monomers in the Presence of a Bis(ortho-chelated) Arylnickel(II) Complex and Different Activated Alkyl Halides". Macromolecules. 29 (27): 8576–8582. Bibcode:1996MaMol..29.8576G. doi:10.1021/ma9608380.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.
