Buccaneer Archipelago
The Buccaneer Archipelago is a group of islands off the coast of Western Australia near the town of Derby in the Kimberley region. The closest inhabited place is Bardi located about 54 kilometres (34 mi) from the western end of the island group.[1]
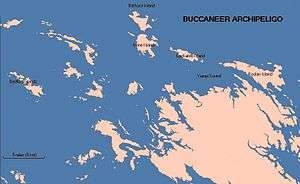
The Archipelago, covering over 50 square kilometres (19 sq mi).[2] is located at the head of King Sound and is composed of about 800 islands found between King Sound and Collier Bay near Yampi Sound.[3] The area experiences a huge tidal range, of over 12 metres (39 ft), which once wreaked havoc on the pearling fleet that operated in the area last century. The islands' rocks are over 2 billion years old, as is the surrounding coastline. The islands themselves were formed more recently as a result of rising sea levels, creating a drowned coastline. The rocks are ancient Precambrian sandstones. The islands are generally rocky, many with high cliffs. The islands are in almost pristine condition as a result of their isolation and difficulty of access. Some are sparsely vegetated with patches of rain-forest, and areas fringed with mangroves where silt has built up.[4]
The traditional owners of the area are the Mayala group made up of the Yawijibaya and Unggarranggu peoples although the Bardi people have traditional rights of fishing and trochus.[5]
The archipelago was named after the English buccaneer and privateer William Dampier, who charted the area in 1688, by Philip Parker King in August 1821.[6]
Islands
| Island | Area | Location |
|---|---|---|
| Admiral Island (Western Australia) | 16°04′00″S 123°24′06″E | |
| Bathurst Island (Western Australia) | 16°02′41″S 123°31′57″E | |
| Bedford Islands | 16°09′29″S 123°20′11″E | |
| Bruen Island | 16°04′00″S 123°22′45″E | |
| Byron Island (Buccaneer Archipelago) | 16°09′45″S 123°26′55″E | |
| Caffarelli Island | 2.12 km2 (0.82 sq mi) | 16°02"36'S 123°16"48'E (lighthouse) |
| Cleft Island (Western Australia) | 16°02′16″S 123°21′01″E | |
| Cockatoo Island (Western Australia) | 16°05′55″S 123°37′00″E | |
| Fraser Island (Western Australia) | 16°03′28″S 123°21′51″E | |
| Goat Island (Western Australia) | ||
| Hidden Island | 19.7 km2 (8 sq mi) | 16°13′32″S 123°28′03″E |
| Irvine Island | 9 km2 (3 sq mi) | 16°04′35″S 123°32′14″E |
| King Hall Island | 16°04′52″S 123°24′29″E | |
| Koolan Island | 27.1 km2 (10 sq mi) | 16°07′31″S 123°44′18″E |
| Long Island (Western Australia) | 11 km2 (4 sq mi).[7] | 16°34′26″S 123°22′11″E |
| Longitude Island | 16°03′34″S 123°24′01″E | |
| Powerful Island | 16°05′57″S 123°25′50″E | |
| Sunday Island (King Sound) | 13.3 km2 (5 sq mi) | 16°24′25″S 123°11′13″E |
References
- "Bonzle Digital Atlas – Map of Buccaneer Archipelago". 2009. Retrieved 23 March 2009.
- "Discover West - Buccaneer Archipelago". 2009. Retrieved 23 March 2009.
- "Ocean Dots - The Island Encyclopedia - Buccaneer Archipelago". 2009. Archived from the original on 23 December 2010. Retrieved 23 March 2009.
- "Derby Visitor Centre". 2009. Archived from the original on 26 December 2008. Retrieved 23 March 2009.
- Luise Anna Hercus and Harold James Koch (2009). Aboriginal Placenames: Naming and Re-naming the Australian Landscape. ANU Press. p. 337. ISBN 9781921666087.
- King, Phillip Parker (1827). Narrative of a Survey of the Intertropical and Western Coasts of Australia. London: John Murray. http://gutenberg.net.au/ebooks/e00028.html#chapter02
- "Status Performance Assessment: Biodiversity conservation of Western Australian Islands" (PDF). Government of Western Australia. 1 April 2010. Archived from the original (PDF) on 14 March 2018. Retrieved 29 August 2014.