Bréguet-Richet Gyroplane
The Bréguet-Richet Gyroplane was an early French experimental quadcopter rotary-wing aircraft developed by Bréguet Aviation.
| Gyroplane No.I and No.II | |
|---|---|
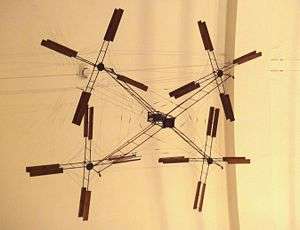 | |
| Bréguet-Richet Gyroplane No.1, 1907. | |
| Role | Rotary-wing test vehicle |
| Manufacturer | Bréguet |
| Designer | Louis Bréguet |
| First flight | 29 September 1907 |
| Number built | 2 |
Design and development
The Gyroplane No.I was one of the earliest attempts to create a practical rotary-wing aircraft. It was designed by the Bréguet brothers with help from Professor Charles Richet. The aircraft had an uncovered open steel framework with a seat for the pilot and a powerplant at the centre. Radiating from the central structure were four wire-braced tubular steel arms, each bearing a superimposed pair of four-bladed rotors. To eliminate the torque effect, two rotor sets were driven clockwise and two counter-clockwise.
Operational service
On 29 September 1907, the Gyroplane No.I was flown for the first time, albeit to an elevation of only 0.6 metres (2.0 ft).[1] It was not a free flight, as four men were used to steady the structure. It was neither controllable nor steerable, but it was the first time that a rotary-wing device had lifted itself and a pilot into the air.[1] It later flew up to 1.52 m (4.99 ft) above the ground. The design was improved and the Gyroplane No.II appeared the following year. No.II had two two-blade rotors of 7.85 m (25.75 ft) diameter and also had fixed wings. Powered by a 41 kW (55 hp) Renault engine, it was reported to have flown successfully more than once in 1908. No.II was damaged in a heavy landing and was rebuilt as the No.IIbis. It flew at least once in April 1909 before being destroyed when the company's works were badly damaged in a severe storm.
Specifications (No.I)
General characteristics
- Crew: one
- Height: 3.7 m (12 ft 2 in)
- Empty weight: 500 kg (1,102 lb)
- Gross weight: 578 kg (1,274 lb)
- Powerplant: 1 × Antoinette water-cooled piston engine, 34 kW (46 hp)
- Main rotor diameter: 4× 8 m (26 ft 3 in)
- Main rotor area: 402.2 m2 (4,329 sq ft) biplane rotors
Performance
- Endurance: 1 minute
- Service ceiling: 0.6 m (2.0 ft)
References
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Bréguet-Richet Gyroplane. |
Notes
- Young 1982, p. 28.
Bibliography
- Young, Warren R. The Helicopters. "The Epic of Flight". Chicago: Time-Life Books, 1982. ISBN 0-8094-3350-8.
- The Illustrated Encyclopedia of Aircraft (Part Work 1982-1985). Orbis Publishing.