Bondoukou
Bondoukou (var. Bonduku, Bontuku) is a city in north-eastern Ivory Coast, 420 km northeast of Abidjan.[3] It is the seat of both Zanzan District and Gontougo Region. It is also a commune and the seat of and a sub-prefecture of Bondoukou Department.
Bondoukou Bonduku; Bontuku | |
|---|---|
City, sub-prefecture, and commune | |
 Bondoukou in 1910 | |
 Bondoukou Location in Ivory Coast | |
| Coordinates: 8°2′N 2°48′W[1] | |
| Country | |
| District | Zanzan |
| Region | Gontougo |
| Department | Bondoukou |
| Government | |
| • Mayor | Kone Hiliassou |
| Elevation | 343 m (1,125 ft) |
| Population (2014)[2] | |
| • Total | 117,453 |
| Time zone | UTC+0 (GMT) |
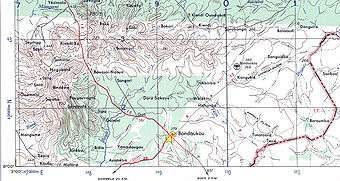
Bondoukou is near the border with Ghana. Just across the border is the Ghanaian town of Sampa. The city lies at the junction of the main A1 highway with roads to Sorobango to the north and Ghana to the east.
History
Bighu was abandoned according to Bakewell, "as a result of bitter internecine struggles." Bonduku became the "premier settlement of the Bighu Juula after the collapse of the older town." "This town was established by the major part of the inhabitants of Bego...the Hausa have given it the name of Bitu...regarding it as simply having changed its location."[4]
Originally a Dyula trading center, Bondoukou was conquered by the Abron, an Akan people, in the early seventeenth century; it soon became the economic hub of the Gyaaman kingdom.[5] On 13 November 1888, the French officer Treich-Laplène signed a Protectorate treaty with the Abron king of Bondoukou, but the city fell to Samori between September 1895 and July 1897, and unlike nearby centers, he did not destroy the old city, but deposed the Abron in favour of the Muslim Dyula. The French incorporated the town into French West Africa in 1899. At the end of the colonial period, the town had shrunk to large village, eclipsed by the nearby administrative center of Loti. In 1964 it was made administrative center for its region, and as since regained its status as the largest town, and is the seat of the Prefect governing Bouna, Tanda, and Bondoukou Departments. In 1980, the town came to prominence as the home of the first secondary school strikes by students opposed to the PDCI-RDA government. On the dividing line between government and rebel zones of control during the Ivorian Civil War, Bondoukou became the main north-eastern base of the United Nations Operation in Côte d'Ivoire (ONUCI).[6]
Population
In the 2014 census, the city had a population of 117,453.[2] This represents a dramatic increase from an estimated 45,000 in 2005,[7] and 60,000 in 2007. The city's role as a trade center has made it home to a diverse population. The walled old city (Medina) includes ethnic neighbourhoods from far flung groups who originally came to the area as part of long distance trade networks. These include the Donzoso of the Donzo-Ouattara Dyula (related to the warrior Ouattara clans of the Kong Empire), the Jiminiso/Limamso of the Timité Dyula (which is home to the most prominent Muslim schools), the Hausa merchant town quarter of Malagaso, as well as the mostly Christian Bambaraso quarter. Other traditional Muslim neighbourhoods, each with their own clan leader and identity, include the Karidyulaso, Kamagaya, Koko, Hwelaso, Neneya, and Koumalaso quarters. Neighborhoods, like the Abron Mont Zanzan area, lie outside the old city, which is bounded by the Wamo river on the southwest. The Baya river also borders the suburbs to the west.[8] Often Muslim, each group centered around their own Mosque, earning the town the nickname "the city of a thousand mosques."[9] Because of the influence of populations from the north, many Bondoukou mosques are of the Sudanic architectural style, more common northern cities like Timbuktu or Djenne.[10] This further led to the town's importance as a center of religious learning.[11] The French introduced Christianity, and the town is also the seat of the Roman Catholic Diocese of Bondoukou. Prominent buildings include the house used by French explorer Louis Gustave Binger, Samori's headquarters, the old market building which houses the "Bondoukou Museum of Art and Traditions" ("Musée des Arts et des Traditions"), and the Limamisso and Kamagaya mosques. Outside the old town, major neighbourhoods include "Mont Zanzan", "Lycée", "TP", and "Camp Militaire."
Outside the town, historic sites include an Akan ceremonial center at Soko (just east), pottery works at Montiamo, the treasure house of the Abron war-leader at Wéletchéi (just north), and the French colonial era plantations at Goli (just west). The town is also known for cultural events, including the yam harvest festival, and the Sakaraboutou (warriors' parade) and Kourouby women's parade (both celebrated at the end of Ramadan).[12] Apart from Diola, Mande, and Akan peoples, the Gontougo Department is home to a patchwork of ethnic groups including the Nafaanra, Koulango, and Lobi.
Administration
In 1978[13] Bondoukou was made one of the 27 communes de plein exercice or self-governing towns in the nation. In the 2011 reorganisation of the subdivisions of Ivory Coast, Bondoukou became a sub-prefecture.
| Date of Election | Name | Party |
|---|---|---|
| 1980 | Fétigué Koulibaly | PDCI-RDA |
| 1985 | Yaya Ouattara | PDCI-RDA |
| 1990 | Lamine Ouattara | PDCI-RDA |
| 1995 | Félix Kouakou Dapa | PDCI-RDA |
| 2001 | Félix Kouakou Dapa | PDCI-RDA |
Services
The town is home to several schools (from primary to post-secondary), a regional hospital and an Ivorian second division Football club, Scaraboutou sports de Bondoukou. Bondoukou has an airport, Soko Airport, with IATA code BDK. In 2014, the population of the sub-prefecture of Bondoukou was 117,453 [14].
Villages
The twenty eight villages of the sub-prefecture of Bondoukou and their population in 2014 are [14]:
- Bondoukou (88 783)
- Goli (434)
- Motiamo (1 779)
- Ouélékéi (1 174)
- Sanguéi (566)
- Soko (6 501)
- Songori (1 432)
- Abéma (566)
- Assouangui (271)
- Bodem (156)
- Boromba (3 070)
- Ganhimi (755)
- Gbagnagassié (321)
- Gbaki (271)
- Gbokoré-Pinango (336)
- Guimini (347)
- Kiendi-Ba (1 437)
- Kouassi-N'dawa (1 654)
- Nagabaré-Gboko (505)
- Pougouvagne (501)
- Sabi (463)
- Sama (151)
- Séréoudé (2 461)
- Similibi (571)
- Sipa (739)
- Sogobo (622)
- Témogossié (860)
- Tissié (727)
Climate
| Climate data for Bondoukou | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average high °C (°F) | 33.7 (92.7) |
35.0 (95.0) |
34.5 (94.1) |
32.8 (91.0) |
31.6 (88.9) |
29.5 (85.1) |
27.9 (82.2) |
27.6 (81.7) |
28.7 (83.7) |
30.5 (86.9) |
32.0 (89.6) |
32.2 (90.0) |
31.3 (88.3) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 26.4 (79.5) |
28.0 (82.4) |
28.2 (82.8) |
27.5 (81.5) |
26.6 (79.9) |
25.2 (77.4) |
24.3 (75.7) |
24.0 (75.2) |
24.3 (75.7) |
25.3 (77.5) |
26.0 (78.8) |
25.5 (77.9) |
25.9 (78.6) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 19.6 (67.3) |
21.6 (70.9) |
22.5 (72.5) |
22.5 (72.5) |
22.2 (72.0) |
21.3 (70.3) |
20.9 (69.6) |
20.7 (69.3) |
20.7 (69.3) |
20.9 (69.6) |
21.1 (70.0) |
19.7 (67.5) |
21.1 (70.0) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 7.9 (0.31) |
26.9 (1.06) |
92.3 (3.63) |
123.7 (4.87) |
156.1 (6.15) |
160.2 (6.31) |
96.5 (3.80) |
90.0 (3.54) |
175.1 (6.89) |
130.5 (5.14) |
31.6 (1.24) |
11.1 (0.44) |
1,101.9 (43.38) |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 227.0 | 221.0 | 212.9 | 205.4 | 207.0 | 157.7 | 111.4 | 90.4 | 118.7 | 186.5 | 196.6 | 202.9 | 2,137.5 |
| Source: NOAA[15] | |||||||||||||
Rural ethnic conflict
The 1990s and 2000s saw periodic ethnic conflict between the Bondoukou Kulango farmers (a Gur people who form the Nkurang of Ghana)[16] and the Lobi people, recently migrated from Bouna Department. Conflicts between the two ethnic groups date from at least 1993, when clashes erupted over attempts by Lobi pastoralists to resettle in the area.[17] Clashes and counter clashes have killed several dozen people in the villages of Abouabou, Gonzaqueville, and Marahui with escalations taking place during the Ivorian Civil War in 2002 and in 2008.[18] The informal ceasefire line of the Civil War ran through Bondoukou Department, leaving most of Zanzan (excluding Bouna Department) under central government control.
References
- "Ivory Coast Cities Longitude & Latitude". sphereinfo.com. Archived from the original on 13 September 2012. Retrieved 18 November 2010.
- "Côte d'Ivoire". geohive.com. Retrieved 5 December 2015.
- Conflit foncier dans le nord ivoirien : 8 morts et 21 blessés. Places Bondoukou 424 km NE of capitol. APA : 8/9/2008
- Wilks,Ivor. Wangara, Akan, and Portuguese in the Fifteenth and Sixteenth Centuries (1997). Bakewell, Peter (ed.). Mines of Silver and Gold in the Americas. Aldershot: Variorum, Ashgate Publishing Limited. p. 17.CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
- Le royaume Abron de Bondoukou, retrieved 2008-09-10
- Bondoukou, Cote d'Ivoire, reflections of UN Worker, 2008.
- bondoukou2000 website, retrieved 2008-09-10.
- As these neighbourhoods are important for the traditional parades, they are detailed in Arnut, pp. 121-150.
- "la ville aux mille mosquées" bondoukou2000 website
- "Mosques of Bondoukou" photo collection Archived December 1, 2008, at the Wayback Machine: Ray Silverman (1987), African Online Digital Library
- Drinking the Word of God, 2002
- Karel Arnaut, Performing displacements and rephrasing attachments. Ethnographic explorations of mobility in art, ritual, media, and politics Archived 2009-03-19 at the Wayback Machine. Chapter II: 'Sakaraboutou is a Bondoukou custom': an investigation into ritual spaces and performative positions. pp.115-202, Doctoral Dissertation, University of Ghet (2004).
"la ville aux mille mosquées" bondoukou2000 website & Traditions on the same site. - Loi no 78-07 du 9 janvier 1978
- "RGPH 2014, Répertoire des localités, Région Gontougo" (PDF). ins.ci. Retrieved 5 August 2019.
- "Bondoukou Climate Normals 1961–1990". National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Retrieved March 8, 2015.
- Ethnologue code "kzc"
- Ethnic violence flares up in Ivory Coast, IOL News, September 08 2008.
- Côte d’Ivoire – Land dispute. Land dispute leaves 8 dead, 21 injured in northern Côte d’Ivoire, APA news 8 September 2008
- Muhammad, Akbar. The Samorian Occupation of Bondoukou: An Indigenous View. The International Journal of African Historical Studies, Vol. 10, No. 2 (1977), pp. 242–258.
- Drinking the Word of God. Expressions of Faith and the Search for Well-Being in Two West African Communities. March 18, 2001 - January 20, 2002. Short history and photo gallery, Michigan State University, retrieved 2008-09-10.
- Portions of this article were translated from the French language Wikipedia article fr:Bondoukou, 2008-09-10.