Blériot 5190
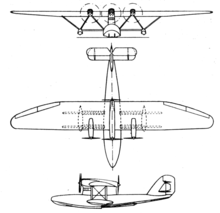
The Blériot 5190 was a French transatlantic mail plane of the 1930s, a large parasol-wing monoplane flying boat. It was of slightly unusual design, with a low-profile hull and the crew compartment housed in the thick pylon that supported the wing. The four engines were arranged with three along the leading edge of the wing, and the fourth on the centreline of the trailing edge. It was constructed for a French government contract to carry airmail to South America.
| Blériot 5190 | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Seaplane Blériot 5190 Santos-Dumont. | |
| Role | Mail plane |
| Manufacturer | Blériot Aéronautique |
| Designer | Filippo Zappata |
| First flight | 3 August 1933 |
| Introduction | 1935 |
| Retired | 1937 |
| Primary user | Aéropostale |
| Number built | 1, plus 3 under construction |
The first example, christened Santos-Dumont flew on 3 August 1933 and by the end of 1934 had completed two proving flights across the South Atlantic, with Lucien Bossoutrot at the commands and the future French Admiralty Chief of Staff Henri Nomy as flight engineer. In February 1935 with Aéropostale's only other transatlantic mailplane, the Latécoère 300 la Croix du Sud, out of commission for maintenance, the Santos-Dumont entered service. From then until April, she carried all of France's transatlantic mail at the rate of one crossing per week until rejoined by la Croix du Sud and a new Farman F.220 named Le Centaure. As part of this small fleet, the Santos-Dumont continued in this role until June 1937. Altogether, by that time, she had made 38 crossings of the Atlantic.
In the meantime, the French government had ordered a further three 5190s from Blériot, and the company had borrowed heavily in order to build the aircraft. Suddenly, the contract was cancelled without explanation or compensation, forcing the firm into bankruptcy. Louis Blériot himself died of a heart attack soon afterwards, on 1 August 1936.
Specifications
General characteristics
- Crew: Four
- Length: 26.00 m (141 ft 0 in)
- Wingspan: 43.00 m (85 ft 3 in)
- Height: 6.90 m (22 ft 8 in)
- Wing area: 236.0 m2 (2,539 sq ft)
- Empty weight: 12,750 kg (28,109 lb)
- Gross weight: 22,000 kg (48,500 lb)
- Powerplant: 4 × Hispano-Suiza 12Nbr , 485 kW (650 hp) each
Performance
- Maximum speed: 210 km/h (131 mph, 114 kn)
- Range: 5,000 km (3,100 mi, 2,700 nmi)
- Service ceiling: 5,100 m (16,730 ft)
References
- Taylor, Michael J. H. (1989). Jane's Encyclopedia of Aviation. London: Studio Editions. p. 162.
- aviafrance.com
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Blériot 5190. |