Bis(triphenylphosphine)iminium chloride
Bis(triphenylphosphine)iminium chloride is the chemical compound with the formula [(C6H5)3P)2N]Cl, often written [(Ph3P)2N]Cl and abbreviated [PPN]Cl or [PNP]Cl. This colorless salt is a source of the PPN+ cation, which is used as an unreactive and weakly coordinating cation to isolate reactive anions. PPN+ is a phosphazene.
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
μ-nitrido-Bis(triphenylphosphorus) chloride | |
| Other names
PNP chloride PPN chloride Bis(triphenylphosphine)iminium chloride Bis(triphenylphosphoranylidene)iminium chloride Bis(triphenylphosphoranylidene)ammonium chloride Hexaphenyldiphosphazenium chloride Selectophore | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.040.139 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C36H30ClNP2 | |
| Molar mass | 574.03 g/mol |
| Appearance | colourless solid |
| Melting point | 260 to 262 °C (500 to 504 °F; 533 to 535 K) |
| moderate | |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms |  |
| GHS Signal word | Warning |
GHS hazard statements |
H315, H319, H332, H335 |
| P261, P264, P271, P280, P302+352, P304+312, P304+340, P305+351+338, P312, P321, P332+313, P337+313, P362, P403+233, P405, P501 | |
| Related compounds | |
Related compounds |
Tetraphenylarsonium chloride Tetrabutylammonium chloride tetrabutylammonium chloride |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Synthesis and structure
PPNCl is prepared in two steps from triphenylphosphine:[1]
- Ph3P + Cl2 → Ph3PCl2
This triphenylphosphine dichloride is related to phosphorus pentachloride. Treatment of this species with hydroxylamine in the presence of Ph3P results in replacement of the P-Cl bonds by P=N bonds:
- 2 Ph3PCl2 + NH2OH·HCl + Ph3P → {[Ph3P]2N}Cl + 4HCl + Ph3PO
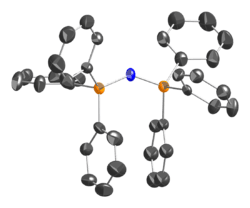
The PNP angle in the cation is flexible, ranging from ~130 to 180° depending on the salt. Bent and linear forms have been observed in the same unit cell.[2] The same shallow potential well for bending is observed in the isoelectronic species bis(triphenylphosphoranylidene)methane, (Ph3P)2C, as well as the more distantly related molecule carbon suboxide. For the solvent-free chloride salt, the PNP bond angle was determined to be 133°.[3] The P-N bond lengths are equivalent at 1.597(2) Å.
Applications
In the laboratory, PPN chloride is the main precursor to PPN+ salts. Using salt metathesis reactions, nitrite, azide, and other small inorganic anions can be obtained with PPN+ cations. The resulting salts PPNNO2, PPNN3 etc. are soluble in polar organic solvents.
PPN+ forms crystalline salts with a range of anions that are otherwise difficult to crystallize. Its effectiveness is partially attributable to its rigidity, reflecting the presence of six phenyl rings. Often PPN+ forms salts that are more air-stable than salts with smaller cations such as those containing quaternary ammonium or alkali metal cations. This effect is attributed to the steric shielding provided by this voluminous cation. Illustrative PPN+ salts of reactive anions include PPN[HFe(CO)4], PPN[Co(CO)4], and PPN[Fe(CO)3NO]. The role of ion pairing in chemical reactions is often clarified by examination of the related salt derived from PPN+.
Related cations
A phosphazenium cation related to PPN+ is {[(CH3)2N)3P]2N}+.[4]
References
- Ruff JK, Schlientz WJ, Dessy RE, Malm JM, Dobson GR, Memering MN (1974). "μ-nitrido-Bis(triphenylphosphorus)(1+ ("PPN") Salts with Metal Carbonyl Anions". Inorg. Synth. 15: 84–90. doi:10.1002/9780470132463.ch19.
- Hardy GE, Zink JI, Kaska WC, Baldwin JC (December 1978). "Structure and triboluminescence of polymorphs of hexaphenylcarbodiphosphorane". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 100 (25): 8001–8002. doi:10.1021/ja00493a035.
- Knapp C, Uzun R (November 2010). "Solvate-free bis-(triphenylphosphine)iminium chloride". Acta Crystallographica Section E. 66 (Pt 12): o3185. doi:10.1107/S1600536810046325. PMC 3011587. PMID 21589480.
- Schwesinger, Reinhard (2001). "1,1,1,3,3,3-Hexakis(dimethylamino)-1λ5,3λ5-diphosphazenium fluoride". e-EROS Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis. pp. 1–2. doi:10.1002/047084289X.rh014m.