Biggs Site
The Biggs Site (15Gp8), also known as the Portsmouth Earthworks Group C, is an Adena culture archaeological site located near South Shore in Greenup County, Kentucky. Group C was originally a large series of concentric circular embankments and ditches surrounding a central conical burial mound. It was part of a larger complex, the Portsmouth Earthworks located across the Ohio River, now mostly obliterated by agriculture and the developing city of Portsmouth, Ohio.[1] The site was surveyed and mapped by E. G. Squier in 1847 for inclusion in the seminal archaeological and anthrolopological work Ancient Monuments of the Mississippi Valley.[2]
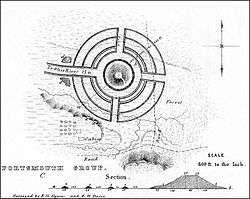 Group C of the Portsmouth Earthworks by Squier and Davis | |
 Location within Kentucky today | |
| Location | South Shore, Kentucky, Greenup County, Kentucky, |
|---|---|
| Region | Greenup County, Kentucky |
| Coordinates | 38°44′8.70″N 82°54′11.92″W |
| History | |
| Cultures | Adena culture |
| Site notes | |
| Architecture | |
| Architectural styles | earthworks |
| Responsible body: private | |
References
- Applegate, Darlene (2008), "Chapter 5:Woodland period", in Pollack, David (ed.), The Archaeology of Kentucky:an update (PDF), 1, Kentucky Heritage Council, pp. 524–525, ISBN 978-1-934492-28-4, archived from the original (PDF) on 2010-11-08
- E. G. Squier and E. H. Davis (1848). Ancient Monuments of the Mississippi Valley. Smithsonian Institution.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.