Bentley BR2
The Bentley B.R.2 was a nine-cylinder British rotary aircraft engine developed during the First World War by the motor car engine designer W. O. Bentley from his earlier Bentley BR.1. Coming as it did near the end of the war, the BR.2 was built in smaller numbers than the earlier BR.1 – its main use being by the Royal Air Force in the early 1920s.[1]
| BR.2 | |
|---|---|
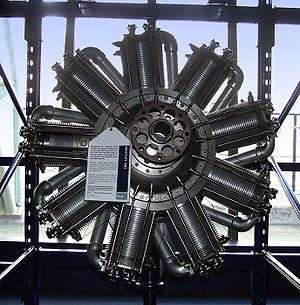 | |
| Preserved Bentley B.R.2 | |
| Type | Rotary engine |
| Manufacturer | Humber Limited |
| First run | 1916 |
| Major applications | Sopwith Snipe |
| Number built | 2,567 |
| Developed from | Bentley BR.1 |
Design and development
The initial variant of the BR.2 developed 230 horsepower (170 kW), with nine cylinders measuring 5.5 by 7.1 inches (140 mm × 180 mm) for a total displacement of 1,522 cubic inches (24.9 L). It weighed 490 pounds (220 kg), only 93 pounds (42 kg) more than the Bentley B.R.1 (A.R.1).
This was the last type of rotary engine to be adopted by the RAF – later air-cooled aircraft engines such as the Cosmos Jupiter and Armstrong Siddeley Jaguar being almost entirely of the fixed radial type. With the BR.2, the rotary engine had reached a point beyond which this type of engine could not be further developed, due to its inherent limitations.[2]
Applications
The type selected as the standard single-seat fighter of the post-war RAF, the Sopwith Snipe, had been designed around the BR.2, as had its ground attack version, the Sopwith TF.2 Salamander. A number of other experimental and minor production types were either designed for, or otherwise fitted with this power plant during the late "war" years and into the early 1920s.

Variants
- BR.2 230
- 1918, 230 hp.
- BR.2 245
- 1918, 245 hp.
Engines on display
A Bentley BR.2 is on public display in the Science Museum (London), another forms part of the aero engine collection at the Royal Air Force Museum Cosford. Another one (serial number 40543, manufactured by Gwynnes) is in the National Military Museum, Romania.
A ¼ scale working replica of the Bentley BR.2 World War I rotary aero engine built by Lewis Kinleside Blackmore is currently on display at the Bentley Memorial Building in Oxfordshire, UK. This was the first model built of this engine and is the subject also of a book by L K Blackmore.
The Canada Aviation and Space Museum in Ottawa, Ontario, Canada has a BR.2 installed in their Sopwith 7F.1 Snipe.
Specifications (BR.2)
Data from Jane's [3]
General characteristics
- Type: 9-cylinder rotary
- Bore: 5.51 in (140 mm)
- Stroke: 7.09 in (180 mm)
- Displacement: 1521.8 in (24.94 L)
- Dry weight: 490 lb (220 kg)
Components
- Valvetrain: Overhead valve
- Cooling system: Air-cooled
Performance
- Power output: 250 hp
- Fuel consumption: 20 gallons per hour
- Oil consumption: 16 pints per hour
- Power-to-weight ratio: 0.5 hp/lb
See also
Related development
Comparable engines
Related lists
References
Notes
- Lumsden 2003, p.88.
- Gunston 1989, p.22.
- Jane's 1993, p.274.
Bibliography
- Gunston, Bill (1986). World Encyclopedia of Aero Engines. Wellingborough: Patrick Stephens. pp. 25–26.
- Gunston, Bill. World Encyclopedia of Aero Engines. Cambridge, England. Patrick Stephens Limited, 1989. ISBN 1-85260-163-9
- Jane's Fighting Aircraft of World War I. London. Studio Editions Ltd, 1993. ISBN 1-85170-347-0
- Lumsden, Alec. British Piston Engines and their Aircraft. Marlborough, Wiltshire: Airlife Publishing, 2003. ISBN 1-85310-294-6.