Bayonnaise Rocks
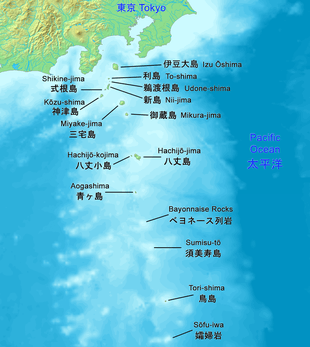
Bayonnaise Rocks (ベヨネース列岩, Beyonēsu-retsugan) is a group of volcanic rocks in the Philippine Sea about 408 kilometres (254 mi) south of Tokyo and 65 kilometres (40 mi) south-southeast of Aogashima, in the south portion of the Izu archipelago, Japan. The rocks were discovered by the French corvette Bayonnaise in 1850, while surveying the islands south of Tokyo Bay.[1]
| Native name: ベヨネース列岩 | |
|---|---|
 | |
 | |
| Geography | |
| Location | Izu Islands |
| Coordinates | 31°53′14″N 139°55′04″E |
| Archipelago | Izu Islands |
| Area | 0.01 km2 (0.0039 sq mi) |
| Highest elevation | 11 m (36 ft) |
| Administration | |
Japan | |
| Prefecture | Tokyo |
| Subprefecture | Hachijō Subprefecture |
| Demographics | |
| Population | 0 |
Geography
The rocks are the exposed portion of the western ridge of a submarine volcanic caldera, approximately 9 kilometres (5.6 mi) in diameter at a depth of approximately 1,000 metres (3,300 ft).[2] The above sea-level portion has a surface area of approximately 0.01 square kilometers, with a summit height of 11 metres (36 ft). and consists of three large rocks and many smaller rocks. [1]
The caldera is known to have erupted in 1869-1871, 1896, 1906, 1915, 1934, 1946, 1952-1955, 1957-1960, and 1970. The last known submarine eruption of the caldera was in 1988, which discolored the local water.[1]
On the northeast rim of the same caldera 12.8 kilometres (8.0 mi) to the east of the Bayonnaise Rocks is a submerged reef named Myōjin-shō (明神礁), which is a post-caldera cone with a depth of approximately 50 metres (160 ft). During a submarine volcanic eruption of 17 September 1952, an ephemeral island was formed, with a height of 10 metres (33 ft), which was created and destroyed several times by volcanic activity until completely disappearing on 23 September 1953. The following day, an eruption killed 31 researchers and crewmen aboard the Maritime Safety Agency survey ship No.5 Kaiyo-Maru. The island reappeared on 11 October, sinking again on 11 March 1954 and reappeared one more time between 5 April and 3 September 1954.[1]
Vegetation is sparse among the Bayonnaise Rocks. The islands are a resting place for migratory birds. Located in the Kuroshio Current, the area has abundant sea life, and is popular with sports fishermen.
See also
- Izu Islands
- Desert island
- List of islands
References
- "66. Beyonesu (Bayonnaise) Rocks (including Myojinsho)" (PDF). Japan Meteorological Agency. Retrieved 26 March 2017.
- Christopher G. Newhall, Daniel Dzurisin: Historical Unrest at large Calderas of the World. Volume 1, U.S. Geological Survey Bulletin 1855, Washington 1988, p. 506; Bathymetric map around "Bayonnaise Rocks" based on Basic Map of the Sea (1:50.000, retrieved 2012-12-13).
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Bayonnaise Rocks. |
- "Beyonesu (Bayonnaise) Rocks: National catalogue of the active volcanoes in Japan" (PDF). - Japan Meteorological Agency
- Myojinsho: Global Volcanism Program - Smithsonian Institution
- Bayonnaise Rocks Volcano - volcanolive.com