Battle of Kissoué
The Battle of Kissoué (17 June 1941) was part of the Allied advance on Damascus in Syria during the Syria-Lebanon campaign in World War II. The battle is noted for the confrontation between Vichy French and the Free French Forces. The Free French met with stiff resistance from the Vichy French.
Background
On 8 June 1941, troops of the 5th Indian Infantry Brigade Group—under Brigadier Wilfrid Lewis Lloyd—had crossed the Syrian border from the British Mandate of Palestine to take Quneitra and Deraa with the objective of opening the way for Free French forces to advance along the roads from these towns to Damascus. This was one of four attacks planned for the campaign by the Allied commander General Henry Maitland Wilson. By 12 June, Deraa, Sheikh Meskine and Ezraa on the Deraa to Damascus road had been captured and the Indian and Free French forces, now named Gentforce and under the unified command of French Major-General Paul Legentilhomme were before Kissoué. Unfortunately, Legentilhomme was wounded almost immediately after taking command and was succeeded by Brigadier Lloyd[1] on 14 June.[2]
Kissoué was a strong defensive position. East of the road the gardens and houses of the town provided cover for infantry and tanks backed by the considerable defence works on the steeply rising Jebel el Kelb and Jebel Abou Atriz behind them. West of the road were the hills of Tel Kissoué, Tel Afar and Jebel Madani which commanded the roads to Damascus from both Quneitra and Deraa. The boulder-strewn country was virtually impassable by wheeled vehicles except on the road and made progress difficult even on foot.[2] Furthermore, the river Awaj flowed in front of the French positions across the Allied line of advance.
The battle
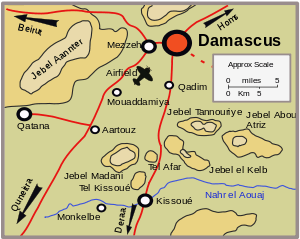
At 04:00 on 15 June, Indian troops made a frontal attack which fortuitously coincided with a relief of the Vichy force's forward troops. After fierce fighting, the village was taken by 08:30. By 09:00, the Indian troops were pushing forward into the hills behind the village which overlooked the main road from the west and within an hour had captured Tel Kissoué.[2] On the river on the far left flank of the advance, the village of Monkelbe had been secured by Free French marines by 11:30.[3]
A second phase of the attack had begun at 11:00 with Free French forces advancing across the river into the hills on the right of the Damascus road. Having captured Jebel Kelb, the advance stalled on Jebel Abou Atriz, while on the far right a flanking move by Free French tanks was stopped by heavy shelling from Vichy artillery. Further depressing news for Lloyd came from the Allied troops holding Quneitra, on the other main road to Damascus from the south, who reported the approach of a strong Vichy force from the north. Furthermore, Lloyd's own lines of communication were being threatened by the capture of Ezraa by Vichy Tunisian troops which had advanced cross country from Tel Soutaine to the east.[4] Ezraa was only 6 mi (9.7 km) to the east of Sheikh Meskine which was on the main road south from Kissoué.
Lloyd decided that a rapid advance on Damascus would best deal with the critical situation. He sent two companies of Free French troops and some artillery south to Sheikh Meskine to bolster reinforce the two squadrons of the Transjordan Frontier Force which had taken defensive positions across the road eastwards from Sheikh Meskine to Dezraa[2] and ordered the Indian brigade to advance. During the night of 15 June, pushing forward through the hills to the left of the Kissoué to Damascus road, Indian troops took Aartouz on the Quneitra to Damascus road, cutting the rearward communications of the Vichy force advancing on Quneitra. On the afternoon of 16 June, it was reported incorrectly that Ezraa had been re-taken[5] by the Allies but the news from Quneitra was less promising. Outnumbered 3:1 and facing tanks against which they had no effective counter, the Allied defenders at Quneitra, a battalion of the Royal Fusiliers (less a company which was at Kissoué), held out until, surrounded and ammunition virtually exhausted, at 19:00 on 16 June the remaining 13 officers and 164 men surrendered.[6][7]
Despite this threat to Gentilforce's supply lines, it was decided to press on to Damascus. This forced the Vichy commander to withdraw his flanking forces.[8]
References
- Compton Mackenzie (1951). Eastern Epic. London: Chatto & Windus. pp. 605 pages.
- Long, Gavin (1953). "Chapter 20 - The French Counter-attack". Volume II – Greece, Crete and Syria (1st edition, 1953) (PDF). Official Histories – Second World War. Canberra: Australian War Memorial.
Footnotes
- Compton Mackenzie, Eastern Epic, p. 110.
- Long (1953), p. 393-394
- Compton Mackenzie, pp. 112-113
- Compton Mackenzie, p. 113.
- Long (1953), p. 403
- Long (1953), p. 402
- Compton Mackenzie, pp. 114–15.
- Compton Mackenzie, p. 115