American wigeon
The American wigeon (Mareca americana), also called a baldpate, is a species of dabbling duck found in North America. Formerly assigned to Anas, this species is classified with the other wigeons in the dabbling duck genus Mareca. It is the New World counterpart of the Eurasian wigeon. Mareca is from the Brazilian-Portuguese word Marréco for a small duck and americana refers to America.[2][3]
| American wigeon | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Male | |
 | |
| Female | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Aves |
| Order: | Anseriformes |
| Family: | Anatidae |
| Genus: | Mareca |
| Species: | M. americana |
| Binomial name | |
| Mareca americana (Gmelin, 1789) | |
 | |
| Synonyms | |
|
Anas americana Gmelin, 1789 | |
Description

The American wigeon is a medium-sized bird; it is larger than a teal, but smaller than a pintail. In silhouette, the wigeon can be distinguished from other dabblers by its round head, short neck, and small bill.[4] It is 42–59 cm (17–23 in) long, with a 76–91 cm (30–36 in) wingspan and a weight of 512–1,330 g (1.129–2.932 lb).[5][6][7] This wigeon has two adult molts per year and a juvenile molt in the first year, as well.[5]
The breeding male (drake) is a striking bird with a mask of green feathers around its eyes and a cream colored cap running from the crown of its head to its bill. This white patch gives the wigeon its other common name, baldpate (pate is another word for head). Their belly is also white.[8] In flight, drakes can be identified by the large white shoulder patch on each wing. These white patches flash as the birds bank and turn. In non-breeding (eclipse) plumage, the drake looks more like the female.[4]
The hens are much less conspicuous, having primarily gray and brown plumage. Both sexes have a pale blue bill with a black tip, a white belly, and gray legs and feet.[4] The wing patch behind the speculum is gray. They can be distinguished from most ducks, apart from Eurasian wigeon, by shape. However, that species has a darker head and all grey underwing. The head and neck coloring of the female is different as opposed to the Eurasian wigeon.[8] It nests on the ground, near water and under cover. It lays 6–12 creamy white eggs. Flocks will often contain American coots.[5]
The American wigeon is a noisy species, and in the field can often be identified by their distinctive calls. Drakes produce a three note whistle, while hens emit hoarse grunts and quacks.[4] The male whistle makes a wheezy whoee-whoe-whoe, whereas the female has a low growl qua-ack.
Distribution and habitat
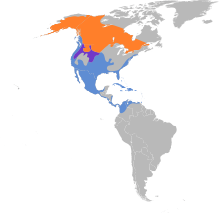
It is common and widespread, breeding in all but the extreme north of Canada and Alaska and also in the Interior West through Idaho, Colorado, the Dakotas, and Minnesota, as well as eastern Washington and Oregon.[5][8] The conservation status of this bird is Least Concern.[1] The majority of the population breeds on wetlands in the Boreal Forest and subarctic river deltas of Canada and Alaska. Although wigeon are found in each flyway, they are most numerous in the Pacific Flyway. Key wintering areas here include the Central Valley of California and Washington's Puget Sound. Farther east, the Texas Panhandle, the Gulf Coast of Louisiana and Texas, and the Caribbean also support large numbers of wintering wigeon.[4]
This dabbling duck is migratory and winters farther south than its breeding range, in the southern half of the United States, Idaho, Washington, Oregon, and the Mid-Atlantic coastal region,[5][8] and further south into Central America, the Caribbean, and northwestern South America.[9] It is a rare but regular vagrant to western Europe,[5] and has been observed in significant numbers in Great Britain and Ireland since at least 1958.[10]
In 2009, an estimated 2.5 million breeding wigeon were tallied in the traditional survey area—a level just below the 1955–2009 average. In recent decades, wigeon numbers have declined in the prairie-pothole region of Canada and increased in the interior and west coast of Alaska. The American wigeon is often the fifth most commonly harvested duck in the United States, behind the mallard, green-winged teal, gadwall, and wood duck.[4]
Behavior

The American wigeon is a bird of open wetlands, such as wet grassland or marshes with some taller vegetation, and usually feeds by dabbling for plant food or grazing, which it does very readily. While on the water, wigeon often gather with feeding coots and divers, and are known to grab pieces of vegetation brought to the surface by diving water birds. For this reason, they are sometimes called "poacher" or "robber" ducks. Wigeon also commonly feed on dry land, eating waste grain in harvested fields and grazing on pasture grasses, winter wheat, clover, and lettuce. Having a largely vegetarian diet, most wigeon migrate in the fall well before northern marshes begin to freeze.[4]
The American wigeon is highly gregarious outside of the breeding season and will form large flocks.[5]
References
- BirdLife International (2012). "Mareca americana". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2012. Retrieved 26 November 2013.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Jobling, James A. (2010). The Helm Dictionary of Scientific Bird Names. London: Christopher Helm. p. 241. ISBN 978-1-4081-2501-4.
- Jobling, James A (2010). The Helm Dictionary of Scientific Bird Names. London: Christopher Helm. pp. 44, 46. ISBN 978-1-4081-2501-4.
- "The American Wigeon". Ducks Unlimited. May–June 2010.
- Floyd, T. (2008). Smithsonian Field Guide to the Birds of North America. New York: Harper Collins.
- "American Wigeon". All About Birds.
- Dunning, John B. Jr., ed. (1992). CRC Handbook of Avian Body Masses. CRC Press. ISBN 978-0-8493-4258-5.
- Dunn, J.; Alderfer, J. (2006). National Geographic Field Guide to the Birds of North America (5th ed.).
- Clements, James (2007). The Clements Checklist of the Birds of the World. Cornell University Press, Ithaca.
- Votier, Stephen C.; Harrop, Andrew H.J.; Denny, Matthew (January 2003). "A review of the status and identification of American Wigeon in Britain & Ireand". British Birds. 96 (1): 2–22. ISSN 0007-0335.
- Harrop, A. (1994). "Field identification of American Wigeon". Birding World. 7: 50–56.
- Jiquet, F. (1999). "Photo forum: Hybrid American Wigeons". Birding World. 12: 247–252.
- Larkin, P. (2000). "Eyelid colour of American Wigeon". British Birds. 93: 39–40.
- Madge, Steve; Burn, Hilary (1988). Waterfowl: an Identification Guide to the Ducks, Geese, and Swans of the World. Boston: Houghton Mifflin. ISBN 0-395-46727-6.
- Olson, Storrs L.; James, Helen F.; Meister, C. A. (1981). "Winter field notes and specimen weights of Cayman Island birds". Bulletin of the British Ornithologists' Club. 101 (3): 339–346. hdl:10088/6535.
- Votier, S. C.; Harrop, A. H. J.; Denny, M. (2003). "A review of status and identification of American Wigeon in Britain and Ireland". British Birds. 96: 2–22.
- Cox, Cameron; Barry, Jessie. "Aging of American and Eurasian Wigeons in female-type plumages" (PDF). Birding. 37 (2): 156–164. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2012-10-19. Retrieved 2011-10-09.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Mareca americana. |
| Wikispecies has information related to Anas americana |
- American Wigeon Species Account – Cornell Lab of Ornithology
- American Wigeon - Anas americana - USGS Patuxent Bird Identification InfoCenter
- "American Wigeon media". Internet Bird Collection.
- American Wigeon photo gallery at VIREO (Drexel University)
- Interactive range map of Anas americana at IUCN Red List maps
