Atlanta, Idaho
Atlanta is an unincorporated community in the western United States, located in Elmore County, Idaho.

Atlanta, Idaho | |
|---|---|
 Atlanta  Atlanta | |
| Coordinates: 43°48′6″N 115°7′36″W | |
| Country | United States |
| State | Idaho |
| County | Elmore |
| Elevation | 5,383 ft (1,641 m) |
| Time zone | UTC-7 (Mountain (MST)) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC-6 (PDT) |
| ZIP code | 83601 |
| Area code(s) | 208, 986 |
| Website | atlantaidaho.net |
It was founded in 1864 during the Civil War as a gold and silver mining community and named by Southerners after a rumored Confederate victory over General Sherman in the Battle of Atlanta, which turned to be wholly false, but the name stuck. Mining activity near Atlanta preceded its establishment as a mining community. The John Stanley party discovered gold on the nearby Yuba River on July 20, 1864, just two days prior to the battle back in Georgia. That November, John Simmons made the discovery of the Atlanta lode which contained both gold and silver.
Atlanta is at an elevation of 5,383 feet (1,641 m) above sea level, surrounded by the Boise National Forest; it is near the headwaters of the Middle Fork of the Boise River, approximately two miles (3 km) east of the mouth of the Yuba River. The Sawtooth Mountains are directly north, the Sawtooth Wilderness starts about a mile (1.6 km) north of Atlanta, at the base of Greylock Mountain, which summits at 9,363 feet (2,854 m).
Idaho City is approximately 35 miles (56 km) due west, as the crow flies. Galena Summit on State Highway 75 is about 25 air miles (40 km) to the east-northeast.
Atlanta is about forty miles (65 km) from two paved highways. It is east of State Highway 21, accessed on unimproved U.S. Forest Service roads. Atlanta is north of U.S. Highway 20, which is accessed from Atlanta by heading south on USFS roads through Rocky Bar, Featherville, and Pine. The junction with US-20 is just east of the Anderson Ranch Reservoir on the South Fork of the Boise River Atlanta can also be accessed by following the unimproved road from Arrowrock Dam which climbs with the Middle Fork of the Boise River.
Though founded as a mining community, and a number of private claims remain in the area, no significant commercial mining has occurred in the area for over 50 years, though more recently inquiries into opening a new plant have seen some headway. In place of mining, Atlanta has diversified into areas such as tourism, back-country activities, and preservation of the town's lengthy historic legacy.[1] In the summer months The Atlanta School offers arts and architecture workshops and artist residencies.
The Atlanta Historic District, a ten-acre (4.0 ha) historic district including 12 contributing buildings was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1978.
Climate
This climatic region is typified by large seasonal temperature differences, with warm to hot (and often humid) summers and cold (sometimes severely cold) winters. According to the Köppen Climate Classification system, Atlanta has a humid continental climate, abbreviated "Dfb" on climate maps.[2]
Gold mining history
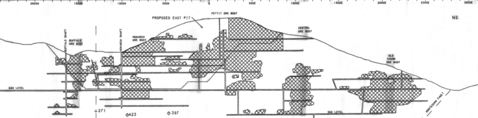
Gold was discovered 157 years ago in 1863, and placer mining started along the Yuba River in 1864. The Atlanta Lode quartz outcrop was discovered in Nov. 1864. Discovery of the Minerva, Tahoma, Last Chance, and Big lodes, with the development of the Buffalo, Monarch, General Pettit and other mines, soon followed. The Monarch Gold and Silver Mining Co. operated from 1866 until 1869.
Arastras initially processed the gold ore, neglecting the silver, as did the early stamp mills. Even the introduction of the Washoe process in 1869 at the Monarch, only resulted in the recovery of 20%. Lantis & Company took over the Monarch property in 1874. The Buffalo mill achieved 55% recovery in 1877. This led to a building boom, as the Buffalo mill and the Monarch employed 60 employees in total, the Atlanta community grew to 500, and a road was constructed to Rocky Bar. Yet, by 1884, most high-grade ore had been processed, and by 1885, Lantis & Company had sunk the Monarch mine shaft to a depth of 600 feet (180 m). The Atlanta Mines Co. purchased the Monarch Mine in 1902, followed by the Buffalo and Last Chance mines. The company built a 150-ton mill connected to the mine via an aerial tramway, and powered by a hydroelectric plant west of Atlanta.
In 1932, the Saint Joseph Lead Company improved the recovery process by introducing an amalgamation-flotation concentrator, ushering in an era of modern production. The Middle Fork road connected Boise with Atlanta in 1938. Talache Mines, Inc., acquired all of the mining operations along the Atlanta Lode in 1939. Mining operations ceased in 1953. The Atlanta Gold Corporation of America acquired the lease in 1985.[3][4]
References
- Swisher, Perry (March 12, 1994). "Idaho's other capital: Atlanta". Moscow-Pullman Daily News. (Idaho-Washington). p. 2B.
- Climate Summary for Atlanta, Idaho
- Kiilsgaard, T.H.; Bacon, L.D. (2004). Preliminary Report on the Geology and Mineral Deposits of the Atlanta Hill Area, Elmore County, Idaho, USGS Open-File Report 2004–1205 (PDF). U.S. Dept. of the Interior, USGS. pp. 1, 17–21.
- The Gold Camps and Silver Cities of Idaho. Middletown: Idaho Bureau of Mines. 2018. pp. 53–63. ISBN 9781501059667.
- "Atlanta, Idaho". Town website. Archived from the original on 2006-11-28. Retrieved 2007-01-24.
- "History and Current Facts of Elmore County". County website. Archived from the original on 2011-07-26. Retrieved 2011-10-11.
- "Atlanta" (PDF). Idaho State Historical Society Series (202). August 1964. Archived from the original (pdf) on 2012-04-05. Retrieved 2011-10-11.
External links
- Official website
- The Atlanta School.org – The Atlanta School
- Visit Idaho.org – Atlanta
- Idaho Heritage.org – Atlanta Pioneer Cemetery
- You Tube.com – landing in Atlanta, Idaho
- KTVB.com – Exploring another Idaho gem, Atlanta
- Flickr.com – photos of Atlanta, Idaho