Aspergillus nomius
Aspergillus nomius is a species of fungus in the genus Aspergillus. It is from the Flavi section.[2] The species was first described in 1987.[1] It has been reported to produce aflatoxin B1, aflatoxin B2, aflatoxin G1, aflatoxin G2, aspergillic acid, kojic acid, nominine, paspaline, pseurotin, and tenuazonic acid.[2] A. nomius has been identified as the cause of human infections.[3]
| Aspergillus nomius | |
|---|---|
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Fungi |
| Division: | Ascomycota |
| Class: | Eurotiomycetes |
| Order: | Eurotiales |
| Family: | Trichocomaceae |
| Genus: | Aspergillus |
| Species: | A. nomius |
| Binomial name | |
| Aspergillus nomius Kurtzman, B.W. Horn & Hesseltine (1987)[1] | |
Growth and morphology
A. nomius has been cultivated on both Czapek yeast extract agar (CYA) plates and Malt Extract Agar Oxoid® (MEAOX) plates. The growth morphology of the colonies can be seen in the pictures below.
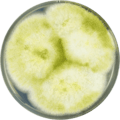 Aspergillus nomius growing on CYA plate
Aspergillus nomius growing on CYA plate Aspergillus nomius growing on MEAOX plate
Aspergillus nomius growing on MEAOX plate
gollark: --choose 100 bee notbee
gollark: You deleted your server? I didn't write code for this.
gollark: +>grant <@!766274162036572171> "no permissions"
gollark: Apiotelephone doesn't carry them.
gollark: --choose 24 bee ¬bee
References
- Kurtzman, C.P.; Horn, B.W.; Hesseltine, C.W. 1987. Aspergillus nomius, a new aflatoxin-producing species related to Aspergillus flavus and Aspergillus tamarii. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek. 53(3):147-158
- Varga, J.; Frisvad, J.C.; Samson, R.A. (2011). "Aflatoxin producing species, and an overview of Aspergillus section Flavi". Studies in Mycology. 69 (1): 57–80. doi:10.3114/sim.2011.69.05. PMC 3161756. PMID 21892243.
- Tam, E.W.T.; Chen, J.H.K.; Lau, E.C.L.; Ngan, A.H.Y.; Fung, K.S.C.; Lee, K.-C.; Lam, C.-W.; Yuen, K.-Y.; Lau, S.K.P.; Woo, P.C.Y. (2013). "Misidentification of Aspergillus nomius and Aspergillus tamarii as Aspergillus flavus: Characterization by Internal Transcribed Spacer, -Tubulin, and Calmodulin Gene Sequencing, Metabolic Fingerprinting, and Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption Ionization–Time of Flight Mass Spectrometry". Journal of Clinical Microbiology. 52 (4): 1153–1160. doi:10.1128/JCM.03258-13. PMC 3993464.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.