Septum
In biology, a septum (Latin for something that encloses; plural septa) is a wall, dividing a cavity or structure into smaller ones.
| Look up septum in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |
Examples
Human anatomy
- Interatrial septum, the wall of tissue that is a sectional part of the left and right atria of the heart
- Interventricular septum, the wall separating the left and right ventricles of the heart
- Lingual septum, a vertical layer of fibrous tissue that separates the halves of the tongue
- Nasal septum: the cartilage wall separating the nostrils of the nose
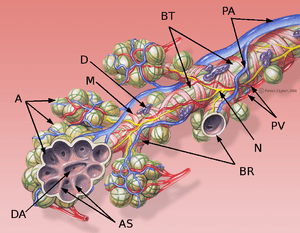
- Alveolar septum: the thin wall which separates the alveoli from each other in the lungs
- Orbital septum, a palpabral ligament in the upper and lower eyelids
- Septum pellucidum or septum lucidum, a thin structure separating two fluid pockets in the brain
- Uterine septum, a malformation of the uterus
- Vaginal septum, a lateral or transverse partition inside the vagina
- Intermuscular septa separating the muscles of the arms and legs
Histological septa are seen throughout most tissues of the body, particularly where they are needed to stiffen soft cellular tissue, and they also provide planes of ingress for small blood vessels. Because the dense collagen fibres of a septum usually extend out into the softer adjacent tissues, microscopic fibrous septa are less clearly defined than the macroscopic types of septa listed above. In rare instances, a septum is a cross-wall. Thus it divides a structure into smaller parts.
Cell biology
The septum (cell biology) is the boundary formed between dividing cells in the course of cell division.
Fungus
- A partition dividing filamentous hyphae into discrete cells in fungi.
Botany
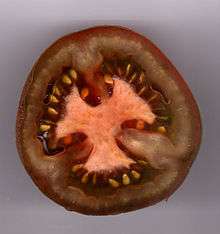
- A partition that separates the locules of a fruit, anther, or sporangium.
Zoology
A coral septum is one of the radial calcareous plates in the corallites of a coral.
Annelids have septa that divide their coelom into segmented chambers.
Many shelled organisms have septa subdividing their shell chamber, including rhizopods, cephalopods and gastropods, the latter seemingly serving as a defence against shell-boring predators.[1][2]
Laboratory technology
- A rubber septum is an engineered membrane that permits transfer of a substance (usually liquid or gas) without contact with air, usually using a syringe with needle.
References
- Ishikawa, Makiko; Kase, Tomoki; Tsutsui, Hidekazu (2018). "Deciphering deterministic factors of predation pressures in deep time". Scientific Reports. 8 (1): 17532. doi:10.1038/s41598-018-35505-1. PMC 6277388. PMID 30510248.
- Vermeij, Geerat J. (1982). "Unsuccessful Predation and Evolution". The American Naturalist. 120 (6): 701–720. doi:10.1086/284025.