Arda (Maritsa)
The Arda (Bulgarian: Арда, romanized: Arda, Greek: Άρδας, romanized: Árdas, Turkish: Arda) is a 290-kilometre (180 mi) long river in Bulgaria and Greece. It is a tributary of the Maritsa (Greek: Έβρος, romanized: Evros). Its source lies in the Bulgarian Rhodope Mountains near the village Arda, part of the municipality of Smolyan. It flows eastward past Rudozem, Kardzhali and Ivaylovgrad and enters Greece in the northern part of the Evros regional unit. It flows into the Maritsa on the border of Greece and Turkey, between the Greek village Kastanies and the Turkish city Edirne. In the Bulgarian section there are three hydroelectric and irrigation dams, Kardzhali Dam, Studen Kladenets and Ivaylovgrad Dam. The Bulgarian section is 229 kilometres (142 mi) long,[1] making the Arda the longest river in the Rhodopes. The medieval Dyavolski most arch bridge crosses the river 10 kilometres (6 mi) from Ardino.
| Arda (Арда), Ardas (Άρδας) | |
|---|---|
 The Arda at Valchi dol, Bulgaria | |
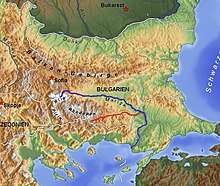 Map of Arda River and Maritsa river | |
| Location | |
| Country | Bulgaria, Greece |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Source | |
| • location | near Smolyan, Rhodopes, Bulgaria |
| • elevation | 1,455 m (4,774 ft) (Ardin vrah) |
| Mouth | |
• location | Maritsa, near Edirne |
• coordinates | 41°39′39″N 26°29′42″E |
| Length | 290 km (180 mi); 229 km (142 mi) in Bulgaria[1] |
| Basin size | 5,795 km2 (2,237 sq mi); 5,213 km2 (2,013 sq mi) in Bulgaria[1] |
| Basin features | |
| Progression | Maritsa→ Aegean Sea |
The three floods of February 18, 2005, when the water level was at 4.8 metres (16 ft), March 1 and March 7, 2005, flooded the low-lying areas, especially in the Kastanies area which turned the area into a lagoon. The merging of the waters of the Maritsa (Evros/Meriç) caused streets and buildings including homes to be flooded and people to be stranded in their homes.
Arda Peak on Livingston Island in the South Shetland Islands, Antarctica and the mineral ardaite are named after the Arda river.
Gallery
 Devil's bridge near Ardino
Devil's bridge near Ardino Arda's Meander in Bulgaria
Arda's Meander in Bulgaria- Near Madzharovo
 Near Madzharovo
Near Madzharovo