Apocholic acid
Apocholic acid is an unsaturated bile acid first characterized in the 1920s.[2] It has questionable carcinogenic activity as experimentally, sarcomas were induced in mice with injection of desoxycholic acid. [3]
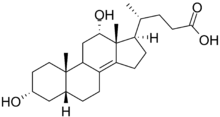 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(4R)-4-[(3R,5R,9R,10S,12S,13R,17R)-3,12-Dihydroxy-10,13-dimethyl-2,3,4,5,6,7,9,11,12,15,16,17-dodecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-17-yl]pentanoic acid | |
| Other names
3α,12α-Dihydroxy-5β,8(14)-cholen-24-oic acid; 3α,12α-Dihydroxy-5β-chol-8(14)en-24-oic acid; 5β,8(14)-Cholen-24-oic acid-3α,12α-diol | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C23H38O4 | |
| Molar mass | 378.553 g·mol−1 |
| Melting point | 175 to 176 °C (347 to 349 °F; 448 to 449 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
The salts and esters of apocholic acid are known as apocholates.
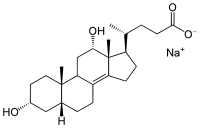 Structure of sodium apocholate
Structure of sodium apocholate
See also
References
- |ALDRICH&N5=SEARCH_CONCAT_PNO|BRAND_KEY&F=SPEC Apocholic acid at Sigma-Aldrich
- Boedecker, F.; Volk, H. (1922). "Unsaturated bile acids. III. Relations of apocholic acid, dihydroxycholenic acid (m. 260) and cholic acid to desoxycholic acid". Berichte der Deutschen Chemischen Gesellschaft B. 55: 2302–2309. doi:10.1002/cber.19220550810.
- Lacassagne, A (June 10, 1961). "Carcinogenic activity of apocholic acid". Nature. 190 (4780): 1007–8. Bibcode:1961Natur.190.1007L. doi:10.1038/1901007a0. PMID 13831121.
External links
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.