Anterior ethmoidal nerve
The anterior ethmoidal nerve is branch of the nasociliary nerve, itself a branch of the ophthalmic nerve. It provides sensory innervation to some structures around the nasal cavity.
| Anterior ethmoidal nerve | |
|---|---|
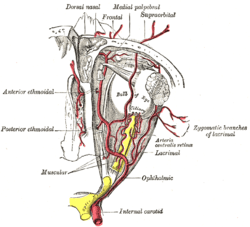 The ophthalmic artery and its branches. (Nerve not pictured, but location is similar to artery.) | |
| Details | |
| From | nasociliary nerve |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | nervus ethmoidalis anterior |
| TA | A14.2.01.030 |
| FMA | 52675 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy | |
Structure
The anterior ethmoidal nerve is a terminal branch of the nasociliary nerve. It branches near the medial wall of the orbit and travels through the anterior ethmoidal foramen to reach the anterior cranial fossa. It then moves forward and passes through the cribriform plate to enter the nasal cavity. It gives off branches to the roof of the nasal cavity and bifurcates into a lateral internal nasal branch and medial internal nasal branch.
The nerve is the continuation of the nasociliary nerve after it enters the anterior ethmoidal foramen into the anterior ethmoidal air cells. The nasociliary nerve arises from the Ophthalmic division of the Trigeminal nerve (CN V) within the orbit. The anterior ethmoidal nerve arises only after the nasociliary has given off its four branches - 1) Ramus communicans to ciliary ganglion, 2) Long ciliary nerves, 3) infratrochlear nerve, 4) Posterior ethmoidal nerve.
After branching off of the nasociliary nerve, the anterior ethmoidal nerve enters the anterior ethmoidal foramen and send sensory fibers to the middle and anterior ethmoidal air cells. The anterior ethmoidal nerve then continues into the cranial cavity at the side of the cribiform plate of the ethmoid bone, sends sensory fibers to the meninges, and then enters the nasal cavity via the nasal slit. Within the nose, this nerve gives off sensory fibers to the anterior part of the nasal septum[1]
The branches it gives rise to are called the internal/septal and external nasal branches of the anterior ethmoidal nerve, and the external branch ultimately innervates skin on the lateral sides of the nose.
Specifically, innervates the septum of the nasal cavity.
References
- Poussel, M. (May 2012). "Nasal stimulation by water down-regulates cough in anesthetized rabbits" (PDF). Respiratory Physiology & Neurobilogy. 183: 20–25. doi:10.1016/j.resp.2012.05.021.