Mafraq Governorate
Mafraq (Arabic: محافظة المفرق Muhāfaẓat al-Mafraq, local dialects Mafrag or Mafra' ) is one of the governorates of Jordan, located to the north-east of Amman, capital of Jordan. It has a population of 287,300 (2010 estimate)[2] making up 4.5% of Jordan's population. Its capital is Mafraq, which is known for its military bases.
Mafraq Governorate محافظة المفرق | |
|---|---|
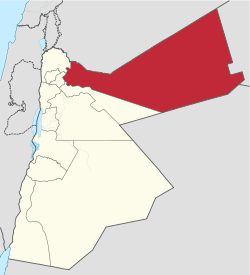 Mafraq Governorate | |
| Country | |
| Capital | Mafraq |
| Government | |
| • Governor | Saleem Rawahneh |
| Area | |
| • Total | 26,551 km2 (10,251 sq mi) |
| Population (2012) | |
| • Total | 300,300 |
| • Density | 11/km2 (29/sq mi) |
| Time zone | GMT +2 |
| • Summer (DST) | +3 |
| Area code(s) | +(962)2 |
| Urban | 39.2% |
| Rural | 60.8% |
| HDI (2017) | 0.711[1] high · 10th |
History

Many Roman and Byzantine sites have been found throughout the governorate, most notably churches dating to the third century AD; believed to be two of the oldest purpose built churches in Christianity: and Roman water dams in Jawa, Ruwaished, and the city of Mafraq. The Jawa Dam is the oldest known dam in the world, dating back to 3000 B.C. Mafraq city also contains a Roman fort.
During the British mandate period, Mafraq housed military facilities which are still in use today. The fifth division of the Jordanian Army is stationed in Mafraq.
Geography
The province is located in the eastern part of the kingdom of Jordan. It is the only governorate in Jordan that has borders with three countries: Iraq to the east, Syria to the north, and Saudi Arabia to the south. It is bordered by Irbid and Jerash governorates to the west, and by Zarqa governorate to the south.
Mafraq governorate covers the second largest area in the kingdom, but yet the second smallest population density (after Ma'an). The climate is dry most of the year. The western region of the province is part of the fertile Houran plateaus, that extend through southern Syria, the Golan heights and northern Jordan. The eastern region is part of the barren Syrian Desert. At the eastern edge of the region is the 940m high Jebel 'Aneiza (or 'Unayzah), at the border tripoint between Jordan, Iraq and Saudi Arabia.[3][4][5]
The Governorate is connected to Iraq through the Karameh Border Crossing, and to Syria through the Jabir Border Crossing.
Demographics
The population of Mafraq Governorate according to the census of 2004 was 244,188 of whom 30% is considered urban and 70% is rural. Jordanian citizens made up about 94% of the population. The Jordanian Department of Statistics population estimate for the year 2010 is 287,300 with a female to male ratio of 48.17 to 51.83 and a population density of 10.8 persons per km2. In 2011 and 2012, the civil war in Syria resulted in the immigration of more than 180,000 Syrian refugees to Jordan, mostly settled in Mafraq and Irbid Governorates. In July 2012, the Zaatari refugee camp was opened in Mafraq Governorate for Syrian refugees. The World Bank 2018 estimate records the population now at 593,900 people.
| Demographics of Mafraq Governorate | 2004 Census[6] | 2011 Estimate |
|---|---|---|
| Female to male ratio | 48.0% to 52.0% | 48.18% to 51.82% |
| Jordanian citizens to foreign nationals | 93.9% to 6.1% | N/A |
| Urban population | 30.0% | 39.2% |
| Rural population | 70.0% | 60.8% |
| Total population | 244,188 | 293,700 |
The population of districts according to census results:[7]
| District | Population (Census 1994) | Population (Census 2004) | Population (Census 2015) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mafraq Governorate | 178,914 | 244,188 | 549,948 |
| Badiah Shamaliyah District (Al-Bādīah ash-Shamāliyah) | ... | 57,706 | 99,231 |
| Badiah Gharbiyah District (Al-Bādīah al-Gharbiyah) | ... | 74,965 | 247,031 |
| Rwaished District (Ar-Rwaīshed) | 10,032 | 9,805 | 7,490 |
| Mafraq Qasabah District (Qaṣabah al-Mafraq) | ... | 101,712 | 196,196 |
Administrative divisions
Mafraq Governorate is divided into four districts (liwa)[8] and fourteen sub-districts (qda):[9]
| District | Arabic Name | Subdivisions | Towns/villages | Administrative Center | Population Census 2004 |
Population estimate 2008 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Mafraq Capital (Mafraq Casabah) District | لواء قصبة المفرق | Mafraq Sub-District Bal'ama Sub-District |
72 | Mafraq city. | 101,712 | 114,550 |
| 2 | Ruwaishid District | لواء الرويشد | Rwaished District | 12 | Ruwaished | 9,805 | 11,040 |
| 3 | North Badiya (Badiah Shamaliyah) District | لواء البادية الشمالية | Salhiya Sub-District Sabha Sub-District |
67 | Sabh | 57,706 | 64,990 |
| 4 | West Badiya (Badiah Gharbiyah) District | لواء البادية الشمالية الغربية | Badiyah Gharbiyah Sub-District Serhan Sub-District |
45 | Sama as-Sarhan قلايدالخيل | 74,965 | 84,420 |
Economy
Agriculture forms a central element of the economy for Mafraq Governorate, especially in the Houran Plateau in the western part of the province. The total area of fruit farms in the province in 2008 was 48.676 km2, with a total production of 101874 tons of fruits mainly apples and peaches, according to the ministry of Agriculture.[10] The total area of vegetable farms in the province for 2008 was 8.295 km2 with a total production of 15540 tons, with cabbage, onions, garlic, and lettuce being the main products.[11]
There is one natural gas production field at Al-Reeshah, it is run by the Jordanian National Petroleum Company. In 2008, British Petroleum purchased the rights to produce natural gas in the field, and is expected to increase its capacity from 21 cubic feet (0.59 m3) to 300 million cubic feet per day in the next five years. The natural gas produced at Al-Reeshah is used entirely for producing electricity at a nearby electricity generating station with a capacity of 120 Megawatts, covering 12% of the total needs of the kingdom for the year 2008.[12]
The city of Mafraq hosts Al al-Bayt University, which is the only university in the governorate.[13]
See also
- Safawi, Jordan, a town
- Umm el-Jimal, village with ancient ruins
References
- "Sub-national HDI - Area Database - Global Data Lab". hdi.globaldatalab.org. Retrieved 2018-09-13.
- "DOS Jordan". Archived from the original on 2011-03-04. Retrieved 2011-12-10.
- Wagner, Wolfgang (2011). Groundwater in the Arab Middle East. New York: Springer. p. 141. ISBN 9783642193514. Retrieved 2 February 2017.
- "Jebel 'Aneiza, Saudi Arabia". geographic.org. Retrieved 2 February 2017.
- Philip's world atlas (New ed.). London: George Philip. 2003. p. 44. ISBN 0540084085.
- Jordan National Census of 2004 Table 3-1 Archived 2011-07-22 at the Wayback Machine
- "Jordan: Administrative Division, Governorates and Districts". citypopulation.de. Retrieved 25 December 2016.
- District subdivisions are in accord with article 10 of the 46th Administrative Divisions System of the Kingdom of Jordan promulgated by the Ministry of Interior and ratified in the year 2000.
- "Population of the Kingdom" (PDF). 2011. Archived from the original (PDF) on 19 January 2017. Retrieved 19 January 2017.
- "Ministry of Agriculture Total area of trees by province report of 2008". Archived from the original on 2012-03-03. Retrieved 2010-02-16.
- "Ministry of Agriculture, Table of the total area of vegetables by province report of 2008". Archived from the original on 2012-03-03. Retrieved 2010-02-16.
- Asharq Alawsat newspaper September 5, 2009
- Al al-Bayt University

