Alūksne Castle
Alūksne Castle (Latvian: Marienburgas pils, Alūksnes pils; German: Marienburg) is a castle of Teutonic Knights in current Alūksne, North-Eastern Latvia.
| Alūksne Castle | |
|---|---|
| Vidzeme, Latvia | |
 Alūksne Castle 1661 from North-West | |
 Alūksne Castle | |
| Coordinates | 57°25′14″N 27°02′55″E |
| Type | Castle |
| Site information | |
| Open to the public | yes |
| Condition | about 5 m high walls visible |
| Site history | |
| Built | 1342 |
| Built by | Livonian Order |
| Materials | boulders, brick |
| Demolished | 1702 (blown up) |
History
The castle was built in 1342 on the largest of the islands in the Lake Alūksne and called Marienburg (after Mary, the mother of Jesus). The first castle was constructed by the Landmeister Burkhard von Dreileben. It was part of a major reinforcement of the Eastern border of Livonia, the same year another major castle nearby (in Vastseliina) was founded as well. Soon thereafter, center of komturei was moved from Gaujiena to Alūksne. [1]
The strength of the castle was repeatedly proven by repelling a number of attacks in the 16th century. Alūksne was captured by the troops of Ivan IV of Russia in 1560 during the Livonian War. It was incorporated into the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth in 1582. The town became part of the Swedish Empire in 1629.
After the fall of the Old Livonia, the castle remained habitable. It was finally destroyed in 1702 in the Great Northern War by its Swedish garrison to avoid falling in the hands of Russians. The ruins remained largely untouched. Today, it houses an open-air scene and forms a part of a recreational area of the Pils (Castle) Island.
Architecture
The initial castle was built of wood. Later, the outer walls were constructed of fieldstone and the convent house of bricks. The plan is in many ways similar to that of Viljandi Castle, including the convent building with a flanking tower. The outer wall originates partly from the same time as the convent house, partly from later periods, notably from the time of the political tensions in the early 16th century. The main gate, protected by two round towers, is also of late medieval origin.[1]
Later, at the end of the 17th century, the castle was supplied with ravelines and ramparts.
Gallery
 The walls from inside, 2010.
The walls from inside, 2010.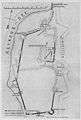 Plan of the castle according to Karl von Lövis of Menar.
Plan of the castle according to Karl von Lövis of Menar.
References
- Tuulse, Armin (1942). Die Burgen in Estland und Lettland, pp 147-148. Dorpater Estnischer Verlag
