Aka-Kol language
The Kol language, Aka-Kol, is an extinct Great Andamanese language, of the Central group. It was spoken in the southeast section of Middle Andaman.
| Kol | |
|---|---|
| Aka-Kol | |
| Native to | India |
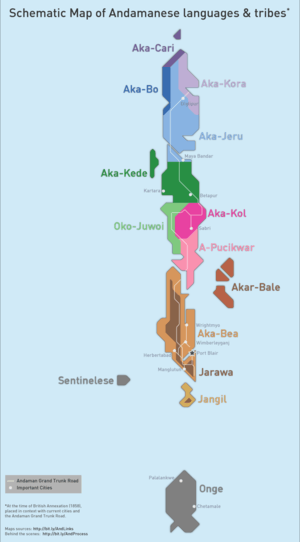
| Region | Andaman Islands; southeast Middle Andaman island. |
| Extinct | by 1921[1] |
Great Andamanese
| |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-3 | aky |
| Glottolog | akak1253[2] |
 | |
History
The Kol were one of the indigenous peoples of the Andaman Islands, one of the ten or so Great Andamanese tribes identified by British colonials in the 1860s. Their language was closely related to the other Great Andamanese languages. They were extinct as a distinct people by 1921.[1]
Grammar
The Great Andamanese languages are agglutinative languages, with an extensive prefix and suffix system.[3] They have a distinctive noun class system based largely on body parts, in which every noun and adjective may take a prefix according to which body part it is associated with (on the basis of shape, or functional association). Thus, for instance, the *aka- at the beginning of the language names is a prefix for objects related to the tongue.[3] An adjectival example can be given by the various forms of yop, "pliable, soft", in Aka-Bea:[3]
- A cushion or sponge is ot-yop "round-soft", from the prefix attached to words relating to the head or heart.
- A cane is ôto-yop, "pliable", from a prefix for long things.
- A stick or pencil is aka-yop, "pointed", from the tongue prefix.
- A fallen tree is ar-yop, "rotten", from the prefix for limbs or upright things.
Similarly, beri-nga "good" yields:
- un-bēri-ŋa "clever" (hand-good).
- ig-bēri-ŋa "sharp-sighted" (eye-good).
- aka-bēri-ŋa "good at languages" (tongue-good.)
- ot-bēri-ŋa "virtuous" (head/heart-good)
The prefixes are,
| Bea | Balawa? | Bajigyâs? | Juwoi | Kol | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| head/heart | ot- | ôt- | ote- | ôto- | ôto- |
| hand/foot | ong- | ong- | ong- | ôn- | ôn- |
| mouth/tongue | âkà- | aka- | o- | ókô- | o- |
| torso (shoulder to shins) | ab- | ab- | ab- | a- | o- |
| eye/face/arm/breast | i-, ig- | id- | ir- | re- | er- |
| back/leg/butt | ar- | ar- | ar- | ra- | a- |
| waist | ôto- |
Body parts are inalienably possessed, requiring a possessive adjective prefix to complete them, so one cannot say "head" alone, but only "my, or his, or your, etc. head".
The basic pronouns are almost identical throughout the Great Andamanese languages; Aka-Bea will serve as a representative example (pronouns given in their basic prefixal forms):
| I, my | d- | we, our | m- |
| thou, thy | ŋ- | you, your | ŋ- |
| he, his, she, her, it, its | a | they, their | l- |
'This' and 'that' are distinguished as k- and t-.
Judging from the available sources, the Andamanese languages have only two cardinal numbers — one and two — and their entire numerical lexicon is one, two, one more, some more, and all.[3]
References
- George van Driem (2001), Languages of the Himalayas: An Ethnolinguistic Handbook of the Greater Himalayan Region : Containing an Introduction to the Symbiotic Theory of Language, BRILL, ISBN 90-04-12062-9,
The Aka-Kol tribe of Middle Andaman became extinct by 1921.
- Hammarström, Harald; Forkel, Robert; Haspelmath, Martin, eds. (2017). "Akakol". Glottolog 3.0. Jena, Germany: Max Planck Institute for the Science of Human History.
- Temple, Richard C. (1902). A Grammar of the Andamanese Languages, being Chapter IV of Part I of the Census Report on the Andaman and Nicobar Islands. Superintendent's Printing Press: Port Blair.