Aeroposta Argentina
Aeroposta Argentina S.A. was an early pioneering airline in Argentina established in the late 1920s, and a subsidiary of the French airmail carrier Aéropostale. It was created on September 5, 1927, as a subsidiary of the Aéropostale (formally, Compagnie générale aéropostale). In 1929, Aéropostale started expanding its airmail service within South America,[1] and provided the first domestic air services on routes to Asuncion, Paraguay, Santiago de Chile, plus Bahía Blanca, Comodoro Rivadavia and Rio Gallegos in southern Argentina.
- This article contains machine-translated text from the Spanish Wikipedia article Aeroposta Argentina S.A.. You can help by improving this Spanish to English translation.
The task to open the new air routes was given to, among others, two well-known French aviators: Antoine de Saint-Exupéry as the director of the newly formed company based in Buenos Aires, and to Jean Mermoz, as the company's chief pilot. Saint-Exupéry conducted Aeroposta's inaugural flight on November 1, 1929, flying from an airfield at Villa Harding Green to Comodoro Rivadavia.[2]
In the early days of commercial aviation, which was still in its infancy, its pioneers had to scout routes and sites for everything from potential emergency landing strips to gasoline depots. Saint-Exupéry's experiences in Argentina would inspire his novel Night Flight, winner of the Prix Femina literature award in 1929 and later made into an identically named Hollywood movie. That same year regular flights commenced to other Argentinian cities: Posadas and Mendoza. The following year service was further expanded to include Comodoro Rivadavia and San Antonio Oeste, closely followed by Río Gallegos.
Aeroposta Argentina remained Argentina's only airline until 1946, when several new ones were created.[3] In 1949 Aeroposta Argentina merged with three other air carriers, ALFA (Sociedad Mixta Aviación del Litoral Fluvial Argentino), FAMA (Flota Aerea Mercante Argentina) and ZONDA (Zonas Oeste y Norte de Aerolineas Argentinas), giving rise to the county's new national airline, Aerolineas Argentinas.[4]
Ancestral parent: Lignes Aériennes Latécoère

Founded at the end of the World War I, the "Lignes Aériennes Latécoère" was established in September 1919. The France–Morocco postal route became its first scheduled air service between Toulouse and Morocco, and which traveled along the cities such as Barcelona and Alicante on the east coast of Spain. On that same time its founder, Pierre-Georges Latécoère, created the "Compagnie Générale d'Entreprise Aéronautique" and in May 1922, the "Société Industrielle des Avions Latécoère".
In order to extend the line between Casablanca and Dakar, Captain Joseph Roig departed on May 3, 1923, with a group of three biplanes, Bréguet XIVs which flew between Agadir, Cap Juby, Villa Cisneros, and Port Etienne, on the west coast of Africa. The arrived at their destination on May 22.
According to the plan he had conceived during the war by Pierre G. Latécoére, Captain Joseph Roig was sent to South America in May 1924 in order to consider extending the line between Natal, Brazil and Buenos Aires.[4] In the capital city Joseph Roig met with officials of the Department of Civil Aviation of the War Office and explained that the aim of the directors of the Compagnie générale d'entreprises aéronautiques (CGEA) was that Buenos Aires would become terminal site of a future South American airmail line between that continent and France, and later to become a clearinghouse of airmail between Argentina, and its neighboring countries.
President Dr. Marcelo Torcuato Alvear was excited about the idea and gave his approval for the company to send a mission to civil aviation. This time, Captain Roig and his group of three biplanes Bréguet XIV Renault, made a reconnaissance flight from Rio de Janeiro to Buenos Aires, landing on 14 January 1925, in El Palomar, accompanied by Paul Vachet pilots, Etienne Lafay and Victor Hamm and mechanics Gauthier, Estival and Chevalier. In unfavorable weather conditions in March 1925, they started back conducting aerial surveys between Rio de Janeiro and Pernambuco (Recife), that would be useful for future pilots of the Atlantic line. Two months later, in June 1925, regular air mail service between Toulouse, Casablanca and Dakar was established.
In order to raise the capital required for the development of the line on the South American continent, Pierre Georges Latécoère travels to Rio de Janeiro on December 3, 1926, to meet with French businessman living in Brazil, Marcel-Lafont Bouilloux . Immediately, in January 1927 and accompanied by the Argentine aviator Vincent Almandos Almonacid, meet both in Buenos Aires with the President of the Republic, Dr. Marcelo Alvear and the urgent request submission of a contract that allows the country to service the proposed use Aeropostal with France.
Representative in his capacity as Trustee of the "Compagnie Générale d'Entreprises Aéronautiques" Vicente Almandos Almonacid writes and signs a document with the Director General of Posts and Telegraphs, Mr. Arthur Goyeneche, the February 8, 1927, establishing an agreement for the transport of mail by air within and neighboring countries, which would be ratified by the Decree of the National Executive 10 June 1927, signed by the President of the Argentina, Dr. Marcelo Torcuato de Alvear and his interior minister, José P. Tamborini. Meanwhile, negotiations between Pierre Georges Latécoère and Marcel Bouilloux-Lafont culminated when the latter purchased,[1] on April 11, 1927, 93% of the shares of "Compagnie Generale d'Entreprises Aéronautiques" at the cost of 30 million francs, taking over the company's directorships, and agreeing to buy Latécoère 25s, 26s and 28s manufactured by the "Société Industrielle des Avions Latécoère". As a result of the transfer of functions, at a special meeting held in Paris on December 12, 1927, they resolved to change the name of Compagnie Générale d'Entreprises Aéronautiques with the new name of Compagnie Générale Aéropostale.[1]
Birth of Aeroposta Argentina S.A.

Surprisingly, on August 13, 1926, an Executive Order amended the Regulations for Navigation on the Argentine Territory, which did not allow the use of Argentine airspace by foreign companies and where the War Office should adopt positions Defense, civil aircraft to peaceful use. In order to conform to these Regulations, Vicente Almandos Almonacid proposes the establishment of a national corporation, a proposal that has the approval of the Chairman Dr. Marcelo T. Alvear and prestigious Argentine jurists.
The Constitutive Act of the Aeroposta Argentina S. A. was signed into law on September 5, 1927, with Argentina being an affiliate of the "Compagnie Générale Aéropostale," by Agustin Melian gentlemen, on behalf of Marcel Bouilloux-Lafont, Alberto Dodero, Gaston Fouvell Lleau Rigo, Alejandro Behety Menendez, Luis Nicol, Guillermo Padilla (Aeronautical Radio Head, Department of Civil Aviation), Raul A. Razzio, Emmanuel Sieyes and Mr. Almonacid, with headquarters on Calle Reconquista No. 240 of the Federal Capital.
On November 1, 1927 Paul Georges Pivot inaugurated the Vachet Natal–Rio–Buenos Aires route using a Latécoère 25 registered as F-AIOZ, which was extended on March 1, 1928, when Jean Mermoz, aboard a Latécoère 25 loaded with 36 bags of mail, inaugurated the world's longest (13,600 km), from Toulouse to Dakar connecting Buenos Aires–Natal by sea until 1935. This route was called the "Mermoz line."
After considering several locations, he chose Almonacid Pacheco, 35 km from Buenos Aires, where he built the airfield in 1928.[4] In one corner of the field, there were three antennas 30 metres tall and housing material which had been used to build the LPD Radio Station "General Pacheco", a powerful multimedia station which was later transferred to the Post and Telecommunications and from where communications were made first with the other bases, since at that time the aircraft had no radio, and later with the company aircraft and ships overseas.
Buenos Aires to Asuncion, Paraguay route
There are two flights of exploration for studies of this route:
- On April 3, 1928, Peter Ficarelli departed aboard a Bréguet XIV (Renault 300 HP) biplane from the General Pacheco Aerodrome in Buenos Aires at 08:00 Hrs in the morning, and after a stopover at the Aeroclub of Rosario, continuing on to Entre Rios, Corrientes, Chaco and Formosa, while taking note of the airfields and flying clubs that might be suitable as airfields.
- On October 31, 1928, Paul Vachet, Chief Traffic Company, departed the General Pacheco Aerodrome aboard a Breguet XIV biplane at 07:00 Hrs carrying several copies of the newspaper La Prensa and arriving at the airport of Asuncion, Paraguay at 18:00 Hrs, defining the final layout of the air route from Buenos Aires to Asuncion, Paraguay.
On Tuesday, January 1, 1929, Argentina Aeroposta started mail services and passenger transport, still without official authorization, at 06:00 Hrs in the morning, leaving the General Pacheco Aerodrome with two Latécoère 25 (Renault 450 HP) monoplanes:
- Paul and Peter Ficarelli Vachet aboard the No. 619, registration F-AIFX led to Ms. Lidia Vachet, engineer Padilla (company director) and the mechanic Gutierrez.
- The Aviator Leonardo Selvetti Argentina, accompanied by mechanical Ferrando and Mr. Di Sandro aboard the No. 631, registration F-AIJZ, named "Colonel Bogado" carried a small number of letters and copies of the newspaper La Prensa.
After stopping at Corrientes, both aircraft landed at the military airport of Campo Grande Paraguay, in the presence of authorities and large audience, but the correspondence had not been transported not released an official capacity for lack of authorization of government Argentina, these historic flights are considered "trial airmails".
Finally, after reforming the "Regulations on Navigation on the Argentine territory," on February 27, 1929, the national government gave the anticipated authorization and thus, Pedro Ficarelli departed aboard an aircraft Latécoère 25 from the General Pacheco Aerodrome on Friday at 06:00 Hrs on March 22, 1929, this being the first official postal flight from Argentina.
Ficarelli Peter lost his life near Asuncion, Paraguay on August 16, 1929, after colliding with a mountain in the Latécoère 25, No. 619, registration F-AIFX, amid thick fog.
Buenos Aires – Mendoza – Santiago de Chile route

In order to explore the best routes to cross the Andes mountain range, which extend down the length of South America, Jean Mermoz and his mechanic Alexandre Collenot conducted the first test flights between Buenos Aires and Santiago de Chile. They began on November 19, 1928, and continued until March 9, 1929, flying towards Mendoza, Argentina aboard their Latécoère 25 (No. 603, registration F-AIEH). At one point they had to land on the narrow ledge of a mountain range and then, after making adjustments to their engine carburetor, managed to take off and reach the safely of Copiapó, Chile.
This experience convinced them that the aircraft best suited to fly the airmail route between Argentina and Chile over the Andes would be a Potez 25, because of its superior climbing ability—needed to rise above the Andes. Five such planes were purchased, registered as: F-AJDX (No. 1520), F-AJDY (No. 1521), F-AIDZ (No. 1522), F-AJZR (No. 2035) and F-AJZS (No. 2036).
Finally, on July 14, 1929, Jean Mermoz and Henri Guillaumet conducted the first Santiago de Chile to Mendoza airmail flight in a Potez 25. Later, on June 13, 1930, Guillaumet crashed his Potez (registration F-AJDZ) on the surface of a frozen lake, Laguna del Diamante, but was found on June 20 by 14-year-old Juan Garcia (a future Argentinian pastor) after a harrowing, death-defying walk out of the Andes. (Garcia would later be decorated with the Legion of Honour for this 71 years after the event by French President Jacques Chirac.[5]) This period of Aeroposta Argentina is graphically explored in Wings of Courage, an IMAX film (its very first in 3D) by French director Jean-Jacques Annaud.[6]
Buenos Aires – Bahía Blanca – Comodoro Rivadavia route
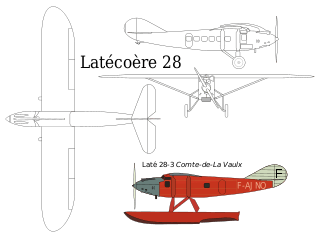
In September 1928, pilot–mechanic Peter Ficarelli Alfredo Vitolo, board a Latécoère 25 and using facilities that the Aero Club of Bahia Blanca had in the place "The Mendoza", made the first reconnaissance flight to Comodoro Rivadavia. In February 1929, Paul Vachet continued exploration flights and began building the infrastructure of future scales.
Between October 29 and November 1, 1929, the final inspection flights were performed by the company's director Antoine de Saint Exupéry, accompanied by pilot Rufino Luro Cambaceres aboard a Latécoère 25, registration F-AIQF, along with the other pilots Prospero Palazzo and Richard Gross in another Latécoère 25, registration F-AIQL.
On November 1, 1929, the Buenos Aires–Bahía Blanca–Comodoro Rivadavia line opened, with stops in San Antonio Oeste (now Antoine de Saint Exupéry Airport) and Trelew. Without prejudice to the first flight was made by Antoine de Saint Exupéry aboard the Latécoère 25, F-AIQL, carrying as passengers for journalists from bahienses: Enrique Julio "La Nueva Provincia," Emilio J. Fence "The Atlantic" and Augustus Hunter "Morning", delivering and receiving mail in each of the scales, "the official inauguration flight" was conducted by Jean Mermoz, accompanied by Richard Gross pilot on board Latécoère 28 aircraft that started in the early morning hours at the General Pacheco Aerodrome, carrying Captain Almandos Almonacid, Director of Aeroposta Argentina, plus officials and journalists.
At Bahía Blanca, was replaced by Richard Gross Palazo Prospero, who was in charge of 'the line' to Comodoro Rivadavia. During the first six months, the head of the line was located in the area of Villa Harding Green, Bahía Blanca, where they had built a metal hangar, two towers for the radio station, a weather station and a villa for office and attention to the passenger. The connection to Buenos Aires, Bahía Blanca was made by rail, from the Constitution Station, traveling all night to arrive at Bahía Blanca in the morning. In May 1930 he began operating from General Pacheco Aerodrome, becoming White Bay on a scale of travel.
Meanwhile, in March 1930, Mermoz flew the first transatlantic airmail in 21 hours aboard a pontoon equipped Latécoère 28 and carrying 130 kg of correspondence, on Wednesday 31 of that month Antoine de Saint-Exupéry, Director of Operations of the Company, made the inaugural flight to Rio Gallegos in the Latécoère 28 aircraft, registration F-AJLO, "El Pampero", carrying passengers as Chairman of the Aeroposta, Mr. Marcel Boilloux Lafont, the Technical Director of the Company, Captain Vicente Almandos Almonacid, and the Viscount Jacques Delalot (Havas Agency Director), Julian Pranville (official Aeropostale) and journalist The reason, Mr. Enrique Gutierrez, being accompanied by Luro Cambaceres in the Latécoère 25, registration F-AIQF.
Pilots Prospero Palazzo and Caesar Brugo lost their lives on June 23, 1936, in Pampa de Salamanca, 60 km from Comodoro Rivadavia aboard a Latécoère 28, No. 293, registration F- AJUX.[7]
The National Aeroposta
Because of the Great Depression, Bouilloux-Lafont, who ran a major banking consortium and transport companies, was irretrievably affected.[8] From early 1930, the French Government refused to release the loan approval that had been agreed in an agreement signed the previous year, and the company's financial situation was aggravated by the Argentinian coup of September 1930, in a revolution that would lead Getúlio Vargas to power in Brazil in October of that year. In December of the same year some ministerial changes that are occurring in France to renew the lease prevent you from operating and guaranteed by the State to get new loans. For the Compagnie Générale Aéropostale is the end, the 31 March 1931 the company is liquidated, which would later be absorbed into the group of companies that would later give rise to Air France in 1933, continuing the activities of its Aéropostale and its other sibling predecessors.
The situation for Argentina Aeroposta was not very different, with the Argentine government also denying funds, and in June 1931 it ceased operations. However, the Director of Postal Services and the Director of Civil Aviation joined the claims of the press and the general public and finally convinced the President of Argentine's provisional government to authorize Aeroposta Argentina SA to resume their services.
By decree of 29 September 1931, the Company is subject to a lease and control of the Directorate General of Civil Aviation and the General Post and Telegraph, for the operation of the line between Bahía Blanca and Rio Gallegos, on an experimental basis for a period of six months, leasing its flight equipment and facilities that the Company had, at a cost of $7,000 per month. Legally, the company was designated as National Aeroposta, although at the corporate level it was still operated as Aeroposta Argentina S.A.
Services were restarted on October 2, 1931, until May 31, 1932, when a new decree extends the authorization from the June 1, 1932, until December 31, granting for the first time, a fixed monthly allowance and the provision of fuel needed to account for YPF, while a third decree, that of March 24, 1933, fixed the operating agreement a term of 10 years, increased the amount of the grant and contemplated the possibility of extending the route to Ushuaia.
In October 1933 Rufino Luro Cambaceres made a reconnaissance flight and promotion by the Patagonia, explaining the authorities and population, the benefits of air transport for both mail and passenger, causing several southern regions of the requests sent to Buenos Aires for the line include its cities like scales.
In early 1935, Argentina Aeroposta purchased obsolete aircraft from Air France that had once belonged to Aéropostale, and in September 1935 and continued service to Rio Grande.
In November 1935 the bylaws of the company were amended, allowing the entry of a group share Argentina.
The Pueyrredón consortium
When, in 1936, new financial difficulties threatened the operations of the line, a new group of Argentine businessmen, headed by Dr. Ernesto Pueyrredón formed a consortium which acquired 97% stake in the company, which ultimately rests with nationals.[4] Officials of the Directorate General of Civil Aviation and by Decree 99,184 of 1 February 1937, authorized the company to extend its flights departing from Buenos Aires and replaces the cash grant and fuel for a monthly contribution of $1.50 per every mile flown for the trip.
In this new contract, which provided for a period of 10 years, the Company must make a 50% discount in the price of tickets for Posts and Telegraphs and the Aeronautics Directorate, had seats available, and reserve up to 2 kg charging for official correspondence, to be carried free of charge and commitment to renew the existing flight material.
In a pivot to Germany, the company bought the first three Junkers Trimotor Ju 52/3m in 1937,[4] registered LV-AAB "Patagonia", LV-BAB "Pampa" and LV-CAB "Tierra del Fuego", plus spare parts, BMW engines and Lorenz and Telefunken radios, in order to modernize its operating equipment. German Lufthansa and other personnel were recruited for flight and maintenance training operating from the Quilmes aerodrome,[9] where, in October of that year, the first regular flights between Buenos Aires and Rio Grande were started, on board the "Patagonia". They were piloted by Paul Selvetti Rohlandt and the Argentines Gross and Irigoyen.
In April 1938, another decree authorizing Aeroposta Argentina S.A. to combine the national and international operating with Air France and Condor Ltda Union in December 1939 decree changing the frequency Buenos Aires – Rio Gallegos and Rio Grande.
Pressure from the United States, its entry into the Second World War, to the closure of Syndicate Condor, Lufthansa subsidiary in Brazil, Bolivia and Peru, Aeroposta in this situation the opportunity to acquire two Junkers Ju 52, the LV-AAJ "Ibaté" in Brazil, in April 1942 and LV-AAN 'Quichua' in Bolivia, in June 1943 and completed a fleet of five Ju 52.
Competitors
Similar service was later offered by airlines created by the Argentine Air Force, which in the early 1940s established LASO (Línea Aérea Sud Oeste) and LANE (Línea Aérea Nordeste), which later became LADE (Líneas Aéreas del Estado) in 1945.[10]
In 1946, the Government of Argentina created the "Sociedades Mixtas", they were: Aeroposta, A.L.F.A. (Aviación del Litoral Fluvial Argentino), Z.O.N.D.A. (that replaced Panagra) and FAMA (Flota Aérea Mercante Argentina) which was to be the first Argentine airline to fly intercontinentally. In 1950 and due to new regulations the private shares were no longer permitted in air-services so all of them, except LADE (Líneas Aéreas del Estado) merged into the Argentine flag carrier Aerolíneas Argentinas.
Commemoration
On January 2, 1979, the surviving pilots of Aeroposta Argentina gathered to commemorate the fiftieth anniversary of its first flight. The attendees were: Virgilio Mira • Alberto Papa • H. Papa • Leonardo Selvetti • Pedro Artigau • Oscar Bujia • Martignoni, and, additionally, señora Ermenilda Almandós Almonacid, daughter of Vincent Almandós Almonacid, founder of Aeroposta Argentina.[11]
See also
- Aéropostale
- Aeropostal Alas de Venezuela
- List of defunct airlines of South America
References
.
Citations
- Ayala, Pablo Maximiliano; Barrientos, Walther Hugo; Morales, Ramón Antonio; Schiller, Elba Sara (ed.). Historia de la Aeroposta Argentina (in Spanish), El Talar, Tigre, Buenos Aires Province, Argentina: Del Partido de Tigre, Escuela Nº 45 (Tigre District School No. 45), March 2000. Retrieved from www.saintexupery.com.ar January 21, 2014; which in turn cites:
- Bousquet, Augusto V. La Aeroposta Argentina y el Correo Aéreo (in Spanish) (Aeroposta Argentina and the Airmail)
- Museo de la Aeroposta Argentina Archived March 26, 2010, at the Wayback Machine (Aeroposta Argentina Museum), Retrieved March 7, 2012. (in Spanish)
- McCloskey, Erin. Argentina: 2 Bradt, part of Bradt Guides: Bradt Travel Guide Series, Publisher Bradt Travel Guides, 2011, ISBN 1841623512, ISBN 978-1841623511.
- Aeroposta Argentina, GeneralPachecoWeb.com website (in Spanish), which in turn cites:
- General Pacheco Historical Association
- d'Agay, Frédéric; Pico, Elsa (trans.) Guide de voyage, Argentine, Aéropostale: Juan Gualberto Garcia, l’enfant qui trouva Henri Guillaumet, Argentina Excepción website. Retrieved November 19, 2012. (in French)
- James, Caryn. Wings of Courage: High Over the Andes, In Enormous Goggles (1995 Film Review), The New York Times, April 21, 1995. Retrieved: September 28, 2012.
- Jorge J. Horat: Palazzo: El Héroe Olvidado (Jorge J. Horat, The Forgotten Hero), SeguridadSolidaria.com website (in Spanish)
- Ses grandes figures: Marcel Bouilloux-Lafont Archived 2014-02-01 at the Wayback Machine (in French), at the Mémoire d'Aéropostale website.
- Newton, Ronald C. The "Nazi Menace" in Argentina, 1931-1947, Stanford University Press, 1992.
-
Björn Larsson; David Zekria. Aeroposta Argentina & Airline Timetables: LASO & LANE which in turn cites:
- R.E.G. Davies. Airlines of Latin America Since 1919, 1983.
- Diploma, firmado el 2 de enero de 1979 por los Pilotos Civiles Precursores Sobrevivientes a la fecha citada, de la Compañia Aeroposta Argentina fundada el 5 de septiembre de 1927, vuelo inicial el 1 de enero de 1929. (in Spanish) (Diploma, signed on January 2, 1979, by the Surviving Civil Pilot Pioneers of the Aeroposta Argentina Company founded September 5 of 1927, initial flight on January 1, 1929 —from the private collection of William A. N. Tarapow).
Bibliography
- Brown, Hannibal (2004). "Patagonia Airmail: Air Mail Routes in Argentina of 1929". In "Visions of a Little Prince". Archived from the original (documentary research) on February 9, 2007. Retrieved January 25, 2011.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- General Pacheco Historical Association. Aeroposta Argentina, GeneralPachecoWeb.com website (in Spanish).
- Larra, Raúl. La conquista aérea del desierto (in Spanish), Buenos Aires: Ediciones Anfora, 1979.
- Mémoire d'Aéropostale. Quelques dates (in French), Mémoire d'Aéropostale website.
- Potenze, Pablo Luciano. Aviación comercial Argentina (1945-1980) (in Spanish), Buenos Aires: Ediciones El Cronista Comercial, 1987, ISBN 9509067288, ISBN 978-9509067288.
External links
- Aeroposta Argentina Museum (in Spanish)
- Wings Of Courage (1995), the first 3D IMAX Movie ever filmed, showing the Aeroposta Argentina of 1930, depicting Mermoz, Saint-Exupery and Henri Guillaumet, who crashes in the Andes.