500 BC
The year 500 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. In the Roman Empire it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Camerinus and Longus (or, less frequently, year 254 Ab urbe condita). The denomination 500 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
| Millennium: | 1st millennium BC |
|---|---|
| Centuries: | |
| Decades: | |
| Years: |
| 500 BC by topic |
| Politics |
|---|
| Categories |
| Gregorian calendar | 500 BC CDXCIX BC |
| Ab urbe condita | 254 |
| Ancient Egypt era | XXVII dynasty, 26 |
| - Pharaoh | Darius I of Persia, 22 |
| Ancient Greek era | 70th Olympiad (victor)¹ |
| Assyrian calendar | 4251 |
| Balinese saka calendar | N/A |
| Bengali calendar | −1092 |
| Berber calendar | 451 |
| Buddhist calendar | 45 |
| Burmese calendar | −1137 |
| Byzantine calendar | 5009–5010 |
| Chinese calendar | 庚子年 (Metal Rat) 2197 or 2137 — to — 辛丑年 (Metal Ox) 2198 or 2138 |
| Coptic calendar | −783 – −782 |
| Discordian calendar | 667 |
| Ethiopian calendar | −507 – −506 |
| Hebrew calendar | 3261–3262 |
| Hindu calendars | |
| - Vikram Samvat | −443 – −442 |
| - Shaka Samvat | N/A |
| - Kali Yuga | 2601–2602 |
| Holocene calendar | 9501 |
| Iranian calendar | 1121 BP – 1120 BP |
| Islamic calendar | 1155 BH – 1154 BH |
| Javanese calendar | N/A |
| Julian calendar | N/A |
| Korean calendar | 1834 |
| Minguo calendar | 2411 before ROC 民前2411年 |
| Nanakshahi calendar | −1967 |
| Thai solar calendar | 43–44 |
| Tibetan calendar | 阳金鼠年 (male Iron-Rat) −373 or −754 or −1526 — to — 阴金牛年 (female Iron-Ox) −372 or −753 or −1525 |
Events
By place
Europe
- Vulca makes Apollo of Veii, from Portonaccio Temple. It's kept at Museo Nazionale di Villa Giulia, Rome.
- The Nordic Bronze Age civilization ends and the Pre-Roman Iron Age begins in Scandinavia, according to the Oscar Montelius periodization system (approximate date).[1]
- Refugees from Teos resettle Abdera.
Middle East
- Darius I of Persia proclaims that Aramaic be the official language of the western half of his empire.
Africa
- Bantu-speaking people migrate into south-west Uganda from Northeastern Africa. (approximate date)
- The Hutu tribe begins around this time, in Middle and Southern Africa.
- approximate date
- Hanno the Navigator's naval exploration of the western coast of Africa could have reached as far south as Gabon.
Asia
- The first republic in Vaishali, Bihar, India is founded.
- States in existence include the Kingdom of Pratipalapura (centred on modern Bhattiprolu, in Guntur district, Andhra Pradesh).
- Yayoi period starts in Ancient Japan (approximate date).
Mesoamerica
- The oldest known Zapotec writing appears (approximate date).
- The Olmecs establish Monte Albán, the sacred city, and continue building pyramids. Founded toward the end of the Middle Formative period at around 500 BC, by the Terminal Formative (ca.100 BC-AD 200) Monte Albán soon becomes the capital of a large-scale expansionist polity that dominates much of the Oaxacan highlands and interacts with other Mesoamerican regional states, such as Teotihuacan to the north (Paddock 1983; Marcus 1983).
By topic
Demographics
- World population reaches 100,000,000[2]—the population is 85,000,000 in Eastern Hemisphere and 15,000,000 in Western Hemisphere, primarily Mesoamerica (Mexico, Central America, Colombia, Peru, Venezuela).
Arts and culture
- She-Wolf, with late 15th century or early 16th century additions (twins), is made. It is now kept at the Museo Capitolino in Rome (approximate date).
Inventions, discoveries, introductions
- Mesoamerican calendars are developed by the Olmec civilisation
Births
- Anaxagoras, Pre-Socratic Greek philosopher (approximate date) (d. 428 BC)[3]
How the world looked
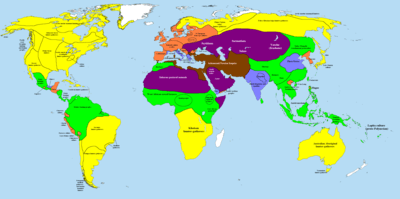 The world's cultural distribution at 500 BC
The world's cultural distribution at 500 BC
gollark: I wonder if I can manage to create a more contentious argument than firecubezeses's.
gollark: I'm just doing this while I procrastinate on some school CS work.
gollark: I personally do 4 spaces mostly but use tabs when writing in bad TUI editors which cannot autoconvert stuff.
gollark: This is also very nice, yes.
gollark: Ugh, Python won't let me use ☭ as an identifier.
References
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to 500 BC. |
- "The Civilisation of Sweden in Heathen Times".
- an average of figures from different sources as listed at the US Census Bureau's Historical Estimates of World Population
- Suzuki, Jeff (2009). Mathematics in Historical Context. MAA. p. 24. ISBN 9780883855706.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.