5,6-Dichloro-1-beta-D-ribofuranosylbenzimidazole
5,6-Dichloro-1-β-d-ribofuranosylbenzimidazole (DRB) is a chemical compound that inhibits transcription elongation by RNA Polymerase II. Sensitivity to DRB is dependent on DRB sensitivity inducing factor (DSIF), negative elongation factor (NELF), and positive transcription elongation factor b (P-TEFb). DRB is a nucleoside analog and also inhibits some protein kinases.[1]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
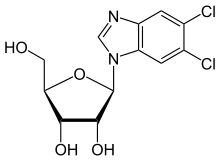
| IUPAC name
(2R,3R,4S,5R)-2-(5,6-Dichlorobenzimidazol-1-yl)-5-(hydroxymethyl)oxolane-3,4-diol | |
| Other names
DRB, Dichlororibofuranosylbenzimidazole | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C12H12Cl2N2O4 | |
| Molar mass | 319.14 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
References
- Yamaguchi, Y.; Takagi, T.; Wada, T.; Yano, K.; Furuya, A.; Sugimoto, S.; Hasegawa, J.; Handa, H. (1999). "NELF, a Multisubunit Complex Containing RD, Cooperates with DSIF to Repress RNA Polymerase II Elongation". Cell. 97 (1): 41–51. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80713-8. PMID 10199401.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.