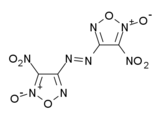
4,4'-Dinitro-3,3'-diazenofuroxan
4,4’-Dinitro-3,3’-diazenofuroxan (DDF) is a powerful experimental high explosive with performance comparable to that of other high-density high-explosives such as octanitrocubane. It is synthesised by oxidative coupling of 4-amino-3-(azidocarbonyl)furoxan followed by Curtius rearrangement and further oxidation.[1][2]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(E)-4-nitro-N-[(E)-(4-nitro-2-oxo-1,2,5-oxadiazol-2-ium-3-ylidene)amino]-2-oxido-1,2,5-oxadiazol-3-imine | |
Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| |
| Properties | |
| C4N8O8 | |
| Molar mass | 288.092 g/mol |
| Density | 2.02 g/cm3 |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | Highly Explosive |
| Explosive data | |
| Detonation velocity | 10,000 m/s |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
See also
- 3,3′‐Diamino‐4,4′‐azoxyfurazan (DAAF)
- 2,4,6-Tris(trinitromethyl)-1,3,5-triazine
- ONC
- Hexanitrohexaazaisowurtzitane
- HNC
- HHTDD
References
- Blinnikov AN, Kulikov AS, Makhova NN, Ovchinnikov IV, Pivina TS. 4-Amino-3-azidocarbonyl Furoxan as an Universal Synthon for the Synthesis of Energetic Compounds of the Furoxan Series. 30th International Annual Conference of ICT, Karlsruhe, Germany, 1999. 58/1–58/10.
- Agrawal JP, Hodgson RD. Organic Chemistry of Explosives. John Wiley & Sons Ltd, 2007. p303. ISBN 978-0-470-02967-1
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.