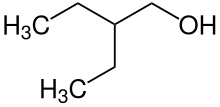
2-Ethyl-1-butanol
2-Ethyl-1-butanol (IUPAC name: 2-ethylbutan-1-ol) is an organic chemical compound. It can be used to facilitate the separation of ethanol from water, which form an azeotrope that otherwise limits the maximum ethanol concentration.[2]
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
2-Ethylbutan-1-ol | |
| Other names
2-Ethyl-1-butanol | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| 1731254 | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.002.384 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 2275 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H14O | |
| Molar mass | 102.177 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Colorless liquid |
| Density | 830 mg mL−1 |
| Melting point | −114.40 °C; −173.92 °F; 158.75 K |
| Boiling point | 145 to 151 °C; 293 to 304 °F; 418 to 424 K |
| 10 g L−1 | |
| Vapor pressure | 206 Pa |
Refractive index (nD) |
1.422 |
| Thermochemistry | |
Heat capacity (C) |
246.65 J K−1 mol−1 |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms |  |
| GHS Signal word | Warning |
GHS hazard statements |
H302, H312 |
| P280 | |
| Flash point | 58 °C (136 °F; 331 K) |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose) |
1.85 g kg−1 (oral, rat) |
| Related compounds | |
Related compounds |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Reactions
2-Ethyl-1-butanol is manufactured industrially by the aldol condensation of acetaldehyde and butyraldehyde, followed by hydrogenation.[3] It may also be prepared by the Guerbet reaction.
Properties and applications
The branching in 2-ethyl-1-butanol makes it harder to crystalize due to packing disruption, which results in a very low freezing point. Esters of 2-ethyl-1-butanol are similarly effected and it therefore finds application as a feedstock in the production of plasticizers and lubricants, where its presence helps reduce viscosity and lower freezing points.
See also
References
- Lide, David R. (1998), Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (87 ed.), Boca Raton, Florida: CRC Press, pp. 3–262, 8–106, 15–20, ISBN 978-0-8493-0594-8
- Roddy, James W. (1981). "Distribution of ethanol-water mixtures to organic liquids". Ind. Eng. Chem. Proc. Des. Dev. 20 (1): 104–108. doi:10.1021/i200012a016.
- McKetta, John J.; Cunningham, William Aaron (1994), Encyclopedia of Chemical Processing and Design, 47, Boca Raton, Florida: CRC Press, p. 117, ISBN 978-0-8247-2451-1, retrieved 2010-01-25