1986–87 Australian region cyclone season
The 1986–87 Australian region cyclone season was the latest starting Australian season on record. A below-average tropical cyclone season, it officially started on 1 November 1986, and officially ended on 30 April 1987, with the last system dissipating on 27 May.
| 1986–87 Australian region cyclone season | |
|---|---|
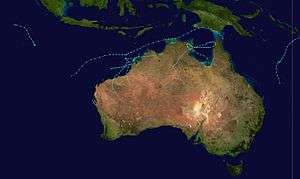 Season summary map | |
| Seasonal boundaries | |
| First system formed | 15 January 1987 |
| Last system dissipated | 27 May 1987 |
| Strongest storm | |
| Name | Elsie |
| • Maximum winds | 185 km/h (115 mph) (10-minute sustained) |
| • Lowest pressure | 940 hPa (mbar) |
| Seasonal statistics | |
| Tropical lows | 9 |
| Tropical cyclones | 7 |
| Severe tropical cyclones | 3 |
| Total fatalities | 0 |
| Total damage | $0,000 (1987 USD) |
| Related articles | |
Seasonal summary
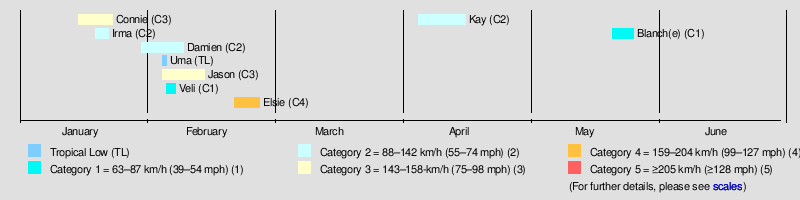
Systems
Severe Tropical Cyclone Connie
| Category 3 severe tropical cyclone (Australian scale) | |
| Category 3 tropical cyclone (SSHWS) | |
  | |
| Duration | 15 January – 23 January |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 155 km/h (100 mph) (10-min) 950 hPa (mbar) |
Connie, 15 to 23 January 1987. Made landfall over Port Hedland on 19 January. Moderate damage was reported in Port Hedland and Whim Creek.
Tropical Cyclone Irma
| Category 2 tropical cyclone (Australian scale) | |
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |
  | |
| Duration | 19 January – 22 January |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 110 km/h (70 mph) (10-min) 978 hPa (mbar) |
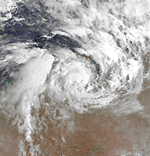
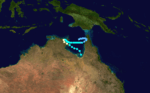
Irma, 19 to 22 January 1987, Gulf of Carpentaria.
Tropical Cyclone Damien
| Category 2 tropical cyclone (Australian scale) | |
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |
  | |
| Duration | 30 January – 9 February |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 95 km/h (60 mph) (10-min) 980 hPa (mbar) |
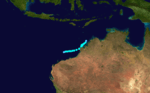
Damien, 30 January to 9 February 1987, near Western Australia.
Severe Tropical Cyclone Jason
| Category 3 severe tropical cyclone (Australian scale) | |
| Category 1 tropical cyclone (SSHWS) | |
  | |
| Duration | 4 February – 14 February |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 140 km/h (85 mph) (10-min) 970 hPa (mbar) |
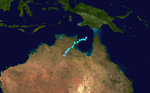
Jason stuck the Northern Territory in February, 1987 damaging 20 buildings.[1]
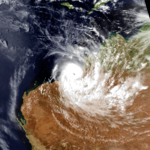
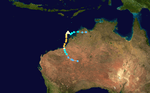
Severe Tropical Cyclone Elsie
| Category 4 severe tropical cyclone (Australian scale) | |
| Category 3 tropical cyclone (SSHWS) | |
  | |
| Duration | 21 February – 27 February |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 185 km/h (115 mph) (10-min) 940 hPa (mbar) |
Elsie, 21 to 27 February 1987, near Western Australia. Catastrophic damage was reported at Mandora Station.
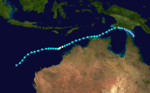
Tropical Cyclone Kay
| Category 2 tropical cyclone (Australian scale) | |
| Category 1 tropical cyclone (SSHWS) | |
  | |
| Duration | 6 April – 17 April |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 110 km/h (70 mph) (10-min) 976 hPa (mbar) |
Kay, 6 to 17 April 1987, Papua-Newguinea and Western Australia.
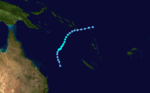
Tropical Cyclone Blanch(e)
| Category 1 tropical cyclone (Australian scale) | |
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |
  | |
| Duration | 22 May (entered basin) – 27 May |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 85 km/h (50 mph) (10-min) 990 hPa (mbar) |
Blanch, entered the Australian region basin on 22 May, and dissipated on 27 May 1987, off the east coast of Australia.
Other systems
The precursor tropical low to Cyclone Uma formed within the region on 4 February, before it crossed 160°E and moved into the South Pacific basin later that day.[2] The precursor tropical low to Cyclone Veli formed during the next day, about 725 km (450 mi) to the south-east of Port Moresby in Papua New Guinea.[2] During the next day the low moved eastwards and gradually developed further, before it became equivalent to a category 1 tropical cyclone on the Australian scale, as it reached its 10-minute sustained windspeeds of 85 km/h (55 mph).[2] As the system continued to move eastwards it crossed 160°E and moved into the South Pacific basin during 7 February, before TCWC Nadi named it Veli later that day on the basis of satellite derived evidence.[2][3]
Seasonal effects
| Name | Dates | Peak intensity | Areas affected | Damages (AU$) |
Damages (US$) |
Deaths | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Category | Wind speed (km/h (mph)) |
Pressure (hPa) | |||||||
| Connie | 15 – 23 January | Category 3 tropical cyclone | 155 km/h (100 mph) | 950 hPa (28.06 inHg) | Western Australia | ||||
| Irma | 19 – 22 January | Category 2 tropical cyclone | 100 km/h (65 mph) | 980 hPa (28.94 inHg) | |||||
| Raja | 21 December – 5 January | Category 3 severe tropical cyclone | 150 km/h (90 mph) | 955 hPa (28.20 inHg) | Wallis and Futuna, Fiji | 14 million | 2 | ||
| Sally | 26 December – 5 January | Category 3 severe tropical cyclone | 150 km/h (90 mph) | 955 hPa (28.20 inHg) | Cook Islands, Austral Islands | 25 million | |||
| Tusi | 13 – 21 January | Category 3 severe tropical cyclone | 150 km/h (90 mph) | 955 hPa (28.20 inHg) | Tokelau, Samoan Islands, Cook Islands | 80 million | None | ||
| Uma | 4 February | Tropical Low | 55 km/h (35 mph) | 997 hPa (29.4 inHg) | None | None | None | None | [2] |
| Veli | 5 – 7 February | Category 1 tropical cyclone | 85 km/h (50 mph) | 987 hPa (29.15 inHg) | None | None | None | None | [2][3] |
| Kay | 19 – 26 April | Category 2 tropical cyclone | 100 km/h (65 mph) | 975 hPa (28.80 inHg) | |||||
| Blanch(e) | 22 – 27 May | Category 2 tropical cyclone | 110 km/h (70 mph) | 990 hPa (29.24 inHg) | |||||
| Season Aggregates | |||||||||
| 9 systems | 20 November – 27 May | 165 km/h (105 mph) | 940 hPa (27.76 inHg) | ||||||
See also
References
- MetService (22 May 2009). "TCWC Wellington Best Track Data 1967–2006". International Best Track Archive for Climate Stewardship.
- Singh, Sudah; Fiji Meteorological Service (1987). DeAngellis, Richard M (ed.). Tropical Cyclone Veli (Mariners Weather Log: Volume 31: Issue 3: Summer 1987). United States National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. pp. 24–25. hdl:2027/uiug.30112104093965. ISSN 0025-3367. OCLC 648466886. Retrieved 29 May 2013.