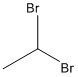
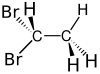
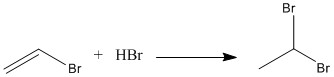1,1-Dibromoethane
1,1-Dibromoethane is a clear, slightly brown, flammable chemical compound.[2] It is classified as the organobromine compound, and has the chemical formula C2H4Br2[3] and it is a position isomer of 1,2-dibromoethane. It is commonly seen in industrial chemistry, where it is used as a fuel additive.[4] It is also used as a grain and soil fumigant for insect control.[5]
| |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
1,1-Dibromoethane[1] | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol) |
|||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.008.351 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
PubChem CID |
|||
| RTECS number |
| ||
| UNII | |||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C2H4Br2 | |||
| Molar mass | 187.862 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | Colorless liquid | ||
| Melting point | −63.0 °C; −81.3 °F; 210.2 K | ||
| Boiling point | 108.1 °C; 226.5 °F; 381.2 K | ||
| 3.4 g/L (25 °C) | |||
| Solubility | soluble in ether, ethanol, acetone,and benzene slight soluble chloroform | ||
| log P | 1.9 (estimated) | ||
Refractive index (nD) |
1.51277 (at 20 °C) | ||
| Hazards | |||
| Safety data sheet | fishersci.com | ||
| GHS Signal word | Danger | ||
GHS hazard statements |
H301, H311, H315, H319, H331 | ||
| P261, P264, P270, P271, P280, P311, P312, P321, P322, P330, P361, P362, P363, P405, P501 | |||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |||
| Flash point | > 93 °C (199 °F; 366 K) | ||
| Related compounds | |||
Related alkanes |
|||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| Infobox references | |||
Synthesis
1,1-Dibromoethane is synthesized through addition of hydrogen bromide onto vinyl bromide with absence of peroxide radical.[6]
Safety
1,1-Dibromoethane is considered as a mild toxic compound, especially with bromines attached as substituents. Bromines on the ethane are strong oxidizing agents. If absorbed through inhalation, 1,1-dibromoethane could potentially cause neuronal effects, tissue damage, and bromism.[7]
References
- "Ethylidene dibromide - Compound Summary". PubChem Compound. USA: National Center for Biotechnology Information. 27 March 2005. Identification. Retrieved 19 June 2012.
- "MSDS". Fisher Scientific, Inc. Retrieved 13 June 2012.
- "Dibromoethane". ChemSpider. Retrieved 13 June 2012.
- "1,1-dibromoethane". PubChem. Retrieved 9 June 2017.
- Larranaga, Michael (10 March 2016). Hawley's Condensed Chemical Dictionary. ISBN 9781118135150. Retrieved 9 June 2017.
- Kharasch, M.; McNab, M.; Mayo, Frank (June 1933). "The Peroxide Effect in the Addition of Reagents to Unsaturated Compounds. II. The Addition of Hydrogen Bromide to Vinyl Bromide". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 55 (6): 2521–2530. doi:10.1021/ja01333a048.
- "1,1-Dibromoethane (T3D1793)". The Toxin and Toxin Target Database. Retrieved 9 June 2017.

.png)