107
77
How can I know where an email really originated from? Is there any way to find it out?
I have heard about email headers, but I don't know where can I see email headers, for example in Gmail. Any help?
107
77
How can I know where an email really originated from? Is there any way to find it out?
I have heard about email headers, but I don't know where can I see email headers, for example in Gmail. Any help?
147
See below for an example of a scam that was sent to me, pretending to be from my friend, claiming she has been robbed and asking me for financial aid. I have changed the names — I am "Bill," and the scammer has sent an email to bill@domain.com, pretending to be alice@yahoo.com. Note that Bill forwards his email to bill@gmail.com.
First, in Gmail, click show original:
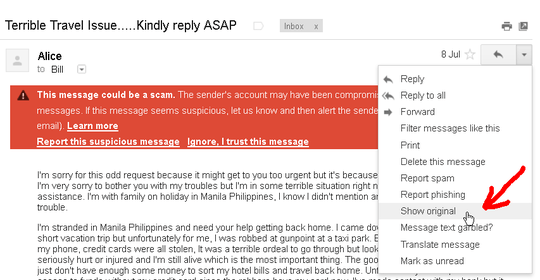
The full email and its headers will open:
Delivered-To: bill@gmail.com
Received: by 10.64.21.33 with SMTP id s1csp177937iee;
Mon, 8 Jul 2013 04:11:00 -0700 (PDT)
X-Received: by 10.14.47.73 with SMTP id s49mr24756966eeb.71.1373281860071;
Mon, 08 Jul 2013 04:11:00 -0700 (PDT)
Return-Path: <SRS0=Znlt=QW=yahoo.com=alice@domain.com>
Received: from maxipes.logix.cz (maxipes.logix.cz. [2a01:348:0:6:5d59:50c3:0:b0b1])
by mx.google.com with ESMTPS id j47si6975462eeg.108.2013.07.08.04.10.59
for <bill@gmail.com>
(version=TLSv1 cipher=RC4-SHA bits=128/128);
Mon, 08 Jul 2013 04:11:00 -0700 (PDT)
Received-SPF: neutral (google.com: 2a01:348:0:6:5d59:50c3:0:b0b1 is neither permitted nor denied by best guess record for domain of SRS0=Znlt=QW=yahoo.com=alice@domain.com) client-ip=2a01:348:0:6:5d59:50c3:0:b0b1;
Authentication-Results: mx.google.com;
spf=neutral (google.com: 2a01:348:0:6:5d59:50c3:0:b0b1 is neither permitted nor denied by best guess record for domain of SRS0=Znlt=QW=yahoo.com=alice@domain.com) smtp.mail=SRS0=Znlt=QW=yahoo.com=alice@domain.com
Received: by maxipes.logix.cz (Postfix, from userid 604)
id C923E5D3A45; Mon, 8 Jul 2013 23:10:50 +1200 (NZST)
X-Original-To: bill@domain.com
X-Greylist: delayed 00:06:34 by SQLgrey-1.8.0-rc1
Received: from elasmtp-curtail.atl.sa.earthlink.net (elasmtp-curtail.atl.sa.earthlink.net [209.86.89.64])
by maxipes.logix.cz (Postfix) with ESMTP id B43175D3A44
for <bill@domain.com>; Mon, 8 Jul 2013 23:10:48 +1200 (NZST)
Received: from [168.62.170.129] (helo=laurence39)
by elasmtp-curtail.atl.sa.earthlink.net with esmtpa (Exim 4.67)
(envelope-from <alice@yahoo.com>)
id 1Uw98w-0006KI-6y
for bill@domain.com; Mon, 08 Jul 2013 06:58:06 -0400
From: "Alice" <alice@yahoo.com>
Subject: Terrible Travel Issue.....Kindly reply ASAP
To: bill@domain.com
Content-Type: multipart/alternative; boundary="jtkoS2PA6LIOS7nZ3bDeIHwhuXF=_9jxn70"
MIME-Version: 1.0
Reply-To: alice@yahoo.com
Date: Mon, 8 Jul 2013 10:58:06 +0000
Message-ID: <E1Uw98w-0006KI-6y@elasmtp-curtail.atl.sa.earthlink.net>
X-ELNK-Trace: 52111ec6c5e88d9189cb21dbd10cbf767e972de0d01da940e632614284761929eac30959a519613a350badd9bab72f9c350badd9bab72f9c350badd9bab72f9c
X-Originating-IP: 168.62.170.129
[... I have cut the email body ...]
The headers are to be read chronologically from bottom to top — oldest are at the bottom. Every new server on the way adds its own message — starting with Received. For example:
Received: from maxipes.logix.cz (maxipes.logix.cz. [2a01:348:0:6:5d59:50c3:0:b0b1])
by mx.google.com with ESMTPS id j47si6975462eeg.108.2013.07.08.04.10.59
for <bill@gmail.com>
(version=TLSv1 cipher=RC4-SHA bits=128/128);
Mon, 08 Jul 2013 04:11:00 -0700 (PDT)
This says that mx.google.com has received the mail from maxipes.logix.cz at Mon, 08 Jul 2013 04:11:00 -0700 (PDT).
Now, to find the real sender of your email, you must find the earliest trusted gateway — last when reading the headers from top. Let's start by finding Bill's mail server. For this, query MX record for the domain. You can use online tools like Mx Toolbox, or on Linux you can query it on command line (note the real domain name was changed to domain.com):
~$ host -t MX domain.com
domain.com MX 10 broucek.logix.cz
domain.com MX 5 maxipes.logix.cz
And you'll see the mail server for domain.com is maxipes.logix.cz or broucek.logix.cz. Hence, the last (first chronologically) trusted "hop" — or last trusted "Received record" or whatever you call it — is this one:
Received: from elasmtp-curtail.atl.sa.earthlink.net (elasmtp-curtail.atl.sa.earthlink.net [209.86.89.64])
by maxipes.logix.cz (Postfix) with ESMTP id B43175D3A44
for <bill@domain.com>; Mon, 8 Jul 2013 23:10:48 +1200 (NZST)
You can trust this because it was recorded by Bill's mail server for domain.com. This server got it from 209.86.89.64. This could be, and very often is, the real sender of the email — in this case the scammer! You can check this IP on a blacklist. — See, he is listed in 3 blacklists! There is yet another record below it:
Received: from [168.62.170.129] (helo=laurence39)
by elasmtp-curtail.atl.sa.earthlink.net with esmtpa (Exim 4.67)
(envelope-from <alice@yahoo.com>)
id 1Uw98w-0006KI-6y
for bill@domain.com; Mon, 08 Jul 2013 06:58:06 -0400
But be careful trusting that this is the real source of the email. The blacklist complaint could just be added by the scammer to wipe out his traces and/or lay a false trail. There is still the possibility that the server 209.86.89.64 is innocent and just a relay for the real attacker at 168.62.170.129. In this case, 168.62.170.129 is clean so we can be nearly certain the attack was done from 209.86.89.64.
Another point to keep in mind is that Alice uses Yahoo! (alice@yahoo.com) and elasmtp-curtail.atl.sa.earthlink.net isn't on the Yahoo! network (you may want to re-check its IP Whois information). Therefore we may safely conclude that this email is not from Alice, and we should not send her money to the Philippines.
it got complex really quick, I just wanted to find location of the sender that's it. I have tried options mentioned above and none of them are revealing the location of the sender, Any suggestions from anyone @LakshmiNarayanan its not working – Md Faisal – 9 years ago
Ooops, wonder which came first, the chicken or the egg? https://lifehacker.com/how-can-i-find-out-where-an-email-really-came-from-1190061668
– datafunk – 6 years ago@datafunk thanks for the link! Nice to see my post around the net :-) I posted the reply here actually, they copied it, but it's ok, they are also citing superuser properly :) – Tomas – 6 years ago
15
Or, you can paste the headers into SpamCop and let it do all the deciphering for you. They'll even send a SPAM notice to the responsible sysadmin(s) if you wish.
– Ex Umbris – 12 years ago2This is painfully common - to the point where I commonly advice people who get such e mails to ask something only the owner of the email addie would know is false ;) – Journeyman Geek – 12 years ago
9@JourneymanGeek Best practice is often to not reply - a reply (or clicking any link, or loading external resources, e.g. images) could provide an indication to mass-spammers that your email address is a valid one, and someone is actually reading it. – Bob – 12 years ago
@Bob: in this case its usually directed towards specific people. Both times it happened to my dad, it was sent to people on the person's address book. Besides, spam filters handle most things – Journeyman Geek – 12 years ago
1
As a sysadmin, I had to deal with a few anonymous, very abusive and unpleasant emails, sent to one of our employees a few years back. Backtracking the headers was a dead end, as the sender had (unfortunately) been savvy enough to use an anonymous remailer (http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Anonymous_remailer). In such cases, there's practically nothing you can do (maybe unless you work for the NSA).
– abstrask – 12 years ago1This answer is awesome, but instructions get very unclear at the "Now, to find the real sender..." paragraph. Any chance we can get some clarity here? – samthebrand – 12 years ago
There were factual mistakes in the update; I don't have time to correct them, rolling back. Please don't make such major changes to the post. – Tomas – 12 years ago
Hey @tomas, I made a few edits, mostly to clear up ambiguities and fix grammatical mistakes. I think the factual mistakes you mention that were made in a previous rolled-back edit could be found in the paragraph beginning with "Now to find the real sender..." I have maintained the content of your original response, which seems to me to be the correct content. FYI, this response will be published at Lifehacker today -- thus the attention. Thx for your contribution. It's really a great answer. – samthebrand – 12 years ago
@SamtheBrand, wow, please post the link afterwards! Yes, you are right, there shift of the meaning occured exactly at that paragraph. I am glad for your interest and sorry for that brief response yesterday, I didn't (and still don't) have much time to make my answer better.. I am pleased by such (unexpected) interest! – Tomas – 12 years ago
1http://whatismyipaddress.com/trace-email Much easier – Lakshmi Narayanan – 11 years ago
10
To find the IP address:
Click on the inverted triangle beside Reply. Select Show Original.
Look for Received: from followed by the IP address between square brackets [ ]. (example: Received: from [69.138.30.1] by web31804.mail.mud.yahoo.com)
If you find more than one Received: from patterns, select the last one.
(Source)
After that, you can use pythonclub site, iplocation.net or ip lookup to find out the location.
that IP is for Mail Server or location of person that sent email? – Sirwan Afifi – 12 years ago
1It's mail server. Not sure if there's a way to determine from which ip email was typed. – Luke – 12 years ago
Selecting the last one "Received:" record is not the best strategy - it could have been added by attacker to draw a red herring across the track. Instead, you must find the last one trusted. See my answer – Tomas – 12 years ago
6
How you get to the headers varies between email clients. Many clients will let you see the original format of the message easily. Others (MicroSoft Outlook) make it more difficult.
To determine who really sent the message, the return-path is helpful. However, it can be spoofed. A Return-path address which does not match the From address is cause for suspicion. There are legitimate reasons for them to be different, such as messages forwarded from mailing lists, or links sent from web sites. (It would be better if the web-site used the Reply-to address to identify the person forwarding the link.)
To determine the origin of the message read from the top down through the received headers. There may be several. Most will have the IP address of the server they received the message form. Some issues you will encounter:
You should always be able to determine which server on the Internet sent the message to you. Tracing further back depends on the configuration of the sending servers.
FYI in recent Microsoft Outlooks you need to open a message into its own window then it's just File, Properties. That's not difficult. – Rup – 12 years ago
1
I use http://whatismyipaddress.com/trace-email. If you use Gmail, click Show original (on More, next to the Reply button, copy the headers, paste them onto this website and click Get source. You'll get the Geo-location information and map in return
0
also there are some tools for analyzing email headers and extract email data for you,
for example :
that can Trace an e-mail back to its geographical location including spam filter
MSGTAG
PoliteMail
Super Email Marketing Software
Zendio
eMailTracketPro is not working ..!I just have downloaded a trial version of it. and it has stuck – Md Faisal – 9 years ago
btw. IP address in gmail Header are in IPv6 format: http://v6decode.com/
– user956584 – 10 years ago