40
13
To troubleshoot a network problem I would like to inquire the real network "speed" for a given network adapter, which can be seen when opening the "status" of a network connection under Windows:
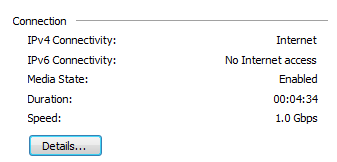
However I want to inquire this over the command line or with a small, separate tool because I need to request this for multiple network connections and don't trust the user to fetch the information properly. The network card "Speed/Duplux" setting is always "Auto Negotiate", so I can't tell from that what "Speed" I will get.
1and if you have sed wmic NIC where NetEnabled=true get Name, Speed | sed -e s/000000000/Gbit/ | sed -e s/000000\b/Mbit/ – Jamie Cook – 2014-11-24T02:04:42.063
2That WMI query worked in Windows 8 cmd, but in Windows 7, I had to use this: wmic NIC where "NetEnabled='true'" get "Name,Speed" It seems that the cmd shell was trying to interpret the ',' as a space or command separator. PowerShell has this problem, also. Thanks for putting me on the right path! – The Dude – 2014-11-25T19:39:14.923
Just what I needed! You are a great person ;n; +1 (P.S. is that bits-per-second?) – Cardinal - Reinstate Monica – 2019-04-26T20:43:33.877
1@CardinalSystem Yes, it's bits per second. – Indrek – 2019-04-27T21:35:32.303