Bridged mode is required for the Virtual Machines to communicate with each other as well as outside world
6.7. Host-only networking Host-only networking is another networking mode that was added with version 2.2 of VirtualBox. It can be thought
of as a hybrid between the bridged and internal networking modes: as
with bridged networking, the virtual machines can talk to each other
and the host as if they were connected through a physical Ethernet
switch. Similarly, as with internal networking however, a physical
networking interface need not be present, and the virtual machines
cannot talk to the world outside the host since they are not connected
to a physical networking interface.
Instead, when host-only networking is used, VirtualBox creates a new
software interface on the host which then appears next to your
existing network interfaces. In other words, whereas with bridged
networking an existing physical interface is used to attach virtual
machines to, with host-only networking a new "loopback" interface is
created on the host. And whereas with internal networking, the traffic
between the virtual machines cannot be seen, the traffic on the
"loopback" interface on the host can be intercepted.
Host-only networking is particularly useful for preconfigured virtual
appliances, where multiple virtual machines are shipped together and
designed to cooperate. For example, one virtual machine may contain a
web server and a second one a database, and since they are intended to
talk to each other, the appliance can instruct VirtualBox to set up a
host-only network for the two. A second (bridged) network would then
connect the web server to the outside world to serve data to, but the
outside world cannot connect to the database.
To change a virtual machine's virtual network interface to "host only"
mode:
either go to the "Network" page in the virtual machine's settings
notebook in the graphical user interface and select "Host-only
networking", or
on the command line, type VBoxManage modifyvm "VM name" --nic
hostonly; see Section 8.8, “VBoxManage modifyvm” for details.
Before you can attach a VM to a host-only network you have to create
at least one host-only interface, either from the GUI: "File" ->
"Preferences" -> "Network" -> "Host-only network" -> "(+)Add host-only
network", or via command line with
VBoxManage hostonlyif create see Section 8.33, “VBoxManage hostonlyif”
for details.
For host-only networking, like with internal networking, you may find
the DHCP server useful that is built into VirtualBox. This can be
enabled to then manage the IP addresses in the host-only network since
otherwise you would need to configure all IP addresses statically.
In the VirtualBox graphical user interface, you can configure all
these items in the global settings via "File" -> "Preferences" ->
"Network", which lists all host-only networks which are presently in
use. Click on the network name and then on the "Edit" button to the
right, and you can modify the adapter and DHCP settings.
Alternatively, you can use VBoxManage dhcpserver on the command line;
please see Section 8.34, “VBoxManage dhcpserver” for details.
Note On Linux and Mac OS X hosts the number of host-only interfaces is
limited to 128. There is no such limit for Solaris and Windows hosts.
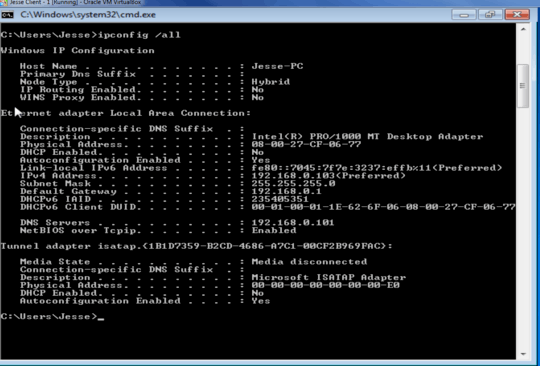
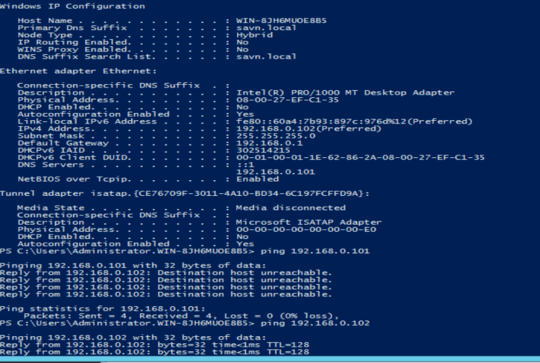
they are just using a host only adapter – user3026473 – 2016-03-27T16:12:53.660
why would that be an issue? just curious? – user3026473 – 2016-03-27T16:15:59.960
they are all in the VM, so its a virtual environment. non of the machines are actually outside of the vm network \ – user3026473 – 2016-03-27T16:17:16.883
with host-only you shouldn't be able to ping from outside which you were able to to, i suspect you haven't configured your host-only correctly, you can read manuals on virtual box to configure it correctly or easy way switch to bridged mode – SeanClt – 2016-03-27T16:23:50.317