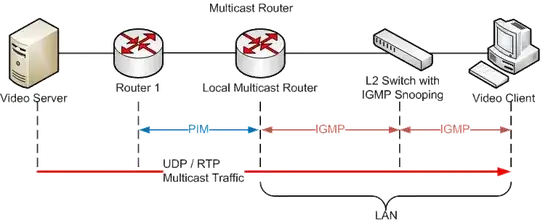
I am trying to understand the difference between IGMP Router Mode and IGMP Proxy Mode here, http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc957920.aspx
There is a question for an exam I am studying that asks
You are the network administrator for the Verigon Corporation. You install a Windows Server 2008 R2 server as a router between your subnet and the Intranet. You want to support multicast applications that use IPv4 addresses. How should you configure the router
The choices are
Add the IGMP Routing protocol. Configure the server's outbound interface for IGMP proxy mode and its inbound interface for IGMP router mode
Add the IGMP Routing protocol. Configure the server's outbound interface for IGMP router mode and its inbound interface for IGMP proxy mode
The answer is 2, but I would think that the answer is 1 because if the server is going OUT to something that is IPv4, won't it use a proxy. See picture from http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc759168%28v=ws.10%29.aspx
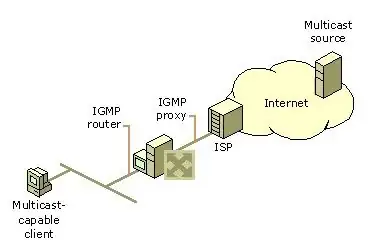
Or maybe the answer is 2 because if IPv4 traffic is coming into IPv6 space, it should come via a proxy, whereas IPv6 traffic can travel on IPv4.
Help!!!!!!!! I've been struggling with this about a week, I even placed a bounty and I really want to understand this things before I take MS Exam 70-642 early next year.
Thank you so much!!!!!!!!