We need to use SQL Server Trace Flag 7646 to help mitigate some full text blocking, but I was dismayed to find that the trace flag "unset" itself, probably when the database server was rebooted.
I've used
DBCC TRACEON (7646, -1)
to set the trace flag and
DBCC TRACESTATUS
to show all trace flags, which told me that it wasn't set (after reboot, I guess). To set the trace flag permanently, I did this:
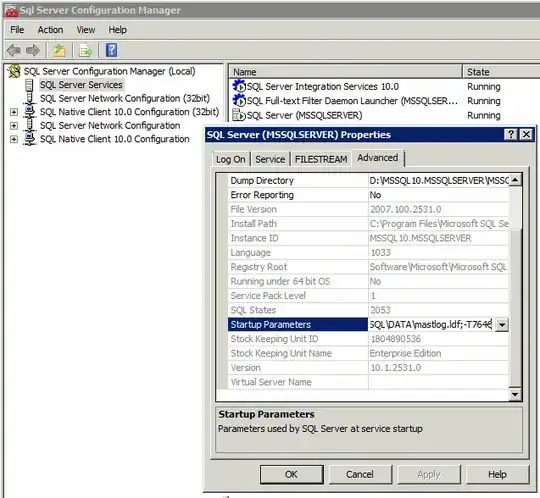
- went to SQL Server Configuration Manager
- viewed properties for SQL Server service
- visited the Advanced tab
- edited the Startup Parameters option
and added
;-T{tracenumber}
to the end, like so...
-dD:\MSSQL10.MSSQLSERVER\MSSQL\DATA\master.mdf;-eD:\MSSQL10.MSSQLSERVER\MSSQL\Log\ERRORLOG;-lD:\MSSQL10.MSSQLSERVER\MSSQL\DATA\mastlog.ldf;-T7646
Is that correct? I am finding conflicting results on the syntax for SQL Server Startup Parameters.