I wouldn't bother using LVM in VMWare solutions. There's some overhead, it's a bit redundant and would require a redesign of your current system. I think this goes back to planning, but you should have an idea of the disk space needs prior to building the server. At least with VMWare, it's extremely easy to add space, as you've noted.
I personally avoid using LVM. Maybe it's an old-school approach, or maybe I'm spoiled by HP SmartArray RAID controllers, but I find that I can predict and plan disk utilization needs based on the application requirements and environment. Most systems have one or two "growth partitions", depending on the application. It may be /home for a multiuser system. /opt for an application server. /var for a system that's logging-heavy or /var/lib/pgsql for a database server... The partition that will need to grow should be the last partition in the table or on its own hardware volume.
Also see: LVM dangers and caveats
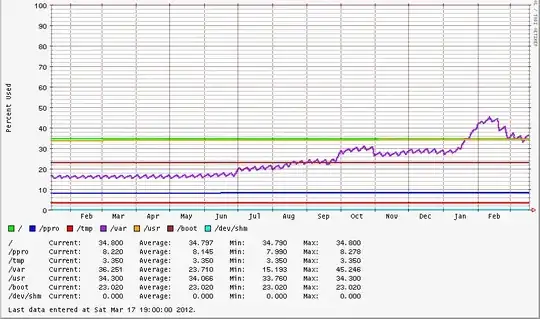
There's a purpose for multiple partitions, based on the Filesystem Hierarchy Standard. In the example below, /var and /appdata have the most activity. /appdata is setup to grow, if necessary. /var has enough headroom for cyclical logging activity. /usr and /boot don't change often. / may grow a bit, but if it becomes an issue, mount another filesystem under that hierarchy. That's fairly consistent across OS distributions.
Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on
/dev/cciss/c0d0p2 9.7G 3.4G 5.9G 37% /
/dev/cciss/c0d0p7 996M 34M 911M 4% /tmp
/dev/cciss/c0d0p6 3.0G 1023M 1.8G 37% /var
/dev/cciss/c0d0p3 5.9G 2.0G 3.6G 37% /usr
/dev/cciss/c0d0p1 99M 23M 71M 25% /boot
/dev/cciss/c0d0p8 79G 6.5G 73G 9% /appdata
tmpfs 2.4G 0 2.4G 0% /dev/shm