My WordPress Performance and Caching Stack
This is a great WordPress performance stack for a low to mid range single server or VPS. I am classifying mid range as single core with around 1G of memory and fairly fast drives.
On your box this would be capable of serving over 10K page views per hour
Server Stack
- Linux - Either Debian Lenny or Ubuntu
- Nginx - Configured as reverse proxy static file cache
- Apache - Apache will handle the PHP offloaded by Nginx on an alternate port
- MySql - Required by WP, make sure your running the latest stable version
- PHP - Latest stable version of 5.2 or 5.3 branch
PHP Cache
- APC - Configure it with mmap memory and shm size of at least 128M
WordPress Performance Plugin Stack
- Nginx proxy cache integrator
- W3 Total Cache - Set page cache to disk enhanced, minify to disk, and object and db to APC.
- Self Hosted CDN - Create 4 cname aliases that point to domain on the server set up just to serve static file
With W3 Total Cache we are using disk for page cache and minify because Nginx will be serving our static files very fast.
How to configure Nginx to serve static files and pass PHP to Apache
The problem with using Apache alone is that it opens up a connection and hits php on every request even for static files. This wastes connections because Apache will keep them open and when you have lots of traffic your connections will be bogged down even if they are not being used.
By default Apache listens for requests on port 80 which is the default web port. First we are going to make changes to our Apache conf and virtual hosts files to listen on port 8080.
Apache Config
httpd.conf
set KeepAlive to off
ports.conf
NameVirtualHost *:8080
Listen 8080
Per Site Virtual Host
<VirtualHost 127.0.0.1:8080>
ServerAdmin info@yoursite.com
ServerName yoursite.com
ServerAlias www.yoursite.com
DocumentRoot /srv/www/yoursite.com/public_html/
ErrorLog /srv/www/yoursite.com/logs/error.log
CustomLog /srv/www/yoursite.com/logs/access.log combined
</VirtualHost>
You should also install mod_rpaf so your logs will contain the real ip addresses of your visitors. If not your logs will have 127.0.0.1 as the originating ip address.
Nginx Config
On Debian you can use the repositories to install but they only contain version 0.6.33. To install a later version you have to add the lenny backports packages
$ nano /etc/apt/sources.list
Add this line to the file deb http://www.backports.org/debian lenny-backports main
$ nano /etc/apt/preferences
Add the following to the file:
Package: nginx
Pin: release a=lenny-backports
Pin-Priority: 999
Issue the following commands to import the key from backports.org to verify packages and update your system's package database:
$ wget -O - http://backports.org/debian/archive.key | apt-key add -
$ apt-get update
Now install with apt-get
apt-get install nginx
This is much easier than compiling from source.
Nginx conf and server files config
nginx.conf
user www-data;
worker_processes 4;
error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log;
pid /var/run/nginx.pid;
events {
worker_connections 1024;
}
http {
include /etc/nginx/mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
access_log /var/log/nginx/access.log;
client_body_temp_path /var/lib/nginx/body 1 2;
gzip_buffers 32 8k;
sendfile on;
#tcp_nopush on;
#keepalive_timeout 0;
keepalive_timeout 65;
tcp_nodelay on;
gzip on;
gzip_comp_level 6;
gzip_http_version 1.0;
gzip_min_length 0;
gzip_types text/html text/css image/x-icon
application/x-javascript application/javascript text/javascript application/atom+xml application/xml ;
include /etc/nginx/conf.d/*.conf;
include /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/*;
}
Now you will need to set up your Nginx virtual hosting. I like to use the sites-enabled method with each v host sym linked to a file in the sites-available directory.
$ mkdir /etc/nginx/sites-available
$ mkdir /etc/nginx/sites-enabled
$ touch /etc/nginx/sites-available/yourservername.conf
$ touch /etc/nginx/sites-available/default.conf
$ ln -s /etc/nginx/sites-available /etc/nginx/sites-enabled
$ nano /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/default.conf
default.conf
Note:
The static cache settings in the following files will only work if the Nginx proxy cache integrator plugin is enabled.
proxy_cache_path /var/lib/nginx/cache levels=1:2 keys_zone=staticfilecache:180m max_size=500m;
proxy_temp_path /var/lib/nginx/proxy;
proxy_connect_timeout 30;
proxy_read_timeout 120;
proxy_send_timeout 120;
#IMPORTANT - this sets the basic cache key that's used in the static file cache.
proxy_cache_key "$scheme://$host$request_uri";
upstream wordpressapache {
#The upstream apache server. You can have many of these and weight them accordingly,
#allowing nginx to function as a caching load balancer
server 127.0.0.1:8080 weight=1 fail_timeout=120s;
}
Per WordPress site conf (For multi site you will only need one vhost)
server {
#Only cache 200 responses, and for a default of 20 minutes.
proxy_cache_valid 200 20m;
#Listen to your public IP
listen 80;
#Probably not needed, as the proxy will pass back the host in "proxy_set_header"
server_name www.yoursite.com yoursite.com;
access_log /var/log/nginx/yoursite.proxied.log;
# "combined" matches apache's concept of "combined". Neat.
access_log /var/log/apache2/nginx-access.log combined;
# Set the real IP.
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
# Set the hostname
proxy_set_header Host $host;
#Set the forwarded-for header.
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
location / {
# If logged in, don't cache.
if ($http_cookie ~* "comment_author_|wordpress_(?!test_cookie)|wp-postpass_" ) {
set $do_not_cache 1;
}
proxy_cache_key "$scheme://$host$request_uri $do_not_cache";
proxy_cache staticfilecache;
proxy_pass http://wordpressapache;
}
location ~* wp\-.*\.php|wp\-admin {
# Don't static file cache admin-looking things.
proxy_pass http://wordpressapache;
}
location ~* \.(jpg|png|gif|jpeg|css|js|mp3|wav|swf|mov|doc|pdf|xls|ppt|docx|pptx|xlsx)$ {
# Cache static-looking files for 120 minutes, setting a 10 day expiry time in the HTTP header,
# whether logged in or not (may be too heavy-handed).
proxy_cache_valid 200 120m;
expires 864000;
proxy_pass http://wordpressapache;
proxy_cache staticfilecache;
}
location ~* \/[^\/]+\/(feed|\.xml)\/? {
# Cache RSS looking feeds for 45 minutes unless logged in.
if ($http_cookie ~* "comment_author_|wordpress_(?!test_cookie)|wp-postpass_" ) {
set $do_not_cache 1;
}
proxy_cache_key "$scheme://$host$request_uri $do_not_cache";
proxy_cache_valid 200 45m;
proxy_cache staticfilecache;
proxy_pass http://wordpressapache;
}
location = /50x.html {
root /var/www/nginx-default;
}
# No access to .htaccess files.
location ~ /\.ht {
deny all;
}
}
Self Hosted CDN conf
For your self hosted CDN conf you only need to set it up to serve static files without the proxy pass
server {
proxy_cache_valid 200 20m;
listen 80;
server_name yourcdndomain.com;
access_log /srv/www/yourcdndomain.com/logs/access.log;
root /srv/www/yourcdndomain.com/public_html/;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
location ~* \.(jpg|png|gif|jpeg|css|js|mp3|wav|swf|mov|doc|pdf|xls|ppt|docx|pptx|xlsx)$ {
# Cache static-looking files for 120 minutes, setting a 10 day expiry time in the HTTP header,
# whether logged in or not (may be too heavy-handed).
proxy_cache_valid 200 120m;
expires 7776000;
proxy_cache staticfilecache;
}
location = /50x.html {
root /var/www/nginx-default;
}
# No access to .htaccess files.
location ~ /\.ht {
deny all;
}
}
Now start the servers
$ /etc/init.d/apache2 restart
$/etc/init.d/nginx start
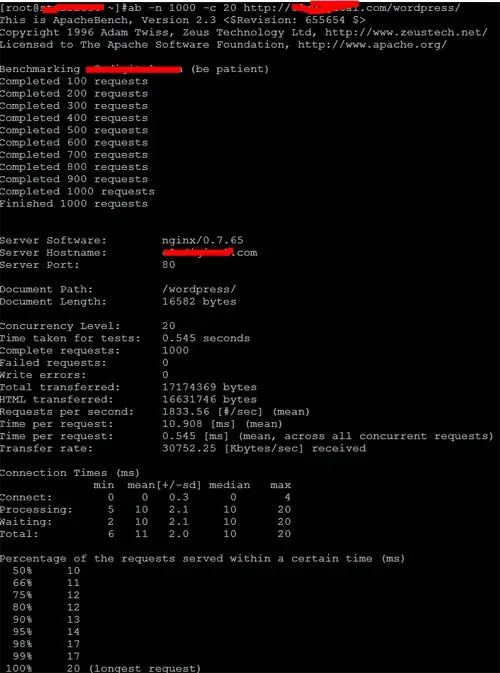
The Benchmark Results
On Apache Bench this setup can theoretically serve 1833.56 requests per second
$ ab -n 1000 -c 20 http://yoursite.com/