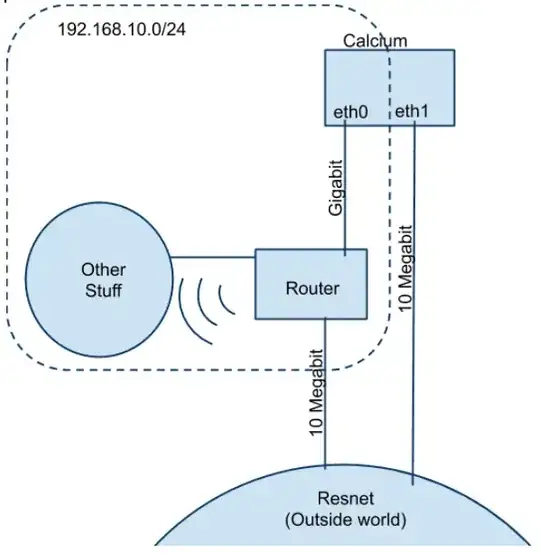
I have my network set up like this. http://docs.google.com/Doc?docid=0AZ1YxuLE4djaZGhqN2s1NmRfMjhjNjc0Ym1meg&hl=en
In words: I have a machine (Calcium, running Arch Linux) that has two network interfaces. eth0 is hoooked up to a router, and is gigabit. Eth1 is hooked up directly to the university network over 10Megabit. The router's uplink is hooked up to the university network as well, and it is also 10Megabit.
Currently (I believe) all traffic on Calcium is going through eth0, through the router, regardless of whether it is internal or external. (How can I confirm this?)
Ideally, traffic that is destined for the internal network (192.168.10.0/24) would travel over eth0 to the router, and wherever it is going. ALL other traffic should go over eth1.